Abstract
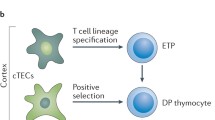
The thymus provides a specialized microenvironment in which a variety of stromal cells of both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic origin regulate development and repertoire selection of T cells. Recent studies have been unraveling the inter- and intracellular signals and transcriptional networks for spatiotemporal regulation of development of thymic stromal cells, mainly thymic epithelial cells (TECs), and the molecular mechanisms of how different TEC subsets control T cell development and selection. TECs are classified into two functionally different subsets: cortical TECs (cTECs) and medullary TECs (mTECs). cTECs induce positive selection of diverse and functionally distinct T cells by virtue of unique antigen-processing systems, while mTECs are essential for establishing T cell tolerance via ectopic expression of peripheral tissue-restricted antigens and cooperation with dendritic cells. In addition to reviewing the role of the thymic stroma in conventional T cell development, we will discuss recently discovered novel functions of TECs in the development of unconventional T cells, such as natural killer T cells and γδT cells.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Von Boehmer H (2004) Selection of the T-cell repertoire: receptor-controlled checkpoints in T-cell development. Adv Immunol 84(84):201–238. doi:10.1016/s0065-2776(04)84006-9
Hogquist KA, Jameson SC (2014) The self-obsession of T cells: how TCR signaling thresholds affect fate ‘decisions’ and effector function. Nat Immunol 15(9):815–823. doi:10.1038/ni.2938
Miller JF (1961) Immunological function of thymus. Lancet 2(720):748–749
Boyd RL, Tucek CL, Godfrey DI, Izon DJ, Wilson TJ, Davidson NJ, Bean AGD, Ladyman HM, Ritter MA, Hugo P (1993) The thymic microenvironment. Immunol Today 14(9):445–459. doi:10.1016/0167-5699(93)90248-J
Gray DH, Ueno T, Chidgey AP, Malin M, Goldberg GL, Takahama Y, Boyd RL (2005) Controlling the thymic microenvironment. Curr Opin Immunol 17(2):137–143. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2005.02.001
Anderson G, Takahama Y (2012) Thymic epithelial cells: working class heroes for T cell development and repertoire selection. Trends Immunol 33(6):256–263. doi:10.1016/j.it.2012.03.005
Klein L, Kyewski B, Allen PM, Hogquist KA (2014) Positive and negative selection of the T cell repertoire: what thymocytes see (and don’t see). Nat Rev Immunol 14(6):377–391. doi:10.1038/nri3667
Bhandoola A, Sambandam A, Allman D, Meraz A, Schwarz B (2003) Early T lineage progenitors: new insights, but old questions remain. J Immunol 171(11):5653–5658
Takahama Y (2006) Journey through the thymus: stromal guides for T-cell development and selection. Nat Rev Immunol 6(2):127–135. doi:10.1038/nri1781
Jensen KDC, Su X, Shin S, Li L, Youssef S, Yarnasaki S, Steinman L, Saito T, Locksley RM, Davis MM, Baumgarth N, Chien Y-H (2008) Thymic selection determines gamma delta T cell effector fate: antigen-naive cells make interleukin-17 and antigen-experienced cells make interferon gamma. Immunity 29(1):90–100. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.04.022
Carding SR, Egan PJ (2002) gamma delta T cells: functional plasticity and heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol 2(5):336–345. doi:10.1038/nri.797
Kronenberg M, Engel I (2007) On the road: progress in finding the unique pathway of invariant NKT cell differentiation. Curr Opin Immunol 19(2):186–193. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2007.02.009
Gapin L, Matsuda JL, Surh CD, Kronenberg M (2001) NKT cells derive from double-positive thymocytes that are positively selected by CDId. Nat Immunol 2(10):971–978. doi:10.1038/ni710
Gordon J, Wilson VA, Blair NF, Sheridan J, Farley A, Wilson L, Manley NR, Blackburn CC (2004) Functional evidence for a single endodermal origin for the thymic epithelium. Nat Immunol 5(5):546–553. doi:10.1038/ni1064
Anderson G, Lane PJL, Jenkinson EJ (2007) Generating intrathymic microenvironments to establish T-cell tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol 7(12):954–963. doi:10.1038/nri2187
Boehm T (2008) Thymus development and function. Curr Opin Immunol 20(2):178–184. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2008.03.001
Nehls M, Pfeifer D, Schorpp M, Hedrich H, Boehm T (1994) New member of the Winged-Helix protein family disrupted in mouse and rat nude mutations. Nature 372(6501):103–107. doi:10.1038/372103a0
Blackburn CC, Augustine CL, Li R, Harvey RP, Malin MA, Boyd RL, Miller JFAP, Morahan G (1996) The nu gene acts cell-autonomously and is required for differentiation of thymic epithelial progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(12):5742–5746. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.12.5742
Nehls M, Kyewski B, Messerle M, Waldschutz R, Schuddekopf K, Smith AJH, Boehm T (1996) Two genetically separable steps in the differentiation of thymic epithelium. Science 272(5263):886–889. doi:10.1126/science.272.5263.886
Vigliano I, Gorrese M, Fusco A, Vitiello L, Amorosi S, Panico L, Ursini MV, Calcagno G, Racioppi L, Del Vecchio L, Pignata C (2011) FOXN1 mutation abrogates prenatal T-cell development in humans. J Med Genet 48(6):413–416. doi:10.1136/jmg.2011.089532
Zuklys S, Gill J, Keller MP, Hauri-Hohl M, Zhanybekova S, Balciunaite G, Na KJ, Jeker LT, Hafen K, Tsukamoto N, Amagai T, Taketo MM, Krenger W, Hollander GA (2009) Stabilized beta-catenin in thymic epithelial cells blocks thymus development and function. J Immunol 182(5):2997–3007. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0713723
Balciunaite G, Keller MP, Balciunaite E, Piali L, Zuklys S, Mathieu YD, Gill J, Boyd R, Sussman DJ, Hollander GA (2002) Wnt glycoproteins regulate the expression of FoxNI, the gene defective in nude mice. Nat Immunol 3(11):1102–1108. doi:10.1038/ni850
Itoi M, Tsukamoto N, Amagai T (2007) Expression of DII4 and CCL25 in Foxn1-negative epithelial cells in the post-natal thymus. Int Immunol 19(2):127–132. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxl129
Senoo M, Pinto F, Crum CP, McKeon F (2007) p63 is essential for the proliferative potential of stem cells in stratified epithelia. Cell 129(3):523–536. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.045
Candi E, Rufini A, Terrinoni A, Giamboi-Miraglia A, Lena AM, Mantovani R, Knight R, Melino G (2007) Delta Np63 regulates thymic development through enhanced expression of FgfR2 and Jag2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(29):11999–12004. doi:10.1073/pnas.0703458104
Liu B, Liu YF, Du YR, Mardaryev AN, Yang W, Chen H, Xu ZM, Xu CQ, Zhang XR, Botchkarev VA, Zhang Y, Xu GL (2013) Cbx4 regulates the proliferation of thymic epithelial cells and thymus function. Development 140(4):780–788. doi:10.1242/dev.085035
Rossi SW, Jenkinson WE, Anderson G, Jenkinson EJ (2006) Clonal analysis reveals a common progenitor for thymic cortical and medullary epithelium. Nature 441(7096):988–991. doi:10.1038/nature04813
