Abstract
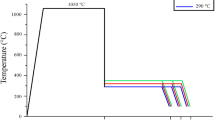
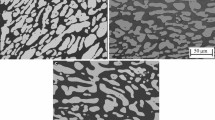
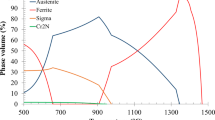
Austempered ductile iron (ADI) has complex microstructure containing a multiphase matrix (called ‘ausferrite’), graphite spheres and oxide inclusions. The corrosion resistance of ADI is related to its microstructure which is determined by heat treatment parameters (like austempering temperature, austempering time, austenitising temperature and austenitising time). In the present paper, the electrochemical behaviour and corrosion resistance of ADI have been investigated by means of the electrochemical microcell technique and classical electrochemical measurements in sodium chloride solution. Particular attention has been paid to the influence of austempering temperature on the microstructure and pitting corrosion. It has been shown that ADI austempered at 430 °C has upper ausferritic microstructure and reveals a better corrosion resistance in sodium chloride solution than ADI austempered at 280 °C. Moreover, the corrosion resistance increases as the volume fracture of ferrite increases and the carbon content of austenite decreases. The good corrosion behaviour of ADI austempered at 430 °C was also related to the good coarsening of the austenite grains and broad ferrite needles (less ferrite/austenite interfaces). It has been demonstrated that silicon is the alloying element hindering the anodic dissolution of the alloy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Labrecque C, Gagne M (1998) Can Metall Q 37:343, doi:10.1016/S0008-4433(98)00031-7
Hsu C-H, Jung-Kai R-JT (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 398:282, doi:10.1016/j.msea.2005.03.092
Ghaderi AR, Nili Ahmadabadi M, Ghsemi HM (2003) Wear 255:410, doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00156-X
Prasad Rao P, Putatunda SK (2003) Mater Sci Eng A 349:136, doi:10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00633-0
Yang J, Putatunda SK (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 406:217, doi:10.1016/j.msea.2005.06.036
Janowak JF, Norton PA (1985) AFS Trans 88:123
Eric O, Jovanovic M, Sidanin L, Rajnovic D, Zec S (2006) Mater Des 27:617, doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2004.11.028
Zimba J, Simbi DJ, Navara E (2003) Cement Concr Compos 25:643, doi:10.1016/S0958-9465(02)00078-1
Darwish N, Elliot R (1993) Mater Sci Technol 9:882
Heydarzadeh Sohi M, Nili Ahmadabadi M, Bahrami Vahdat A (2004) J Mater Process Technol 153-154:203, doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.04.308
Hemanth J (2000) J Mater Process Technol 101:159, doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(00)00424-6
Pepe A, Galliano P, Cere S, Aparicio M, Duran A (2005) Mater Lett 59:2219, doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2005.03.001
Krawiec H, Stypuła B, Stoch J, Mikołajczyk M (2006) Corros Sci 48:595, doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2005.02.019
Krawiec H, Vignal V, Banas J (2006) J Electrochem Soc 153:B231, doi:10.1149/1.2197635
Bohni H, Suter T, Assi F (2000) Technol Surf Coat 130:80, doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(00)00681-2
Putatunda SK (2001) Mater Sci Eng A 297:31
Roberts CS, Aime T (1953) J Met 197:203
Pourbaix M (1974) Atlas of electrochemical equilibria in aqueous solution, 2nd English edition, Chapter IV. National Association of Corrosion Engineers, Houston, Texas, USA, pp 452–455
Monchoux JP, Verdu C, Tougeres G, Reynaud A (2001) Acta Mater 49:4355, doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(01)00230-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krawiec, H., Lelito, J., Tyrała, E. et al. Relationships between microstructure and pitting corrosion of ADI in sodium chloride solution. J Solid State Electrochem 13, 935–942 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0636-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0636-x