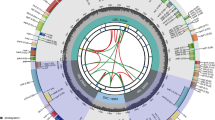
Abstract
Xanthium sibiricum has been used widely in Chinese medicine for many years. Although of medicinal value, some species in the Xanthium are reported to be toxic and thus correct identification is essential. Whereas previous identification methods based on molecular characteristics are insufficient for in-depth authentication, chloroplast genome sequences provide more information that can assist in genome-wide evolutionary research. In this study, we sequenced complete chloroplast (cp) genome of X. sibiricum using next-generation sequencing technology and the complete sequence was deposited in Genbank with the accession number MH473582. This is the first reported sequence for the complete cp genome of Xanthium. The complete X. sibiricum cp genome is 151,897 bp in length, comprising one pair of inverted repeats (IRs) of 24,905 bp, separated by one small single copy region (SSC; 17,900 bp) and one large single copy region (LSC; 84,187 bp). The genome contains 115 unique genes, which code for 81 proteins, four rRNAs and 30 tRNAs. All four rRNA genes and seven tRNA genes, ycf15, ycf2, rpl2, rps12, rpl23, ndhB and rps7, are duplicated in the IR regions. The X. sibiricum cp genome has 40 repeat sequences and 59 simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci. Both Maximum parsimony (MP) and maximum likelihood (ML) trees provide very strong bootstrap support (100%) for the sister relationship of X. sibiricum with Ambrosia in the subtribe Ambrosiinae. Our study provides molecular information for further studies with which to identify X. sibiricum among closely related species and other angiosperms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed I (2015) Chloroplast genome sequencing: some reflections. Next Generation Sequencing Applic 2:119. https://doi.org/10.4172/2469-9853.1000119
Amiryousefi A, Hyvönen J, Poczai P (2018) IRscope: an online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 34:3030–3031. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty220
An HJ, Jeong HJ, Lee EH, Kim YK, Hwang WJ, Yoo SJ, Hong SH, Kim HM (2004) Xanthii fructus inhibits inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Inflammation 28:263–270
Bausher MG, Singh ND, Lee SB, Jansen RK, Daniell H (2006) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck var ‘ridge pineapple’: organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms. BMC Pl Biol 6:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-6-21
Beier S, Thiel T, Münch T, Scholz U, Mascher M (2017) MISA-web: a web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 33:2583–2585. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx198
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Botha CJ, Lessing D, Rösemann M, van Wilpe E, Williams JH (2014) Analytical confirmation of Xanthium strumarium poisoning in cattle. J Veterin Diagn Invest 26:640–645. https://doi.org/10.1177/1040638714542867
Carbonell-Caballero J, Alonso R, Ibañez V, Terol J, Talon M, Dopazo J (2015) A phylogenetic analysis of 34 chloroplast genomes elucidates the relationships between wild and domestic species within the genus Citrus. Molec Biol Evol 32:2015–2035. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msv082
Chen X, Zhou J, Cui Y, Wang Y, Duan B, Yao H (2018) Identification of Ligularia herbs using the complete chloroplast genome as a super-barcode. Frontiers Pharmacol 9:695. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00695
Choi KS, Park KT, Park S (2017) The chloroplast genome of Symplocarpus renifolius: a comparison of chloroplast genome structure in Araceae. Genes 8:324. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8110324
Curci PL, Sonnante G (2016) The complete chloroplast genome of Cynara humilis. Mitochondrial DNA A 27:2345–2346. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2015.1025257
Curci PL, De Paola D, Danzi D, Vendramin GG, Sonnante G (2015) Complete chloroplast genome of the multifunctional crop Globe Artichoke and comparison with other Asteraceae. PLoS ONE 10:e0120589. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120589
Doorduin L, Gravendeel B, Lammers Y, Ariyurek Y, Chin-A-Woeng T, Vrieling K (2011) The complete chloroplast genome of 17 individuals of pest species Jacobaea vulgaris: SNPs, microsatellites and barcoding markers for population and phylogenetic studies. DNA Res 18:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsr002
Du YP, Bi Y, Yang FP, Zhang MF, Chen XQ, Xue J, Zhang XH (2017) Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Lilium: insights into evolutionary dynamics and phylogenetic analyses. Sci Rep 7:5751. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06210-2