Bleul CC, Corbeaux T, Reuter A, Fisch P, Monting JS, Boehm T (2006) Formation of a functional thymus initiated by a postnatal epithelial progenitor cell. Nature 441(7096):992–996. doi:10.1038/nature04850
Shakib S, Desanti GE, Jenkinson WE, Parnell SM, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G (2009) Checkpoints in the development of thymic cortical epithelial cells. J Immunol 182(1):130–137
Baik S, Jenkinson EJ, Lane PJL, Anderson G, Jenkinson WE (2013) Generation of both cortical and Aire(+) medullary thymic epithelial compartments from CD205(+) progenitors. Eur J Immunol 43(3):589–594. doi:10.1002/eji.201243209
Ribeiro AR, Rodrigues PM, Meireles C, Di Santo JP, Alves NL (2013) Thymocyte selection regulates the homeostasis of IL-7-expressing thymic cortical epithelial cells in vivo. J Immunol 191(3):1200–1209. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1203042
Ohigashi I, Zuklys S, Sakata M, Mayer CE, Zhanybekova S, Murata S, Tanaka K, Hollaender GA, Takahama Y (2013) Aire-expressing thymic medullary epithelial cells originate from beta 5t-expressing progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(24):9885–9890. doi:10.1073/pnas.1301799110
Ribeiro AR, Meireles C, Rodrigues PM, Alves NL (2014) Intermediate expression of CCRL1 reveals novel subpopulations of medullary thymic epithelial cells that emerge in the postnatal thymus. Eur J Immunol 44(10):2918–2924. doi:10.1002/eji.201444585
Alves NL, Takahama Y, Ohigashi I, Ribeiro AR, Baik S, Anderson G, Jenkinson WE (2014) Serial progression of cortical and medullary thymic epithelial microenvironments. Eur J Immunol 44(1):16–22
Klug DB, Carter C, Gimenez-Conti IB, Richie ER (2002) Cutting edge: thymocyte-independent and thymocyte-dependent phases of epithelial patterning in the fetal thymus. J Immunol 169(6):2842–2845
Ripen AM, Nitta T, Murata S, Tanaka K, Takahama Y (2011) Ontogeny of thymic cortical epithelial cells expressing the thymoproteasome subunit beta 5t. Eur J Immunol 41(5):1278–1287. doi:10.1002/eji.201041375
Nitta T, Muro R, Shimizu Y, Nitta S, Oda H, Ohte Y, Goto M, Yanobu-Takanashi R, Narita T, Takayanagi H, Yasuda H, Okamura T, Murata S, Suzuki H (2015) The thymic cortical epithelium determines the TCR repertoire of IL-17-producing gamma delta T cells. EMBO Rep 16(5):638–653. doi:10.15252/embr.201540096
Hollander GA, Wang B, Nichogiannopoulou A, Platenburg PP, van Ewijk W, Burakoff SJ, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Terhorst C (1995) Developmental control point in induction of thymic cortex regulated by a subpopulation of prothymocytes. Nature 373(6512):350–353. doi:10.1038/373350a0
Roberts NA, Desanti GE, Withers DR, Scott HR, Jenkinson WE, Lane PJ, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G (2009) Absence of thymus crosstalk in the fetus does not preclude hematopoietic induction of a functional thymus in the adult. Eur J Immunol 39(9):2395–2402. doi:10.1002/eji.200939501
Hozumi K, Mailhos C, Negishi N, Hirano K, Yahata T, Ando K, Zuklys S, Hollander GA, Shima DT, Habu S (2008) Delta-like 4 is indispensable in thymic environment specific for T cell development. J Exp Med 205(11):2507–2513. doi:10.1084/jem.20080134
Koch U, Fiorini E, Benedito R, Besseyrias V, Schuster-Gossler K, Pierres M, Manley NR, Duarte A, Macdonald HR, Radtke F (2008) Delta-like 4 is the essential, nonredundant ligand for Notch1 during thymic T cell lineage commitment. J Exp Med 205(11):2515–2523. doi:10.1084/jem.20080829
Calderon L, Boehm T (2012) Synergistic, context-dependent, and hierarchical functions of epithelial components in thymic microenvironments. Cell 149(1):159–172. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.049
Hara T, Shitara S, Imai K, Miyachi H, Kitano S, Yao H, Tani-ichi S, Ikuta K (2012) Identification of IL-7-producing cells in primary and secondary lymphoid organs using IL-7-GFP knock-in mice. J Immunol 189(4):1577–1584. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1200586
Moore TA, von Freeden-Jeffry U, Murray R, Zlotnik A (1996) Inhibition of gamma delta T cell development and early thymocyte maturation in IL-7−/− mice. J Immunol 157(6):2366–2373
Shitara S, Hara T, Liang B, Wagatsuma K, Zuklys S, Hollander GA, Nakase H, Chiba T, Tani-ichi S, Ikuta K (2013) IL-7 produced by thymic epithelial cells plays a major role in the development of thymocytes and TCRgammadelta + intraepithelial lymphocytes. J Immunol 190(12):6173–6179. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1202573
Boudil A, Matei IR, Shih HY, Bogdanoski G, Yuan JS, Chang SG, Montpellier B, Kowalski PE, Voisin V, Bashir S, Bader GD, Krangel MS, Guidos CJ (2015) IL-7 coordinates proliferation, differentiation and Tcra recombination during thymocyte beta-selection. Nat Immunol 16(4):397–405. doi:10.1038/ni.3122
Plotkin J, Prockop SE, Lepique A, Petrie HT (2003) Critical role for CXCR4 signaling in progenitor localization and T cell differentiation in the postnatal thymus. J Immunol 171(9):4521–4527
Benz C, Heinzel K, Bleul CC (2004) Homing of immature thymocytes to the subcapsular microenvironment within the thymus is not an absolute requirement for T cell development. Eur J Immunol 34(12):3652–3663. doi:10.1002/eji.200425248
Ara T, Itoi M, Kawabata K, Egawa T, Tokoyoda K, Sugiyama T, Fujii N, Amagai T, Nagasawa T (2003) A role of CXC chemokine ligand 12/stromal cell-derived factor-1/pre-B cell growth stimulating factor and its receptor CXCR4 in fetal and adult T cell development in vivo. J Immunol 170(9):4649–4655
Misslitz A, Pabst O, Hintzen G, Ohl L, Kremmer E, Petrie HT, Forster R (2004) Thymic T cell development and progenitor localization depend on CCR7. J Exp Med 200(4):481–491. doi:10.1084/jem.20040383
Trampont PC, Tosello-Trampont AC, Shen Y, Duley AK, Sutherland AE, Bender TP, Littman DR, Ravichandran KS (2010) CXCR4 acts as a costimulator during thymic beta-selection. Nat Immunol 11(2):162–170. doi:10.1038/ni.1830
Rode I, Boehm T (2012) Regenerative capacity of adult cortical thymic epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(9):3463–3468. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118823109
Bunting MD, Comerford I, Seach N, Hammett MV, Asquith DL, Korner H, Boyd RL, Nibbs RJ, McColl SR (2013) CCX-CKR deficiency alters thymic stroma impairing thymocyte development and promoting autoimmunity. Blood 121(1):118–128. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-06-434886
Lucas B, White AJ, Ulvmar MH, Nibbs RJ, Sitnik KM, Agace WW, Jenkinson WE, Anderson G, Rot A (2015) CCRL1/ACKR4 is expressed in key thymic microenvironments but is dispensable for T lymphopoiesis at steady state in adult mice. Eur J Immunol 45(2):574–583. doi:10.1002/eji.201445015
Prockop SE, Palencia S, Ryan CM, Gordon K, Gray D, Petrie HT (2002) Stromal cells provide the matrix for migration of early lymphoid progenitors through the thymic cortex. J Immunol 169(8):4354–4361
Takahama Y, Letterio JJ, Suzuki H, Farr AG, Singer A (1994) Early progression of thymocytes along the CD4/CD8 developmental pathway is regulated by a subset of thymic epithelial cells expressing transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med 179(5):1495–1506
