Pentax (lens)
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (October 2010) |

Pentax lenses were first badged as Takumar. The Takumar branded lenses were well respected for their line of Super Takumar, which designated the high performance coating applied to the lens as well as the optical formulas used to make them. The majority of the industry at the time was still satisfied with the variations of the "plumb" coating process and later some of the two and three layer processes as well. Asahi Pentax soon introduced the Takumar Super-Multi-Coated line of lenses which was a 7 layer process as the industry had just caught up with similar forms of 5 layer multi-coated optics. Eventually Asahi Optical and Pentax slowly shifted much of their lens production under the Pentax name and transitioned some of the successful designs that were first introduced under the Takumar name to use Asahi/Pentax badging as well as beginning to use the "smc" abbreviation. Eventually the Asahi partnership disappeared and the Pentax name became solely used. Pentax lenses saw many feature changes to answer the market, such as: incorporating "Auto-Aperture" with the M42, the light weight and compactness with the 'M' series, Aperture Priority overrides with the 'A' series, and Auto-Focus with the 'F' series. Modern Pentax lenses for digital SLR cameras have seen the elimination of the aperture ring completely as found on Pentax DA and D-FA series lenses. They use the Pentax KAF mount (and its variants, KAF2, KAF3 and KAF4). All of these lenses have an autofocus feature, either operated from the camera body or from an internal SDM motor. Pentax compatible lenses are also made by third-party companies.
History[edit]
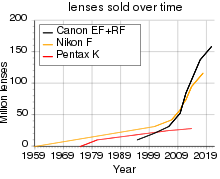
Takumar brand lenses were supplied with Pentax cameras from the late 1950s until the mid 1970s using the M42 (Pentax) Screwmount. Asahi Optical soon began supplying lenses using the Pentax name from 1975, when they introduced the bayonet (K) mount, although Takumar-branded M42 screw lenses continued to be available new for a period. The semi-official 'K' family lenses are mostly of the original Takumar Super-Multi-Coated production or in other words the 7-layer process multi-coated versions that have been adapted from the M42 mount to the K-mount. The change to the bayonet also had an impact in the industry as many other brands utilized the M42 mount and enjoyed the compatibility. Similarly, the introduction of the 7-layer coating first used with the Takumar name and later as Pentax raised controversy. It had doubters to its durability as well as its claims of flare control. Pentax's had confidence in the technology and demonstrated this by keeping a lock on the patent for quite a while. Asahi Optical and Pentax did not keep a strictly closed door on R&D as they had active partnerships with Zeiss and Tokina as well as others. Pentax has often been active in special run lenses such as for example the Infrared quartz element lens. In addition to the 35mm line, Pentax added professional medium format 645 and 67 cameras lenses to its lineup. Pentax's digital interchangeable-lens camera bodies maintain compatibility with any Pentax K mount and even the M42 screwmount (with a Pentax adapter) ever made. 35mm and 645 lenses optimized for digital cameras are currently in production.
Timeline of innovations[edit]
- 1962: Pentax launched the world's first diagonal fish-eye lens for 35mm SLR cameras. That lens was the Takumar 18mm F11 Fish-eye.[1]
- 1965: Pentax introduced the 6x7 SLR medium format system.
- 1967: Pentax introduced the world's most efficient fish-eye lens with a maximum brightness of f/4. Takumar Fish-eye 17mm f/4.[2]
- 1971: Pentax was the first to use SMC (Super Multi Coating) on all of their lenses.[3] This technology was a milestone in the optical world and is considered one of the best on the market.[4]
- 1975: World's first distortion-free ultra-wide angle lens (one aspherical element). That lens was the SMC Takumar f/3.5 15mm ultra-wide angle.[5]
- 1981: Pentax was the first to create an TTL-autofocus camera and started the development of autofocus systems. That camera was the Pentax ME-F.[6]
- 1984: Pentax introduces the Pentax 645 SLR medium format system.
- 1991: Pentax was the first to introduce Power Zoom on bayonet mount lenses for SLR cameras. That lenses included the FA* 250-600mm f5.6.[1]
- 1991: Pentax was the first to introduce focusing distance measurement for SLR cameras. That technology was introduced with the FA and FA* series lenses from 1991.[7]
- 1995: Pentax introduces the world’s first fish-eye zoom lens. That lenses was the F 17-28mm F3.5-4.5 Fish-eye Zoom.[1]
- 2000: Pentax develops and commercializes the world's first diffractive DVD/CD-compatible hybrid pickup lens.[1]
- 2009: Pentax introduces the world’s first autofocus fisheye lens. That lens is the DA 10-17mm ED (IF) Fish-Eye.[1]
- 2011: Pentax introduces the world’s smallest and lightest interchangeable lens camera (ILC). That camera was the Pentax Q.
