Abstract
Titanium carbide quantum dots functionalized with ε-poly-L-lysine (PLL) were synthesized by sonication cutting and hydrothermal synthesis. The deprotonated Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots (Ti3C2 MQDs) exhibit excitation wavelength-dependent blue photoluminescence with typical excitation/emission peaks at 330/415 nm and a quantum yield of 22% due to strong quantum confinement. The fluorescence of ε-poly-L-lysine protected Ti3C2 MQDs (PLL-protected Ti3C2 MQDs) is reduced via an inner filter effect after the addition of cytochrome c (cyt-c). Response to cyt-c is linear in the 0.2 to 40 μM concentration range and the detection limit is 20.5 nM. In the presence of trypsin, cyt-c is hydrolyzed to small peptides, and the Fe3+ ion in cyt-c probably is reduced to Fe2+ with the aid of the digestive enzyme. This results in the restoration of the blue fluorescence of the modified MQDs. Fluorescence increases linearly in the 0.5 to 80 μg mL−1 trypsin concentration range with the detection limit of 0.1 μg mL−1. The method was successfully applied to the determination of cyt-c and trypsin in spiked serum samples.

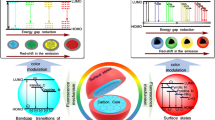
Schematic of a method for the fluorometric “turn-off-on” determination of cytochrome c and trypsin based on ε-poly-L-lysine (PLL) protect MXene quantum dots (Ti3C2 MQDs).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barsoum MW (2000) The MN+1AXN phases: a new class of solids: thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Prog Solid State Ch 28:201–281
Ren CE, Hatzell KB, Alhabeb M, Ling Z, Mahmoud KA, Gogotsi Y (2015) Charge-and size-selective ion sieving through Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes. J Phys Chem Lett 6:4026–4031
Yu XF, Li YC, Cheng JB, Liu ZB, Li QZ, Li WZ, Yang X, Xiao B (2015) Monolayer Ti2CO2: a promising candidate for NH3 sensor or capturer with high sensitivity and selectivity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:13707–13713
Liu H, Duan CY, Yang CH, Shen WQ, Wang F, Zhu ZF (2015) A novel nitrite biosensor based on the direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin immobilized on MXene-Ti3C2. Sensors Actuators B Chem 218:60–66
Wang F, Yang CH, Duan CY, Xiao D, Tang Y, Zhu JF (2015) An organ-like titanium carbide material (MXene) with multilayer structure encapsulating hemoglobin for a mediator-free. Biosensor J Elec-trochem Soc 162:B16–B21
Xue Q, Zhang HJ, Zhu MS, Pei ZX, Li HF, Wang ZF, Huang Y, Huang Y, Deng QH, Zhou J, Du SY, Huang Q, Zhi CY (2017) Photoluminescent Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for multicolor cellular imaging. Adv Mater 29:1604847
Chen X, Sun XK, Xu W, Pan GC, Zhou DL, Zhu JY, Wang H, Bai X, Dong B, Song HW (2018) Ratiometric photoluminescence sensing based on Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for the intracellular pH sensor. Nanoscale 10:1111–1118
Xu Q, Ding L, Wen YY, Yang WJ, Zhou HJ, Chen XZ, Jason S, Zhou AG, Wee-Jun O, Li N (2018) High photoluminescence quantum yield of 18.7% by nitrogen-doped Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots. J Mater Chem 6:6360–6369
Chen TT, Tian X, Liu CL, Ge J, Chu X, Li Y (2015) Fluorescence activation imaging of cytochrome c released from mitochondria using aptameric nanosensor. J Am Chem Soc 137:982–989
Sakaida I, Kimura T, Yamasaki T, Fukumoto Y, Watanabe K, Aoyama M, Okita K (2005) Cytochrome c is a possible new marker for fulminant hepatitis in humans. J Gastroenterol 40:179–185
Manickam P, Kaushik A, Karunakaran C, Bhansali S (2017) Recent advances in cytochrome c biosensing technologies. Biosens Bioelectron 87:654–668
Wang T, Zhang S, Mao C, Song J, Niu H, Jin B, Tian Y (2012) Enhanced Electrochemiluminescence of CdSe quantum dots composited with Graphene oxide and chitosan for sensitive sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 31:369–375
Hu XW, Mao CJ, Song JM, Niu HL, Zhang SY, Huang HP (2013) Fabrication of GO/PANi/CdSe Nanocomposites for sensitive Electrochemiluminescence. Biosens Bioelectron 41:372–378
Picklo MJ, Zhang J, Nguyen VQ, Graham DG, Montine TJ (1999) High-pressure liquid chromatography quantitation of cytochrome c using 393 nm detection. Anal Biochem 276:166–170
Hu YL, He Y, Han YX, Ge YL, Song GW, Zhou JG (2018) Poly(styrene-4-sulfonate)-protected copper nanoclusters as a fluorometric probe for sequential detection of cytochrome c and trypsin. Microchim Acta 185:383