Bousso P, Bhakta NR, Lewis RS, Robey E (2002) Dynamics of thymocyte-stromal cell interactions visualized by two-photon microscopy. Science 296(5574):1876–1880. doi:10.1126/science.1070945
Bhakta NR, Oh DY, Lewis RS (2005) Calcium oscillations regulate thymocyte motility during positive selection in the three-dimensional thymic environment. Nat Immunol 6(2):143–151. doi:10.1038/ni1161
Phee H, Dzhagalov I, Mollenauer M, Wang Y, Irvine DJ, Robey E, Weiss A (2010) Regulation of thymocyte positive selection and motility by GIT2. Nat Immunol 11(6):503–511. doi:10.1038/ni.1868
Korthals M, Schilling K, Reichardt P, Mamula D, Schluter T, Steiner M, Langnase K, Thomas U, Gundelfinger E, Premont RT, Tedford K, Fischer KD (2014) AlphaPIX RhoGEF supports positive selection by restraining migration and promoting arrest of thymocytes. J Immunol 192(7):3228–3238. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1302585
Sijts EJ, Kloetzel PM (2011) The role of the proteasome in the generation of MHC class I ligands and immune responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(9):1491–1502. doi:10.1007/s00018-011-0657-y
Tanaka K, Kasahara M (1998) The MHC class I ligand-generating system: roles of immunoproteasomes and the interferon-gamma-inducible proteasome activator PA28. Immunol Rev 163:161–176
Kloetzel PM (2001) Antigen processing by the proteasome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(3):179–187. doi:10.1038/35056572
Murata S, Sasaki K, Kishimoto T, S-i Niwa, Hayashi H, Takahama Y, Tanaka K (2007) Regulation of CD8+ T cell development by thymus-specific proteasomes. Science 316(5829):1349–1353. doi:10.1126/science.1141915
Tomaru U, Ishizu A, Murata S, Miyatake Y, Suzuki S, Takahashi S, Kazamaki T, Ohara J, Baba T, Iwasaki S, Fugo K, Otsuka N, Tanaka K, Kasahara M (2009) Exclusive expression of proteasome subunit {beta}5t in the human thymic cortex. Blood 113(21):5186–5191. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-11-187633
Nitta T, Murata S, Sasaki K, Fujii H, Ripen AM, Ishimaru N, Koyasu S, Tanaka K, Takahama Y (2010) Thymoproteasome shapes immunocompetent repertoire of CD8+ T cells. Immunity 32(1):29–40. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.10.009
Xing Y, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA (2013) Thymoproteasome subunit-beta 5T generates peptide-MHC complexes specialized for positive selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(17):6979–6984. doi:10.1073/pnas.1222244110
Takada K, Van Laethem F, Xing Y, Akane K, Suzuki H, Murata S, Tanaka K, Jameson SC, Singer A, Takahama Y (2015) TCR affinity for thymoproteasome-dependent positively selecting peptides conditions antigen responsiveness in CD8(+) T cells. Nat Immunol 16(10):1069–1076. doi:10.1038/ni.3237
Sasaki K, Takada K, Ohte Y, Kondo H, Sorimachi H, Tanaka K, Takahama Y, Murata S (2015) Thymoproteasomes produce unique peptide motifs for positive selection of CD8(+) T cells. Nat Commun 6:7484. doi:10.1038/ncomms8484
Takahama Y, Nitta T, Mat Ripen A, Nitta S, Murata S, Tanaka K (2010) Role of thymic cortex-specific self-peptides in positive selection of T cells. Semin Immunol 22(5):287–293. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2010.04.012
Honey K, Rudensky AY (2003) Lysosomal cysteine proteases regulate antigen presentation. Nat Rev Immunol 3(6):472–482. doi:10.1038/nri1110
Bowlus CL, Ahn J, Chu T, Gruen JR (1999) Cloning of a novel MHC-encoded serine peptidase highly expressed by cortical epithelial cells of the thymus. Cell Immunol 196(2):80–86. doi:10.1006/cimm.1999.1543
Nakagawa T, Roth W, Wong P, Nelson A, Farr A, Deussing J, Villadangos JA, Ploegh H, Peters C, Rudensky AY (1998) Cathepsin L: critical role in Ii degradation and CD4 T cell selection in the thymus. Science 280(5362):450–453
Honey K, Nakagawa T, Peters C, Rudensky A (2002) Cathepsin L regulates CD4(+) T cell selection independently of its effect on invariant chain: a role in the generation of positively selecting peptide ligands. J Exp Med 195(10):1349–1358. doi:10.1084/jem.20011904
Gommeaux J, Gregoire C, Nguessan P, Richelme M, Malissen M, Guerder S, Malissen B, Carrier A (2009) Thymus-specific serine protease regulates positive selection of a subset of CD4(+) thymocytes. Eur J Immunol 39(4):956–964. doi:10.1002/eji.200839175
Viret C, Lamare C, Guiraud M, Fazilleau N, Bour A, Malissen B, Carrier A, Guerder S (2011) Thymus-specific serine protease contributes to the diversification of the functional endogenous CD4 T cell receptor repertoire. J Exp Med 208(1):3–11. doi:10.1084/jem.20100027
Viret C, Leung-Theung-Long S, Serre L, Lamare C, Vignali DA, Malissen B, Carrier A, Guerder S (2011) Thymus-specific serine protease controls autoreactive CD4 T cell development and autoimmune diabetes in mice. J Clin Invest 121(5):1810–1821. doi:10.1172/JCI43314
Nedjic J, Aichinger M, Emmerich J, Mizushima N, Klein L (2008) Autophagy in thymic epithelium shapes the T-cell repertoire and is essential for tolerance. Nature 455(7211):396–400. doi:10.1038/nature07208
Stritesky GL, Xing Y, Erickson JR, Kalekar LA, Wang X, Mueller DL, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA (2013) Murine thymic selection quantified using a unique method to capture deleted T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(12):4679–4684. doi:10.1073/pnas.1217532110
McCaughtry TM, Baldwin TA, Wilken MS, Hogquist KA (2008) Clonal deletion of thymocytes can occur in the cortex with no involvement of the medulla. J Exp Med 205(11):2575–2584. doi:10.1084/jem.20080866
Wekerle H, Ketelsen UP (1980) Thymic nurse cells–Ia-bearing epithelium involved in T-lymphocyte differentiation? Nature 283(5745):402–404
Wekerle H, Ketelsen UP, Ernst M (1980) Thymic nurse cells. Lymphoepithelial cell complexes in murine thymuses: morphological and serological characterization. J Exp Med 151(4):925–944
Pezzano M, Samms M, Martinez M, Guyden J (2001) Questionable thymic nurse cell. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65(3):390–403. doi:10.1128/MMBR.65.3.390-403.2001
Nakagawa Y, Ohigashi I, Nitta T, Sakata M, Tanaka K, Murata S, Kanagawa O, Takahama Y (2012) Thymic nurse cells provide microenvironment for secondary T cell receptor alpha rearrangement in cortical thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(50):20572–20577. doi:10.1073/pnas.1213069109
Guo J, Hawwari A, Li H, Sun Z, Mahanta SK, Littman DR, Krangel MS, He YW (2002) Regulation of the TCRalpha repertoire by the survival window of CD4(+)CD8(+) thymocytes. Nat Immunol 3(5):469–476. doi:10.1038/ni791
Ni PP, Solomon B, Hsieh CS, Allen PM, Morris GP (2014) The ability to rearrange dual TCRs enhances positive selection, leading to increased allo- and autoreactive T cell repertoires. J Immunol 193(4):1778–1786. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1400532
Sano S, Takahama Y, Sugawara T, Kosaka H, Itami S, Yoshikawa K, Miyazaki J, van Ewijk W, Takeda J (2001) Stat3 in thymic epithelial cells is essential for postnatal maintenance of thymic architecture and thymocyte survival. Immunity 15(2):261–273