- 2012: Pentax first introduced the HD coating as the successor of the successful SMC coating.[8]
Mounts[edit]
- M37 (screw mount, branded Takumar, Asahiflex only)
- M42 (screw mount, branded Takumar, all other Pre-K Mount 35mm bodies, e.g. the Pentax Spotmatic)
- ES M42 Mount (Introduced in 1971. Allows open aperture metering with Super Multi-Coated Takumar lenses with Pentax ES and ESII cameras. 3rd Party ES lenses include Sigma YS, Sigma XQ, Vivitar TX, and Tamron Adaptall mounts.)
- K-mount (bayonet mount, all 35mm SLR and DSLR bodies since introduction of the K series in 1975 as well as the K-01 MILC body)
- Pentax 6×7 mount (bayonet mount, some of them branded Takumar, for the medium format Pentax 6×7 and Pentax 67 film SLR bodies)
- Pentax 645 mount (bayonet mount for the medium format Pentax 645 series SLR and DSLR bodies)
- Pentax 110 mount (bayonet mount for the 110 film Pentax Auto 110 and Pentax Auto 110 super SLR bodies)
- Q-mount (bayonet mount for the Pentax Q series MILC bodies)
Lens designations[edit]

Below is a list of K-Mount Lens Lines produced by Pentax.[9]
K lenses[edit]
The first generation of Pentax K-mount lenses. Officially not referred to as K series lenses, they usually are given this designation to distinguish them from later K-mount lenses (such as the M, A, F, FA and DA series). These were exclusively manual focus lenses with no electronic features. The name of each lens started with an upper case "SMC" for the earlier versions and the lower case "smc" for the later versions. For example SMC/smc Pentax 28mm F3.5, where SMC/smc stands for Super-Multi-Coated, the lens coating introduced in the early 1970s at the end of the M42-mount era.
M lenses[edit]
The M series of lenses followed on from the earlier K series lenses. As with the earlier lenses, these were manual K-mount lenses without any electronic features. They behave just like the K series but are generally smaller in size, to match the more compact bodies of the same era, e.g. the Pentax MX and the Pentax ME Super.
A lenses[edit]
Another K-mount lens, the A series of lenses saw the introduction of "automatic" aperture settings. The lenses had an aperture ring (unlike the later DA series), and thus the aperture could be set manually, but they also had an "A" mode, which allowed the camera to control the aperture automatically.
F lenses[edit]

The F series were the first autofocus lenses (excluding the rare smc Pentax-AF 35-70mm F2.8, made only for the ME-F camera). The autofocus is of screw-drive type, still supported by all Pentax DSLRs. They featured an aperture ring, which allowed the aperture to be controlled manually. Thus F lenses are able to be used on older cameras which do not support automatic setting of the aperture, such as the Pentax K1000.
FA lenses[edit]
These lenses are designed with use for full-frame film SLR cameras. As with the F series, they feature an aperture ring providing compatibility with older camera bodies. Autofocus is like the F series of screw-drive type. The FA* lenses are professional grade lenses and the FA Limited lenses are all metal high quality primes. The FA series has been superseded by the DA and D FA series optimized for digital cameras, but as of March 2017 the three FA limited as well as the FA 35 mm f2 and 50 mm f1.4 are still in production.[10]
FA-J lenses[edit]
The FA-J series consisted of three lower-priced zoom lenses, that were largely identical to the FA series of lenses, but like later DA series lenses lacked the aperture ring. As a result, they are not fully compatible with some older manual film cameras, as there was no method of setting the aperture other than through the camera body.
D FA lenses[edit]

These lenses are coated with glazes that make the lenses more suitable for digital cameras. However, they also support older 35mm camera formats, as they provide full frame coverage. The series originally consisted only of two macro lenses – a 50mm and a 100mm – which both featured an aperture ring. In 2009 the 100mm was replaced by a weather resistant (WR) version without an aperture ring,[11] that was co-developed with Tokina.[12] The series was revived in February 2015 when the D FA* 70-200mm f2.8 and D FA 150-450mm f4.5-5.6 telephoto zoom lenses were announced[13] along with first pictures of a (then unnamed) K-1 mock-up.[14]
DA lenses[edit]
The DA lenses were designed specifically for the Pentax digital cameras incorporating an APS-C digital sensor. As the APS-C sensor has a smaller surface area than 35mm film, these lenses are not generally considered to be compatible with older cameras. They also lack an aperture ring, limiting their use on cameras that do not support automatic aperture settings. Most of the DA zoom lenses are available in weather resistant (WR) versions to match the weather sealed capabilities of the medium to upper level Pentax DSLR camera bodies. While older models still have the in-body screw drive autofocus system, newer designs marked "DC", "SDM" or "PLM" feature silent, in-lens autofocus motors.