Gao L, Yi X, Yang YX, Su YJ, Wang T (2009) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a tree fern Alsophila spinulosa: insights into evolutionary changes in fern chloroplast genomes. BMC Evol Biol 9:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-9-130
Haberle RC, Fourcade HM, Boore JL, Jansen RK (2008) Extensive rearrangements in the chloroplast genome of Trachelium caeruleum are associated with repeats and tRNA genes. J Molec Evol 66:350–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-008-9086-4
Henriquez CL, Arias T, Pires JC, Croat TB, Schaal BA (2014) Phylogenomics of the plant family Araceae. Molec Phylogen Evol 75:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2014.02.017
Hollingsworth PM, Graham SW, Little DP (2011) Choosing and using a plant DNA barcode. PLoS ONE 6:e19254. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019254
Hong S-Y, Cheon K-S, Yoo K-O, Lee H-O, Cho K-S, Suh J-T, Kim S-J, Nam J-H, Sohn H-B, Kim Y-H (2017) Complete chloroplast genome sequences and comparative analysis of Chenopodium quinoa and C. album. Frontiers Pl Sci 8:1696. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01696
Jeong YM, Chung WH, Mun JH, Kim N, Yu HJ (2014) De novo assembly and characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Gene 551:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.08.038
Kan S, Chen G, Han C, Chen Z, Song X, Ren M, Jiang H (2011) Chemical constituents from the roots of Xanthium sibiricum. Nat Prod Res 25:1243–1249. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.20
Karis PO (1993) Heliantheae sensu lato (Asteraceae), clades and classification. Pl Syst Evol 188:139–195
Karis PO (1995) Cladistics of the subtribe Ambrosiinae (Asteraceae: Heliantheae). Syst Bot 20:40–54
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucl Acids Res 30:3059–3066. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf436
Kuang DY, Wu H, Wang YL, Gao LM, Zhang SZ, Lu L, Bonen L (2011) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Magnolia kwangsiensis (Magnoliaceae): implication for DNA barcoding and population genetics. Genome 54:663–673. https://doi.org/10.1139/G11-026
Kumar S, Hahn FM, McMahan CM, Cornish K, Whalen MC (2009) Comparative analysis of the complete sequence of the plastid genome of Parthenium argentatum and identification of DNA barcodes to differentiate Parthenium species and lines. BMC Pl Biol 9:131. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-9-131
Kurtz S, Schleiermacher C (1999) REPuter: fast computation of maximal repeats in complete genomes. Bioinformatics 15:426–427. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/15.5.426
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Li X, Yang Y, Robrt JH, Maurizio R, Yitao W, Chen S (2015) Plant DNA barcoding: from gene to genome. Biol Rev 90:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12104
Li B, Lin F, Huang P, Guo W, Zheng Y (2017a) Complete chloroplast genome Sequence of Decaisnea insignis: genome organization, genomic resources and comparative analysis. Sci Rep 7:10073. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10409-8
Li Y, Xu W, Zou W, Jiang D, Liu X (2017b) Complete chloroplast genome sequences of two endangered Phoebe (Lauraceae) species. Bot Stud 58:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-017-0192-8
Li Z, Long H, Zhang L, Liu Z, Cao H, Shi M, Tan X (2017c) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of tung tree (Vernicia fordii): organization and phylogenetic relationships with other angiosperms. Sci Rep 7:1869. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02076-6
Lima MS, Woods LC, Cartwright MW, Smith DR (2016) The (in) complete organelle genome: exploring the use and non-use of available technologies for characterizing mitochondrial and plastid chromosomes. Molec Ecol Resources 16:1279–1286. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12585
Lohse M, Drechsel O, Bock R (2007) OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW): a tool for the easy generation of high-quality custom graphical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Curr Genet 52:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-007-0161-y
Löve D, Dansereau L (1959) Biosystematic studies on Xanthium: taxonomic appraisal and ecological status. Canad J Bot 37:173–208
Lowe TM, Chan PP (2016) tRNAscan-SE On-line: integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucl Acids Res 44:W54–W57. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw413
Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W, Yuan J, He G, Chen Y, Pan Q, Liu Y, Tang J, Wu G, Zhang H, Shi Y, Liu Y, Yu C, Wang B, Lu Y, Han C, Cheung DW, Yiu SM, Peng S, Xiaoqian Z, Liu G, Liao X, Li Y, Yang H, Wang J, Lam TW, Wang J (2012) SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 1:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-217X-1-18
Maliga P (2004) Plastid transformation in higher plants. Annual Rev Pl Biol 55:289–313. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141633
Martin MD, Quiroz-Claros E, Brush GS, Zimmer EA (2018) Herbarium collection based phylogenetics of the ragweeds (Ambrosia, Asteraceae). Molec Phylogen Evol 120:335–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2017.12.023
Mendez MC, dos Santos RC, Riet-Correa F (1998) Intoxication by Xanthium cavanillesii in cattle and sheep in southern Brazil. Veterin Human Toxicol 40:144–147
Miao B, Turner BL, Mabry TJ (1995) Systematic implications of chloroplast DNA variation in the subtribe Ambrosiinae (Asteraceae: Heliantheae). Amer J Bot 82:924–932
Millspaugh CF, Sherff EE (1919) Revision of the North American species of Xanthium. Field Mus Nat Hist Pub Bot Ser 4:9–49
Nikles S, Heuberger H, Hilsdorf E, Schmücker R, Seidenberger R, Bauer R (2015) Influence of processing on the content of toxic carboxyatractyloside andatractyloside and the microbiological status of Xanthium sibiricum fruits (Cang’erzi). Pl Med 81:1213–1220. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1546207
Palmer JD (1983) Chloroplast DNA exists in two orientations. Nature 301:92. https://doi.org/10.1038/301092a0
Pauwels M, Vekemans X, Gode C, Frerot H, Castric V, Saumitou-Laprade P (2012) Nuclear and chloroplast DNA phylogeography reveals vicariance among European populations of the model species for the study of metal tolerance Arabidopsis halleri (Brassicaceae). New Phytol 193:916–928. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.04003.x
Provan J, Powell W, Hollingsworth PM (2001) Chloroplast microsatellites: new tools for studies in plant ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 16:142–147
Salih RH, Majesky Ľ, Schwarzacher T, Gornall R, Heslop-Harrison P (2017) Complete chloroplast genomes from apomictic Taraxacum (Asteraceae): identity and variation between three microspecies. PLoS ONE 12:e0168008. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0168008
Sato Y, Oketani H, Yamada T, Singyouchi K, Ohtsubo T, Kihara M, Shibata H, Higuti T (1997) A xanthanolide with potent antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Pharm Pharmacol 49:1042–1044
Sell P, Murrell G (2006) Flora of Great Britain and Ireland. Campanulaceae—Asteraceae, vol. 4. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Shen X, Wu M, Liao B, Liu Z, Bai R, Xiao S, Li X, Zhang B, Xu J, Chen S (2017) Complete chloroplast genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the medicinal plant Artemisia annua. Molecules 22:1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081330
Sithichoke T, Pichahpuk U, Duangjai S (2011) Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Hevea brasiliensis reveals genome rearrangement, RNA editing sites and phylogenetic relationships. Gene 475:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2011.01.002
Strother JL (2006) Xanthium. In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (eds.), Flora of North America, vol. 21, pp 19–20. Oxford University Press, New York
Stuart BP, Cole RJ, Gosser HS (1981) Cocklebur (Xanthium strumarium, L. var. strumarium) intoxication in swine: review and redefinition of the toxic principle. Veterin Pathol 18:368–383. https://doi.org/10.1177/030098588101800310
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molec Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Terakami S, Matsumura Y, Kurita K, Kanamori H, Katayose Y, Yamamoto T, Katayama H (2012) Complete sequence of the chloroplast genome from pear (Pyrus pyrifolia): genome structure and comparative analysis. Tree Genet Genome 8:841–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-012-0469-8
Timme RE, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Jansen RK (2007) A comparative analysis of the Lactuca and Helianthus (Asteraceae) plastid genomes: identification of divergent regions and categorization of shared repeats. Amer J Bot 94:302–312. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.94.3.302
Tomasello S (2018) How many names for a beloved genus? - Coalescent-based species delimitation in Xanthium L. (Ambrosiinae, Asteraceae). Molec Phylogen Evol 127:135–145
Tomasello S, Heubl G (2017) Phylogenetic analysis and molecular characterization of Xanthium sibiricum using DNA barcoding, PCR-RFLP, and specific primers. Pl Med 83:946–953. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-106585