Munoz JJ, Alfaro D, Garcia-Ceca J, Alonso CL, Jimenez E, Zapata A (2006) Thymic alterations in EphA4-deficient mice. J Immunol 177(2):804–813
Assarsson E, Chambers BJ, Hogstrand K, Berntman E, Lundmark C, Fedorova L, Imreh S, Grandien A, Cardell S, Rozell B, Ljunggren H-G (2007) Severe defect in thymic development in an insertional mutant mouse model. J Immunol 178(8):5018–5027
Vantourout P, Hayday A (2013) Six-of-the-best: unique contributions of gamma delta T cells to immunology. Nat Rev Immunol 13(2):88–100. doi:10.1038/nri3384
Haas JD, Ravens S, Dueber S, Sandrock I, Oberdoerfer L, Kashani E, Chennupati V, Foehse L, Naumann R, Weiss S, Krueger A, Foerster R, Prinz I (2012) Development of interleukin-17-producing gamma delta T cells is restricted to a functional embryonic wave. Immunity 37(1):48–59. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.06.003
Cai Y, Xue F, Fleming C, Yang J, Ding C, Ma Y, Liu M, Zhang HG, Zheng J, Xiong N, Yan J (2014) Differential developmental requirement and peripheral regulation for dermal Vgamma4 and Vgamma6T17 cells in health and inflammation. Nat Commun 5:3986. doi:10.1038/ncomms4986
Roberts NA, White AJ, Jenkinson WE, Turchinovich G, Nakamura K, Withers DR, McConnell FM, Desanti GE, Benezech C, Parnell SM, Cunningham AF, Paolino M, Penninger JM, Simon AK, Nitta T, Ohigashi I, Takahama Y, Caamano JH, Hayday AC, Lane PJL, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G (2012) Rank signaling links the development of invariant gamma delta T cell progenitors and Aire(+) medullary epithelium. Immunity 36(3):427–437. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.01.016
Gray DH, Seach N, Ueno T, Milton MK, Liston A, Lew AM, Goodnow CC, Boyd RL (2006) Developmental kinetics, turnover, and stimulatory capacity of thymic epithelial cells. Blood 108(12):3777–3785. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-02-004531
Hamazaki Y, Fujita H, Kobayashi T, Choi Y, Scott HS, Matsumoto M, Minato N (2007) Medullary thymic epithelial cells expressing Aire represent a unique lineage derived from cells expressing claudin. Nat Immunol 8(3):304–311. doi:10.1038/ni1438
Gabler J, Arnold J, Kyewski B (2007) Promiscuous gene expression and the developmental dynamics of medullary thymic epithelial cells. Eur J Immunol 37(12):3363–3372. doi:10.1002/eji.200737131
Gray D, Abramson J, Benoist C, Mathis D (2007) Proliferative arrest and rapid turnover of thymic epithelial cells expressing Aire. J Exp Med 204(11):2521–2528. doi:10.1084/jem.20070795
Khan IS, Mouchess ML, Zhu ML, Conley B, Fasano KJ, Hou Y, Fong L, Su MA, Anderson MS (2014) Enhancement of an anti-tumor immune response by transient blockade of central T cell tolerance. J Exp Med 211(5):761–768. doi:10.1084/jem.20131889
Metzger TC, Khan IS, Gardner JM, Mouchess ML, Johannes KP, Krawisz AK, Skrzypczynska KM, Anderson MS (2013) Lineage tracing and cell ablation identify a post-Aire-expressing thymic epithelial cell population. Cell Rep 5(1):166–179. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.08.038
Nishikawa Y, Nishijima H, Matsumoto M, Morimoto J, Hirota F, Takahashi S, Luche H, Fehling HJ, Mouri Y, Matsumoto M (2014) Temporal lineage tracing of Aire-expressing cells reveals a requirement for Aire in their maturation program. J Immunol 192(6):2585–2592. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1302786
Lkhagvasuren E, Sakata M, Ohigashi I, Takahama Y (2013) Lymphotoxin beta receptor regulates the development of CCL21-expressing subset of postnatal medullary thymic epithelial cells. J Immunol 190(10):5110–5117. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1203203
Yano M, Kuroda N, Han H, Meguro-Horike M, Nishikawa Y, Kiyonari H, Maemura K, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Takahashi S, Ikawa T, Satoh R, Kawamoto H, Mouri Y, Matsumoto M (2008) Aire controls the differentiation program of thymic epithelial cells in the medulla for the establishment of self-tolerance. J Exp Med 205(12):2827–2838. doi:10.1084/jem.20080046
White AJ, Nakamura K, Jenkinson WE, Saini M, Sinclair C, Seddon B, Narendran P, Pfeffer K, Nitta T, Takahama Y, Caamano JH, Lane PJL, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G (2010) Lymphotoxin signals from positively selected thymocytes regulate the terminal differentiation of medullary thymic epithelial cells. J Immunol 185(8):4769–4776. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1002151
Shores EW, Van Ewijk W, Singer A (1991) Disorganization and restoration of thymic medullary epithelial cells in T cell receptor-negative scid mice: evidence that receptor-bearing lymphocytes influence maturation of the thymic microenvironment. Eur J Immunol 21(7):1657–1661. doi:10.1002/eji.1830210711
Philpott KL, Viney JL, Kay G, Rastan S, Gardiner EM, Chae S, Hayday AC, Owen MJ (1992) Lymphoid development in mice congenitally lacking T cell receptor alpha beta-expressing cells. Science 256(5062):1448–1452
Surh CD, Ernst B, Sprent J (1992) Growth of epithelial-cells in the thymic medulla is under the control of mature t-cells. J Exp Med 176(2):611–616. doi:10.1084/jem.176.2.611
Negishi I, Motoyama N, Nakayama K, Nakayama K, Senju S, Hatakeyama S, Zhang Q, Chan AC, Loh DY (1995) Essential role for ZAP-70 in both positive and negative selection of thymocytes. Nature 376(6539):435–438. doi:10.1038/376435a0
Burkly L, Hession C, Ogata L, Reilly C, Marconi LA, Olson D, Tizard R, Cate R, Lo D (1995) Expression of relB is required for the development of thymic medulla and dendritic cells. Nature 373(6514):531–536. doi:10.1038/373531a0
Weih F, Carrasco D, Durham SK, Barton DS, Rizzo CA, Ryseck RP, Lira SA, Bravo R (1995) Multiorgan inflammation and hematopoietic abnormalities in mice with a targeted disruption of RelB, a member of the NF-kappa B/Rel family. Cell 80(2):331–340
Naspetti M, Aurrand-Lions M, DeKoning J, Malissen M, Galland F, Lo D, Naquet P (1997) Thymocytes and RelB-dependent medullary epithelial cells provide growth-promoting and organization signals, respectively, to thymic medullary stromal cells. Eur J Immunol 27(6):1392–1397. doi:10.1002/eji.1830270615
Kajiura F, Sun S, Nomura T, Izumi K, Ueno T, Bando Y, Kuroda N, Han H, Li Y, Matsushima A, Takahama Y, Sakaguchi S, Mitani T, Matsumoto M (2004) NF-kappa B-inducing kinase establishes self-tolerance in a thymic stroma-dependent manner. J Immunol 172(4):2067–2075
Akiyama T, Maeda S, Yamane S, Ogino K, Kasai M, Kajiura F, Matsumoto M, Inoue J (2005) Dependence of self-tolerance on TRAF6-directed development of thymic stroma. Science 308(5719):248–251. doi:10.1126/science.1105677
Kinoshita D, Hirota F, Kaisho T, Kasai M, Izumi K, Bando Y, Mouri Y, Matsushima A, Niki S, Han H, Oshikawa K, Kuroda N, Maegawa M, Irahara M, Takeda K, Akira S, Matsumoto M (2006) Essential role of IkappaB kinase alpha in thymic organogenesis required for the establishment of self-tolerance. J Immunol 176(7):3995–4002