Some lenses of this product line such as the DA 10-17 Fisheye were co-developed with Tokina.[15]
DA-L lenses[edit]
These are lighter and cheaper versions of DA series zoom lenses. They have a plastic (as opposed to steel) mount and lack the quick-shift focusing system of their heavier siblings. They are only sold in kits with entry-level bodies.
DA* lenses[edit]

The DA* lenses are designed for use with Pentax digital SLR cameras. DA* lenses have higher quality optics and feature a higher level of weather sealing (AW) than most DA lenses (WR). The DA* lenses are more expensive and generally feature improved light transmission and larger aperture openings for better low light performance. Some DA* lenses also feature both body driven screw drive focusing and the Pentax SDM (Supersonic Drive Motor) lens based focus mechanism.
Some lenses of this product line were co-developed with Tokina. Examples include the DA* 16-50 and DA* 50-135.
DA Limited lenses[edit]
These are high quality (mostly prime) lenses with the lens housing made of metal. They usually have a wider maximum aperture compared to zooms but narrower as compared to other prime lenses. This is a compromise as DA Limited lenses are usually made to be much more compact than other primes lenses. In August 2013 the DA Limited lenses were upgraded with Pentax new HD coating, replacing the previous smc coating.[16] The new HD lenses are also available in both silver and black, as opposed to only black.
The DA 35/2.8 Macro was co-developed with Tokina.[12] As of February 2015, the DA 20-40mm F2.8-4 Limited DC WR announced in November 2013[17] stands out for being both the only zoom as well as the only weather resistant lens of the series.
Lens variations[edit]
Below is a list of lenses in production as of April 2021.[10][18]
| Series | Prime Lenses | Zoom Lenses |
|---|---|---|
| K series | 34 | 7 |
| M series | 22 | 8 |
| A series | 19 | 11 |
| A* series | 9 | - |
| F series | 7 | 10 |
| F* series | 2 | 1 |
| FA series | 12 | 17 |
| FA Limited series | 3 | - |
| FA* series | 8 | 3 |
| FA J series | - | 3 |
| D FA series | 3 | 5 |
| D FA* series | 2 | 1 |
| DA series | 4 | 18 |
| DA Limited series | 10 | 1 |
| DA* series | 3 | 4 |
| DA XS series | 1 | - |
| DA L series | - | 6 |
Controls, features and changes[edit]

Image stabilisation[edit]
Unlike Canon and Nikon, Pentax, as well as Sony, provides "shake reduction" (SR) functionality within the camera, instead of inside each lens to be purchased. This is advantageous as any lens can be used with full SR functionality, and the lenses are more economical to manufacture as they do not require any shake reduction equipment inside.
Weather sealing[edit]
Many Pentax lenses, like their medium- to high-end camera bodies, are weather-sealed, allowing for their continued use in poor weather and wet locations. Lenses marked as WR bear a “simplified weather-resistant construction […] which makes it difficult for water to enter the lens” compared to the DA* and AW lenses, which are “dust-proof and water-resistant”.[20] Pentax currently provides weather-sealed premium lenses up 560 mm. The largest lens produced by Pentax was the Reflex 2000mm, with non-mirrored lenses available up to the A* 1200mm. As with most manufacturers, telephotos of this range are no longer in production. Pentax provided premium focal lengths well beyond 1200mm, such as their 3800mm through the Pentax telescope division.
Full manual focus[edit]
First introduced at Pentax 2003 with the DA 16-45mm, the Quick-Shift focus system made it possible that the focus ring don't move during autofocus operations. Also after focusing using the autofocus, the focus ring can be turned to allow immediate focus adjustment for manual focus without the need for an AF/MF switching operation.[8]
Powered zoom[edit]
Some FA and FA* lenses did come with an integrated motor and two additional electronic contacts for power zoom functionality. This allows to change the focal length with a small twist of the zoom ring at three different speeds.[21] Most Pentax digital SLRs today do support the first two basic functions of Power Zoom lenses.
Supersonic Drive Motor (SDM)[edit]
The Pentax-developed SDM autofocus systems, with SDM standing for "Supersonic Drive Motor", departs from the previous Pentax system which utilizes a screw-drive autofocus motor inside the camera body. Instead, SDM lenses incorporate an autofocus micro-motor as part of the lens itself. All current production Pentax Digital SLR bodies are compatible with SDM lenses. However the DA* 55mm, DA 17-70mm and DA 18-135mm lenses are not compatible with some older Pentax digital SLR's such as the K110D, first version K100D and earlier models (The K100D Super is compatible, provided it has up to date firmware).[22]
The SDM mechanism is claimed to provide smoother and quieter focusing.[23] The first Pentax cameras to support SDM lens were the K10D (firmware 1.30 or later) and K100D Super. These and subsequent Pentax DSLR bodies support both SDM and in-camera screw-driven AF.