Tomasello S, Stuessy TF, Oberprieler C, Heubl G (2019) Ragweeds and relatives: molecular phylogenetics of Ambrosiinae (Asteraceae). Molec Phylogen Evol 130:104–114
Turgut M, Alhan CC, Gürgöze M, Kurt A, Doğan Y, Tekatli M, Akpolat N, Aygün AD (2005) Carboxyatractyloside poisoning in humans. Ann Trop Paediatr 25:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1179/146532805X45728
von Linnaeus C (1753) Species plantarum. Impensis Laurentii Salvii, Stockholm
Walker JF, Zanis MJ, Emery NC (2014) Comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genome sequence and inversion variation in Lasthenia burkei (Madieae, Asteraceae). Amer J Bot 101:722–729. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1400049
Walker JF, Jansen RK, Zanis MJ, Emery NC (2015) Sources of inversion variation in the small single copy (SSC) region of chloroplast genomes. Amer J Bot 102:1751–1752. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1500299
Wang L, Wuyun TN, Du HY, Wang DP, Cao D (2016) Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Eucommia ulmoides: genome structure and evolution. Tree Genet Genome 12:12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-0970-6
Wicke S, Schneeweiss GM, dePamphilis CW, Müller KF, Quandt D (2011) The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: gene content, gene order, gene function. Pl Molec Biol 76:273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9762-4
Widder FJ (1923) Die Arten der Gattung Xanthium. Beiträge zu einer Monographie. Repert Spec Nov Regn Veget 20:1–223
Witte ST, Osweiler GD, Stahr HM, Mobley G (1990) Cocklebur toxicosis in cattle associated with the consumption of mature Xanthium strumarium. J Veterin Diagn Invest 2:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1177/104063879000200402
Wyman SK, Jansen RK, Boore JL (2004) Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 20:3252–3255. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth352
Yang J, Yue M, Niu C, Ma XF, Li ZH (2017) Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of four endangered herbals of Notopterygium. Genes 8:124. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8040124
Yi DK, Kim KJ (2012) Complete chloroplast genome sequences of important oilseed crop Sesamum indicum L. PLoS ONE 7:e35872. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035872
Zhang Y, Li L, Yan TL, Liu Q (2014) Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Praxelis (Eupatorium catarium Veldkamp), an important invasive species. Gene 549:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.07.041
Zhao Y, Yang H, Zheng YB, Wong YO, Leung PC (2008) The effects of Fructus Xanthii extract on cytokine release from human mast cell line (HMC-1) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 30:543–552. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923970802135385
Acknowledgements
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions to improve our manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Excellent Doctor Innovation Project of Shaanxi Normal University (S2015YB03), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2016TS057), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (GK201604008; GK201702010; GK201701006); The key R & D plan of Shaanxi province (2018ZDXMSF-079), This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61673251, No. 61760101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Michal Ronikier.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Information on Electronic Supplementary material
Information on Electronic Supplementary material
Online Resource 1. Commands used in cp genome assembly.
Online Resource 2. The list of taxa and accession numbers of the chloroplast genome sequences used in phylogenetic analysis.
Online Resource 3. Alignment of 46 concatenated protein-coding genes used in ML and MP analysis.
Online Resource 4. Complete plastome sequence of Xanthium sibiricum.
Online Resource 5. The simple sequence repeats in Xanthium sibiricum cp genome.
Online Resource 6. The maximum parsimony (MP) phylogenetic tree based on 46 protein-coding genes in the chloroplast genomes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somaratne, Y., Guan, DL., Wang, WQ. et al. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Xanthium sibiricum provides useful DNA barcodes for future species identification and phylogeny. Plant Syst Evol 305, 949–960 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-019-01614-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-019-01614-1