Zhu M, Chin RK, Christiansen PA, Lo JC, Liu X, Ware C, Siebenlist U, Fu YX (2006) NF-kappaB2 is required for the establishment of central tolerance through an Aire-dependent pathway. J Clin Invest 116(11):2964–2971. doi:10.1172/JCI28326
Zhang B, Wang Z, Ding J, Peterson P, Gunning WT, Ding HF (2006) NF-kappaB2 is required for the control of autoimmunity by regulating the development of medullary thymic epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 281(50):38617–38624. doi:10.1074/jbc.M606705200
Zhang X, Wang H, Claudio E, Brown K, Siebenlist U (2007) A role for the IkappaB family member Bcl-3 in the control of central immunologic tolerance. Immunity 27(3):438–452. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.017
Boehm T, Scheu S, Pfeffer K, Bleul CC (2003) Thymic medullary epithelial cell differentiation, thymocyte emigration, and the control of autoimmunity require lympho-epithelial cross talk via LTbetaR. J Exp Med 198(5):757–769. doi:10.1084/jem.20030794
Rossi SW, Kim M-Y, Leibbrandt A, Parnell SM, Jenkinson WE, Glanville SH, McConnell FM, Scott HS, Penninger JM, Jenkinson EJ, Lane PJL, Anderson G (2007) RANK signals from CD4(+)3(−) inducer cells regulate development of Aire-expressing epithelial cells in the thymic medulla. J Exp Med 204(6):1267–1272. doi:10.1084/jem.20062497
Akiyama T, Shimo Y, Yanai H, Qin J, Ohshima D, Maruyama Y, Asaumi Y, Kitazawa J, Takayanagi H, Penninger JM, Matsumoto M, Nitta T, Takahama Y, J-i Inoue (2008) The tumor necrosis factor family receptors RANK and CD40 cooperatively establish the thymic medullary microenvironment and self-tolerance. Immunity 29(3):423–437. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.06.015
Hikosaka Y, Nitta T, Ohigashi I, Yano K, Ishimaru N, Hayashi Y, Matsumoto M, Matsuo K, Penninger JM, Takayanagi H, Yokota Y, Yamada H, Yoshikai Y, J-I Inoue, Akiyama T, Takahama Y (2008) The cytokine RANKL produced by positively selected thymocytes Fosters medullary thymic epithelial cells that express autoimmune regulator. Immunity 29(3):438–450. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.06.018
Irla M, Hugues S, Gill J, Nitta T, Hikosaka Y, Williams IR, Hubert F-X, Scott HS, Takahama Y, Hollaender GA, Reith W (2008) Autoantigen-specific interactions with CD4(+) thymocytes control mature medullary thymic epithelial cell cellularity. Immunity 29(3):451–463. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.08.007
Irla M, Guerri L, Guenot J, Serge A, Lantz O, Liston A, Imhof BA, Palmer E, Reith W (2012) Antigen recognition by autoreactive CD4(+) thymocytes drives homeostasis of the thymic medulla. PLoS ONE 7(12):e52591. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052591
Irla M, Guenot J, Sealy G, Reith W, Imhof BA, Serge A (2013) Three-dimensional visualization of the mouse thymus organization in health and immunodeficiency. J Immunol 190(2):586–596. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1200119
Jenkinson SR, Williams JA, Jeon H, Zhang J, Nitta T, Ohigashi I, Kruhlak M, Zuklys S, Sharrow S, Adams A, Granger L, Choi Y, Siebenlist U, Bishop GA, Hollander GA, Takahama Y, Hodes RJ (2013) TRAF3 enforces the requirement for T cell cross-talk in thymic medullary epithelial development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(52):21107–21112. doi:10.1073/pnas.1314859111
Williams JA, Zhang J, Jeon H, Nitta T, Ohigashi I, Klug D, Kruhlak MJ, Choudhury B, Sharrow SO, Granger L, Adams A, Eckhaus MA, Jenkinson SR, Richie ER, Gress RE, Takahama Y, Hodes RJ (2014) Thymic medullary epithelium and thymocyte self-tolerance require cooperation between CD28-CD80/86 and CD40-CD40L costimulatory pathways. J Immunol 192(2):630–640. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1302550
White AJ, Withers DR, Parnell SM, Scott HS, Finke D, Lane PJL, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G (2008) Sequential phases in the development of Aire-expressing medullary thymic epithelial cells involve distinct cellular input. Eur J Immunol 38(4):942–947. doi:10.1002/eji.200738052
White AJ, Jenkinson WE, Cowan JE, Parnell SM, Bacon A, Jones ND, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G (2014) An essential role for medullary thymic epithelial cells during the intrathymic development of invariant NKT cells. J Immunol 192(6):2659–2666. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1303057
Zhu M, Chin RK, Tumanov AV, Liu X, Fu YX (2007) Lymphotoxin beta receptor is required for the migration and selection of autoreactive T cells in thymic medulla. J Immunol 179(12):8069–8075
Seach N, Ueno T, Fletcher AL, Lowen T, Mattesich M, Engwerda CR, Scott HS, Ware CF, Chidgey AP, Gray DH, Boyd RL (2008) The lymphotoxin pathway regulates Aire-independent expression of ectopic genes and chemokines in thymic stromal cells. J Immunol 180(8):5384–5392
Mouri Y, Yano M, Shinzawa M, Shimo Y, Hirota F, Nishikawa Y, Nii T, Kiyonari H, Abe T, Uehara H, Izumi K, Tamada K, Chen L, Penninger JM, Inoue J, Akiyama T, Matsumoto M (2011) Lymphotoxin signal promotes thymic organogenesis by eliciting RANK expression in the embryonic thymic stroma. J Immunol 186(9):5047–5057. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1003533
Akiyama N, Shinzawa M, Miyauchi M, Yanai H, Tateishi R, Shimo Y, Ohshima D, Matsuo K, Sasaki I, Hoshino K, Wu G, Yagi S, Inoue J, Kaisho T, Akiyama T (2014) Limitation of immune tolerance-inducing thymic epithelial cell development by Spi-B-mediated negative feedback regulation. J Exp Med 211(12):2425–2438. doi:10.1084/jem.20141207
Otero DC, Baker DP, David M (2013) IRF7-dependent IFN-beta production in response to RANKL promotes medullary thymic epithelial cell development. J Immunol 190(7):3289–3298. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1203086
Hauri-Hohl M, Zuklys S, Hollander GA, Ziegler SF (2014) A regulatory role for TGF-beta signaling in the establishment and function of the thymic medulla. Nat Immunol 15(6):554–561. doi:10.1038/ni.2869
Papadopoulou AS, Dooley J, Linterman MA, Pierson W, Ucar O, Kyewski B, Zuklys S, Hollander GA, Matthys P, Gray DH, De Strooper B, Liston A (2012) The thymic epithelial microRNA network elevates the threshold for infection-associated thymic involution via miR-29a mediated suppression of the IFN-alpha receptor. Nat Immunol 13(2):181–187. doi:10.1038/ni.2193
Zuklys S, Mayer CE, Zhanybekova S, Stefanski HE, Nusspaumer G, Gill J, Barthlott T, Chappaz S, Nitta T, Dooley J, Nogales-Cadenas R, Takahama Y, Finke D, Liston A, Blazar BR, Pascual-Montano A, Hollander GA (2012) MicroRNAs control the maintenance of thymic epithelia and their competence for T lineage commitment and thymocyte selection. J Immunol 189(8):3894–3904. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1200783
Ueno T, Saito F, Gray DHD, Kuse S, Hieshima K, Nakano H, Kakiuchi T, Lipp M, Boyd RL, Takahama Y (2004) CCR7 signals are essential for cortex-medulla migration of developing thymocytes. J Exp Med 200(4):493–505. doi:10.1084/jem.20040643