Zhang XM, Qin YP, Ye HL, Ma XT, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2018) Silicon nanoparticles coated with an epitope-imprinted polymer for fluorometric determination of cytochrome c. Microchim Acta 185:173
Cao L, Li XQ, Qin LX, Kang SZ, Li GD (2017) Graphene quantum dots supported by graphene oxide as a sensitive fluorescence nanosensor for cytochrome c detection and intracellular imaging. J Mater Chem B 5:6300–6306
Amin Rehab M, Elfeky Souad A, Thomas V (2017) Fluorescence-based CdTe nanosensor for sensitive detection of cytochrome C. Biosens Bioelectron 98:415–420
Xian Y, Liu F, Xian Y, Zhou Y, Jin L (2006) Preparation of methylene blue-doped silica nanoparticle and its application to Electroanalysis heme proteins. Electrochim Acta 51:6527–6532
Poturnayova A, Castillo G, Subjakova V, Tatarko M, Snejdarkova M, Hianik T (2017) Optimization of cytochrome c detection by acoustic and electrochemical methods based on Aptamer sensors. Sens. Actuator B-Chem 238:817–827
Chinnakotla S, Radosevich DM, Dunn TB (2014) Long-term outcomes of Total Pancreatectomy and islet auto transplantation for hereditary/genetic pancreatitis. J Am Coll Cardiol 218:530–543
Pallagi P, Venglovecz V, Rakonczay ZJ (2011) Trypsin reduces pancreatic ductal bicarbonate secretion by inhibiting CFTR cl-channels and luminal. Gastroenterology 141:2228–U413
Braganza JM, Lee SH (2011) McCloy RF. Chronic pancreatitis 377:1184–1197
Li HX, Yang MM, Kong DS (2019) Sensitive fluorescence sensor for point-of-care detection of trypsin using glutathione-stabilized gold nanoclusters sensors. Sens. Actuator B-Chem 282:366–372
Hong ML, Li LJ, Han HX (2014) A label-free fluorescence assay for trypsin based on the Electron transfer between oligonucleotide-stabilized Ag Nanoclusters and cytochrome c. Anal Sci 30:811–815
Salehnia F, Hosseini M, Ganjali MR (2017) A fluorometric aptamer based assay for cytochrome C using fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets. Microchim Acta 184(7):2157–2163
Zhou Z, Liu W, Wang Y, Ding F, Liu X, Zhao Q, Rao H (2019) A fluorometric and colorimetric method for determination of trypsin by exploiting the gold nanocluster-induced aggregation of hemoglobin-coated gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186(5):272
Yan PT, Zhang RJ, Jia J, Wu C, Zhou AG, Xu J, Zhang XS (2015) Enhanced supercapacitive performance of delaminated two-dimensional titanium carbide/carbon nanotube composites in alkaline electrolyte. J. Power Sources 284:38–43
Luo J, Tao X, Zhang J, Xia Y, Huang H, Zhang L, Gan Y, Liang C, Zhang W (2016) Se4+ ion decorated highly conductive Ti3C2 MXene: promising lithium-ion anodes with enhanced volumetric capacity and cyclic performance. ACS Nano 10:2491–2499
Liu S, Tian JQ, Wang L, Zhang YW, Qin XY, Luo YL, Asiri AM, Al-Youbi AO, Sun XP (2012) Hydrothermal treatment of grass: a low-cost, green route to nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, PhotoluminAdv. Mater 24:2037–2041
Li XM, Rui MC, Song JZ, Shen ZH, Zeng HB (2015) Carbon and Graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic and energy devices: a review. Adv Funct Mater 25:4929–4947
Fan JY, Chu PK (2010) Group IV nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, and biological applications. Small 6:2080–2098
Brown GC, Borutaite V (2008) Regulation of apoptosis by the redox state of cytochrome c. Borutaite, Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg 1777:877–881
Liang H, Klie RF, Oeguet S (2016) First-principles study of size-and edge-dependent properties of MXene nanoribbons. Phys Rev B 93:115412
Rakhi RB, Ahmed B, Hedhili MN, Anjum DH, Al-shareef HN (2015) Effect of Postetch annealing gas composition on the structural and electrochemical properties of Ti2CTx MXene Elec-trodes for Supercapacitor applications. Chem Mater 27:5314–5323
Li X, Zhu SJ, Xu B, Ma K, Zhang JH, Yang B, Tian WJ (2013) Self-assembled graphene quantum dots induced by cytochrome c: a novel biosensor for trypsin with remarkable fluorescence enhancement. Nanoscale 5:7776–7779
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21707030) and Wuhan Youth Science and technology plan (2016070204010133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 485 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Zhou, J., He, Y. et al. ε-Poly-L-lysine-protected Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots with high quantum yield for fluorometric determination of cytochrome c and trypsin. Microchim Acta 186, 770 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3945-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3945-0