Gray DH, Tull D, Ueno T, Seach N, Classon BJ, Chidgey A, McConville MJ, Boyd RL (2007) A unique thymic fibroblast population revealed by the monoclonal antibody MTS-15. J Immunol 178(8):4956–4965
Kwan J, Killeen N (2004) CCR7 directs the migration of thymocytes into the thymic medulla. J Immunol 172(7):3999–4007
Kurobe H, Liu C, Ueno T, Saito F, Ohigashi I, Seach N, Arakaki R, Hayashi Y, Kitagawa T, Lipp M, Boyd RL, Takahama Y (2006) CCR7-dependent cortex-to-medulla migration of positively selected thymocytes is essential for establishing central tolerance. Immunity 24(2):165–177. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2005.12.011
McCaughtry TM, Wilken MS, Hogquist KA (2007) Thymic emigration revisited. J Exp Med 204(11):2513–2520. doi:10.1084/jem.20070601
Nitta T, Nitta S, Lei Y, Lipp M, Takahama Y (2009) CCR7-mediated migration of developing thymocytes to the medulla is essential for negative selection to tissue-restricted antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(40):17129–17133. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906956106
Hopken UE, Wengner AM, Loddenkemper C, Stein H, Heimesaat MM, Rehm A, Lipp M (2007) CCR7 deficiency causes ectopic lymphoid neogenesis and disturbed mucosal tissue integrity. Blood 109(3):886–895. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-03-013532
Davalos-Misslitz AC, Rieckenberg J, Willenzon S, Worbs T, Kremmer E, Bernhardt G, Forster R (2007) Generalized multi-organ autoimmunity in CCR7-deficient mice. Eur J Immunol 37(3):613–622. doi:10.1002/eji.200636656
Reinhardt A, Ravens S, Fleige H, Haas JD, Oberdorfer L, Lyszkiewicz M, Forster R, Prinz I (2014) CCR7-mediated migration in the thymus controls gammadelta T-cell development. Eur J Immunol 44(5):1320–1329. doi:10.1002/eji.201344330
Lei Y, Ripen AM, Ishimaru N, Ohigashi I, Nagasawa T, Jeker LT, Bosl MR, Hollander GA, Hayashi Y, Malefyt Rde W, Nitta T, Takahama Y (2011) Aire-dependent production of XCL1 mediates medullary accumulation of thymic dendritic cells and contributes to regulatory T cell development. J Exp Med 208(2):383–394. doi:10.1084/jem.20102327
Matloubian M, Lo CG, Cinamon G, Lesneski MJ, Xu Y, Brinkmann V, Allende ML, Proia RL, Cyster JG (2004) Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature 427(6972):355–360. doi:10.1038/nature02284
Allende ML, Dreier JL, Mandala S, Proia RL (2004) Expression of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor, S1P1, on T-cells controls thymic emigration. J Biol Chem 279(15):15396–15401. doi:10.1074/jbc.M314291200
Zachariah MA, Cyster JG (2010) Neural crest-derived pericytes promote egress of mature thymocytes at the corticomedullary junction. Science 328(5982):1129–1135. doi:10.1126/science.1188222
Pappu R, Schwab SR, Cornelissen I, Pereira JP, Regard JB, Xu Y, Camerer E, Zheng YW, Huang Y, Cyster JG, Coughlin SR (2007) Promotion of lymphocyte egress into blood and lymph by distinct sources of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 316(5822):295–298. doi:10.1126/science.1139221
Love PE, Bhandoola A (2011) Signal integration and crosstalk during thymocyte migration and emigration. Nat Rev Immunol 11(7):469–477. doi:10.1038/nri2989
Klein L, Kyewski B (2000) “Promiscuous” expression of tissue antigens in the thymus: a key to T-cell tolerance and autoimmunity? J Mol Med (Berl) 78(9):483–494
Klein L, Klugmann M, Nave KA, Tuohy VK, Kyewski B (2000) Shaping of the autoreactive T-cell repertoire by a splice variant of self protein expressed in thymic epithelial cells. Nat Med 6(1):56–61. doi:10.1038/71540
Derbinski J, Schulte A, Kyewski B, Klein L (2001) Promiscuous gene expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells mirrors the peripheral self. Nat Immunol 2(11):1032–1039. doi:10.1038/ni723
Derbinski J, Gabler J, Brors B, Tierling S, Jonnakuty S, Hergenhahn M, Peltonen L, Walter J, Kyewski B (2005) Promiscuous gene expression in thymic epithelial cells is regulated at multiple levels. J Exp Med 202(1):33–45. doi:10.1084/jem.20050471
DeKoning J, DiMolfetto L, Reilly C, Wei Q, Havran WL, Lo D (1997) Thymic cortical epithelium is sufficient for the development of mature T cells in relB-deficient mice. J Immunol 158(6):2558–2566
Pinto S, Michel C, Schmidt-Glenewinkel H, Harder N, Rohr K, Wild S, Brors B, Kyewski B (2013) Overlapping gene coexpression patterns in human medullary thymic epithelial cells generate self-antigen diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(37):E3497–E3505. doi:10.1073/pnas.1308311110
Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Klein L, Chen ZB, Berzins SP, Turley SJ, von Boehmer H, Bronson R, Dierich A, Benoist C, Mathis D (2002) Projection of an immunological self shadow within the thymus by the aire protein. Science 298(5597):1395–1401. doi:10.1126/science.1075958
Heino M, Peterson P, Kudoh J, Nagamine K, Lagerstedt A, Ovod V, Ranki A, Rantala I, Nieminen M, Tuukkanen J, Scott HS, Antonarakis SE, Shimizu N, Krohn K (1999) Autoimmune regulator is expressed in the cells regulating immune tolerance in thymus medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257(3):821–825. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0308
Heino M, Peterson P, Sillanpaa N, Guerin S, Wu L, Anderson G, Scott HS, Antonarakis SE, Kudoh J, Shimizu N, Jenkinson EJ, Naquet P, Krohn KJ (2000) RNA and protein expression of the murine autoimmune regulator gene (Aire) in normal, RelB-deficient and in NOD mouse. Eur J Immunol 30(7):1884–1893
Zuklys S, Balciunaite G, Agarwal A, Fasler-Kan E, Palmer E, Hollander GA (2000) Normal thymic architecture and negative selection are associated with Aire expression, the gene defective in the autoimmune-polyendocrinopathy–candidiasis–ectodermal dystrophy (APECED). J Immunol 165(4):1976–1983
Liston A, Lesage S, Wilson J, Peltonen L, Goodnow CC (2003) Aire regulates negative selection of organ-specific T cells. Nat Immunol 4(4):350–354. doi:10.1038/ni906
Liston A, Gray DH, Lesage S, Fletcher AL, Wilson J, Webster KE, Scott HS, Boyd RL, Peltonen L, Goodnow CC (2004) Gene dosage–limiting role of Aire in thymic expression, clonal deletion, and organ-specific autoimmunity. J Exp Med 200(8):1015–1026. doi:10.1084/jem.20040581
Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Chen ZB, Berzins SP, Benoist C, Mathis D (2005) The cellular mechanism of Aire control of T cell tolerance. Immunity 23(2):227–239. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2005.07.005
Aschenbrenner K, D’Cruz LM, Vollmann EH, Hinterberger M, Emmerich J, Swee LK, Rolink A, Klein L (2007) Selection of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells specific for self antigen expressed and presented by Aire+ medullary thymic epithelial cells. Nat Immunol 8(4):351–358. doi:10.1038/ni1444
Malchow S, Leventhal DS, Nishi S, Fischer BI, Shen L, Paner GP, Amit AS, Kang C, Geddes JE, Allison JP, Socci ND, Savage PA (2013) Aire-dependent thymic development of tumor-associated regulatory T cells. Science 339(6124):1219–1224. doi:10.1126/science.1233913
Yang S, Fujikado N, Kolodin D, Benoist C, Mathis D (2015) Immune tolerance. Regulatory T cells generated early in life play a distinct role in maintaining self-tolerance. Science 348(6234):589–594. doi:10.1126/science.aaa7017
Nagamine K, Peterson P, Scott HS, Kudoh J, Minoshima S, Heino M, Krohn KJ, Lalioti MD, Mullis PE, Antonarakis SE, Kawasaki K, Asakawa S, Ito F, Shimizu N (1997) Positional cloning of the APECED gene. Nat Genet 17(4):393–398. doi:10.1038/ng1297-393
Aaltonen J, Bjorses P, Perheentupa J, HorelliKuitunen N, Palotie A, Peltonen L, Lee YS, Francis F, Hennig S, Thiel C, Lehrach H, Yaspo ML (1997) An autoimmune disease, APECED, caused by mutations in a novel gene featuring two PHD-type zinc-finger domains. Nat Genet 17(4):399–403. doi:10.1038/ng1297-399
Ramsey C, Winqvist O, Puhakka L, Halonen M, Moro A, Kampe O, Eskelin P, Pelto-Huikko M, Peltonen L (2002) Aire deficient mice develop multiple features of APECED phenotype and show altered immune response. Hum Mol Genet 11(4):397–409
Kuroda N, Mitani T, Takeda N, Ishimaru N, Arakaki R, Hayashi Y, Bando Y, Izumi K, Takahashi T, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S, Ueno T, Takahama Y, Uchida D, Sun SJ, Kajiura F, Mouri Y, Han HW, Matsushima A, Yamada G, Matsumoto M (2005) Development of autoimmunity against transcriptionally unrepressed target antigen in the thymus of aire-deficient mice. J Immunol 174(4):1862–1870
Giraud M, Yoshida H, Abramson J, Rahl PB, Young RA, Mathis D, Benoist C (2012) Aire unleashes stalled RNA polymerase to induce ectopic gene expression in thymic epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(2):535–540. doi:10.1073/pnas.1119351109
Waterfield M, Khan IS, Cortez JT, Fan U, Metzger T, Greer A, Fasano K, Martinez-Llordella M, Pollack JL, Erle DJ, Su M, Anderson MS (2014) The transcriptional regulator Aire coopts the repressive ATF7ip-MBD1 complex for the induction of immunotolerance. Nat Immunol 15(3):258–265. doi:10.1038/ni.2820
Venanzi ES, Melamed R, Mathis D, Benoist C (2008) The variable immunological self: genetic variation and nongenetic noise in Aire-regulated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(41):15860–15865. doi:10.1073/pnas.0808070105
Abramson J, Giraud M, Benoist C, Mathis D (2010) Aire’s partners in the molecular control of immunological tolerance. Cell 140(1):123–135. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.030
Giraud M, Jmari N, Du L, Carallis F, Nieland TJ, Perez-Campo FM, Bensaude O, Root DE, Hacohen N, Mathis D, Benoist C (2014) An RNAi screen for Aire cofactors reveals a role for Hnrnpl in polymerase release and Aire-activated ectopic transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(4):1491–1496. doi:10.1073/pnas.1323535111
Gillard GO, Farr AG (2005) Contrasting models of promiscuous gene expression by thymic epithelium. J Exp Med 202(1):15–19. doi:10.1084/jem.20050976
Gillard GO, Dooley J, Erickson M, Peltonen L, Farr AG (2007) Aire-dependent alterations in medullary thymic epithelium indicate a role for Aire in thymic epithelial differentiation. J Immunol 178(5):3007–3015
Dooley J, Erickson M, Farr AG (2008) Alterations of the medullary epithelial compartment in the Aire-deficient thymus: implications for programs of thymic epithelial differentiation. J Immunol 181(8):5225–5232
Ruan QG, Tung K, Eisenman D, Setiady Y, Eckenrode S, Yi B, Purohit S, Zheng WP, Zhang Y, Peltonen L, She JX (2007) The autoimmune regulator directly controls the expression of genes critical for thymic epithelial function. J Immunol 178(11):7173–7180
Laan M, Kisand K, Kont V, Moll K, Tserel L, Scott HS, Peterson P (2009) Autoimmune regulator deficiency results in decreased expression of CCR4 and CCR7 ligands and in delayed migration of CD4+ thymocytes. J Immunol 183(12):7682–7691. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804133
St-Pierre C, Trofimov A, Brochu S, Lemieux S, Perreault C (2015) Differential features of AIRE-induced and AIRE-independent promiscuous gene expression in thymic epithelial cells. J Immunol 195(2):498–506. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1500558
Macedo C, Evangelista AF, Marques MM, Octacilio-Silva S, Donadi EA, Sakamoto-Hojo ET, Passos GA (2013) Autoimmune regulator (Aire) controls the expression of microRNAs in medullary thymic epithelial cells. Immunobiology 218(4):554–560. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2012.06.013
Ucar O, Tykocinski LO, Dooley J, Liston A, Kyewski B (2013) An evolutionarily conserved mutual interdependence between Aire and microRNAs in promiscuous gene expression. Eur J Immunol 43(7):1769–1778. doi:10.1002/eji.201343343
Sansom SN, Shikama-Dorn N, Zhanybekova S, Nusspaumer G, Macaulay IC, Deadman ME, Heger A, Ponting CP, Hollander GA (2014) Population and single-cell genomics reveal the Aire dependency, relief from Polycomb silencing, and distribution of self-antigen expression in thymic epithelia. Genome Res 24(12):1918–1931. doi:10.1101/gr.171645.113
Chin RK, Zhu M, Christiansen PA, Liu W, Ware C, Peltonen L, Zhang X, Guo L, Han S, Zheng B, Fu YX (2006) Lymphotoxin pathway-directed, autoimmune regulator-independent central tolerance to arthritogenic collagen. J Immunol 177(1):290–297
Bos R, van Duikeren S, van Hall T, Kaaijk P, Taubert R, Kyewski B, Klein L, Melief CJ, Offringa R (2005) Expression of a natural tumor antigen by thymic epithelial cells impairs the tumor-protective CD4+ T-cell repertoire. Cancer Res 65(14):6443–6449. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0666
Cloosen S, Arnold J, Thio M, Bos GM, Kyewski B, Germeraad WT (2007) Expression of tumor-associated differentiation antigens, MUC1 glycoforms and CEA, in human thymic epithelial cells: implications for self-tolerance and tumor therapy. Cancer Res 67(8):3919–3926. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2112
Zhu ML, Nagavalli A, Su MA (2013) Aire deficiency promotes TRP-1-specific immune rejection of melanoma. Cancer Res 73(7):2104–2116. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3781
Wu L, Shortman K (2005) Heterogeneity of thymic dendritic cells. Semin Immunol 17(4):304–312. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2005.05.001
Bonasio R, Scimone ML, Schaerli P, Grabie N, Lichtman AH, von Andrian UH (2006) Clonal deletion of thymocytes by circulating dendritic cells homing to the thymus. Nat Immunol 7(10):1092–1100. doi:10.1038/ni1385
Moore NC, Anderson G, McLoughlin DE, Owen JJ, Jenkinson EJ (1994) Differential expression of Mtv loci in MHC class II-positive thymic stromal cells. J Immunol 152(10):4826–4831
Ferrero I, Anjuere F, MacDonald HR, Ardavin C (1997) In vitro negative selection of viral superantigen-reactive thymocytes by thymic dendritic cells. Blood 90(5):1943–1951
Gallegos AM, Bevan MJ (2004) Central tolerance to tissue-specific antigens mediated by direct and indirect antigen presentation. J Exp Med 200(8):1039–1049. doi:10.1084/jem.20041457
Atibalentja DF, Byersdorfer CA, Unanue ER (2009) Thymus-blood protein interactions are highly effective in negative selection and regulatory T cell induction. J Immunol 183(12):7909–7918. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902632
Baba T, Badr Mel S, Tomaru U, Ishizu A, Mukaida N (2012) Novel process of intrathymic tumor-immune tolerance through CCR2-mediated recruitment of Sirpalpha + dendritic cells: a murine model. PLoS ONE 7(7):e41154. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041154
Hadeiba H, Lahl K, Edalati A, Oderup C, Habtezion A, Pachynski R, Nguyen L, Ghodsi A, Adler S, Butcher EC (2012) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells transport peripheral antigens to the thymus to promote central tolerance. Immunity 36(3):438–450. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.01.017
Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM, Hafler DA (2010) FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10(7):490–500. doi:10.1038/nri2785
Josefowicz SZ, Lu LF, Rudensky AY (2012) Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu Rev Immunol 30:531–564. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141623
Fontenot JD, Dooley JL, Farr AG, Rudensky AY (2005) Developmental regulation of Foxp3 expression during ontogeny. J Exp Med 202(7):901–906. doi:10.1084/jem.20050784
Lio CWJQ, Hsieh CS (2008) A two-step process for thymic regulatory T cell development. Immunity 28(1):100–111. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.11.021
Tai X, Erman B, Alag A, Mu J, Kimura M, Katz G, Guinter T, McCaughtry T, Etzensperger R, Feigenbaum L, Singer DS, Singer A (2013) Foxp3 transcription factor is proapoptotic and lethal to developing regulatory T cells unless counterbalanced by cytokine survival signals. Immunity 38(6):1116–1128. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.02.022
Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Williams LM, Dooley JL, Farr AG, Rudensky AY (2005) Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription factor FoxP3. Immunity 22(3):329–341. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2005.01.016
Cowan JE, Parnell SM, Nakamura K, Caamano JH, Lane PJL, Jenkinson EJ, Jenkinson WE, Anderson G (2013) The thymic medulla is required for Foxp3(+) regulatory but not conventional CD4(+) thymocyte development. J Exp Med 210(4):675–681. doi:10.1084/jem.20122070
Hinterberger M, Aichinger M, da Costa OP, Voehringer D, Hoffmann R, Klein L (2010) Autonomous role of medullary thymic epithelial cells in central CD4(+) T cell tolerance. Nat Immunol 11(6):U512–U580. doi:10.1038/ni.1874
Perry JSA, Lio CWJ, Kau AL, Nutsch K, Yang Z, Gordon JI, Murphy KM, Hsieh CS (2014) Distinct contributions of aire and antigen-presenting-cell subsets to the generation of self-tolerance in the thymus. Immunity 41(3):414–426. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.08.007
Millet V, Naquet P, Guinamard RR (2008) Intercellular MHC transfer between thymic epithelial and dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol 38(5):1257–1263. doi:10.1002/eji.200737982
Koble C, Kyewski B (2009) The thymic medulla: a unique microenvironment for intercellular self-antigen transfer. J Exp Med 206(7):1505–1513. doi:10.1084/jem.20082449
Fuertbauer E, Zaujec J, Uhrin P, Raab I, Weber M, Schachner H, Bauer M, Schutz GJ, Binder BR, Sixt M, Kerjaschki D, Stockinger H (2013) Thymic medullar conduits-associated podoplanin promotes natural regulatory T cells. Immunol Lett 154(1–2):31–41. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2013.07.007
Watanabe N, Wang YH, Lee HK, Ito T, Wang YH, Cao W, Liu YJ (2005) Hassall’s corpuscles instruct dendritic cells to induce CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in human thymus. Nature 436(7054):1181–1185. doi:10.1038/nature03886
Watanabe N, Hanabuchi S, Soumelis V, Yuan W, Ho S, de Waal Malefyt R, Liu YJ (2004) Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin promotes dendritic cell-mediated CD4+ T cell homeostatic expansion. Nat Immunol 5(4):426–434. doi:10.1038/ni1048
Hanabuchi S, Lto T, Park WR, Watanabe N, Shaw JL, Roman E, Arima K, Wang YH, Voo KS, Cao W, Liu YJ (2010) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells induce the generation of FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells in human thymus. J Immunol 184(6):2999–3007. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804106
McCarthy NI, Cowan JE, Nakamura K, Bacon A, Baik S, White AJ, Parnell SM, Jenkinson EJ, Jenkinson WE, Anderson G (2015) Osteoprotegerin-mediated homeostasis of rank + thymic epithelial cells does not limit Foxp3+ regulatory T cell development. J Immunol 195(6):2675–2682. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1501226
Boyden LM, Lewis JM, Barbee SD, Bas A, Girardi M, Hayday AC, Tigelaar RE, Lifton RP (2008) Skint1, the prototype of a newly identified immunoglobulin superfamily gene cluster, positively selects epidermal gamma delta T cells. Nat Genet 40(5):656–662. doi:10.1038/ng.108
Barbee SD, Woodward MJ, Turchinovich G, Mention J-J, Lewis JM, Boyden LM, Lifton RP, Tigelaar R, Hayday AC (2011) Skint-1 is a highly specific, unique selecting component for epidermal T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(8):3330–3335. doi:10.1073/pnas.1010890108
Turchinovich G, Hayday AC (2011) Skint-1 identifies a common molecular mechanism for the development of interferon-gamma-secreting versus interleukin-17-secreting gamma delta T cells. Immunity 35(1):59–68. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.04.018
Drennan MB, Franki AS, Dewint P, Van Beneden K, Seeuws S, van de Pavert SA, Reilly EC, Verbruggen G, Lane TE, Mebius RE, Deforce D, Elewaut D (2009) Cutting edge: the chemokine receptor CXCR3 retains invariant NKT cells in the thymus. J Immunol 183(4):2213–2216. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0901213
Kim JS, Smith-Garvin JE, Koretzky GA, Jordan MS (2011) The requirements for natural Th17 cell development are distinct from those of conventional Th17 cells. J Exp Med 208(11):2201–2207. doi:10.1084/jem.20110680
Marks BR, Nowyhed HN, Choi JY, Poholek AC, Odegard JM, Flavell RA, Craft J (2009) Thymic self-reactivity selects natural interleukin 17-producing T cells that can regulate peripheral inflammation. Nat Immunol 10(10):U1125–U1128. doi:10.1038/ni.1783
Jenkinson WE, McCarthy NI, Dutton EE, Cowan JE, Parnell SM, White AJ, Anderson G (2015) Natural Th17 cells are critically regulated by functional medullary thymic microenvironments. J Autoimmun 63:13–22. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2015.06.008
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants to T.N. from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, and Technology in Japan (25111516, 25460606), National Center for Global Health and Medicine (24-112), Astellas Foundation, Inamori Foundation, Kanae Foundation, Naito Foundation, and Ichiro Kanehara Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nitta, T., Suzuki, H. Thymic stromal cell subsets for T cell development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73, 1021–1037 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2107-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2107-8