Camera compatibility[edit]
All Pentax K-mount auto-focus cameras are backward compatible with K-mount lenses dating back as far as 1975 without need for an adapter. Cameras with a "crippled K-Mount" cannot read the set f-stop of K and M series lenses and must stop-down momentarily to meter in case the adjusted aperture is a stopped down one. All Pentax and Samsung D-Xenogon lenses are interchangeable since Samsung adopted K-mount on their GX camera bodies.[24] The Samsung GX-10 and GX-20 are the only two Samsung models compatible with SDM lenses. Pentax KAF3 lenses do only have an own internal autofocus motor and are not fully compatible with some early DSLR models like the *istD.
| Bayonet > | K, M | A | F, FA, D-FA | FA Powerzoom | FA-J | DA, DA-L | DA-SDM, DA-DCM (KAF3) | DA, D-FA (KAF4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main changes: Camera |
First K-mount version | A-position, electrical contacts | Screw drive, with contacts for serial communication | Two contacts for Powerzoom | Aperture ring abandoned | Small image circle | In lens autofocus motor | electromagnetic aperture control |
| K (K-series, M-series, LX) | M, Av | M, Av | M, Av | M, Av | X | X | X | X |
| KA (A-series, P-series) | M, Av | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P | Tv, P | (Tv, P)1 | (Tv, P)1 | X |
| KAF | M, Av | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | Tv, P, AF | (Tv, P)1 | (Tv, P)1 | X |
| KAF2 (MZ-S, MZ-3, MZ-5 etc.) | M, Av | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF, PZ | Tv, P, AF | (Tv, P)1 | (Tv, P)1 | X |
| KA2 (MZ-M/ZX-M) | M, Av | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P | Tv, P | (Tv, P)1 | (Tv, P)1 | X |
| KAF without aperture simulator (MZ-30/ZX-30, *ist) | M | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | (M, Av, Tv, P, AF)1 | (M, Av, Tv, P)1 | X |
| KAF digital without aperture simulator (*istD, *istDS, *istDL, K100D, K110D) | M+, Av0 | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P | X |
| KAF2 digital Powerzoom without aperture simulator (K10D) | M+, Av0 | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF, PZ 2 | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, SDM/DCM 2 | X |
| KAF2 digital SDM without aperture simulator (K100D Super, K20D, K200D, K-m, K-7, K-5, K-5II, K-x, K-01) | M+, Av0 | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, SDM/DCM | X |
| KAF2 digital SDM without aperture simulator and with ED-interface: K-70. After update of firmware: K-50, K-1, K-3, K-3II, K-S2, K-S1. |
M+, Av0 | M, Av, Tv, P | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, AF | M, Av, Tv, P, SDM/DCM | M, Av, Tv, P, SDM/DCM/PLM |
Legend:
- 1 – Image circle not sufficient or borders with vignetting or optical aberrations
- 2 – K10D can be updated to change from Powerzoom-use to SDM-drive.
- AF – Screw drive autofocus
- Av – Aperture priority
- Av0 – Aperture priority only with open aperture
- M – manual exposure with exposure display
- M+ – manual exposure with automatic working aperture metering, no exposure display
- P – Program AE
- PLM - Autofocus with pulse motor
- PZ – Powerzoom (K10D with limited capatibility only)
- SDM/DC – Autofocus with supersonic- or direct current motor (K10D with firmware version 1.3)
- Tv – Time priority
- X – not useful, because smallest aperture always set
Comments:
- On cameras with KAF/KAF2-mount without aperture simulator during Av metering the aperture has to be adjusted on the camera.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e "Course of history". pentax.com. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ "Asahi fish-eye-Takumar".
- ^ "About Super-Multi Coating (SMC)". Bojidar Dimitrov's Pentax K-Mount Page. Archived from the original on 3 February 2018. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ Szymon Starczewski. "Pentax smc FA 43 mm f/1.9 Limited review - Ghosting, flares and transmission". LensTip.com. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ "List of Pentax Masterpieces". aohc.it (Asahi Optical Historical Club). Archived from the original on 2004-06-23. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Pentax Timeline". Ricoh Imaging. Archived from the original on 2017-12-15. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ "World's first lenses featuring power-zoom and focusing distance measurement". aohc.it (Asahi Optical Historical Club). Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ a b Ole Oest. "Pentax Lens Power Zoom". Mosphotos.com. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ "Pentax K-Mount Lenses Explained: The differences between various Pentax lens series".
- ^ a b "Pentax K-Mount Lens Line Up" (PDF). ricoh-imaging.co.jp. Ricoh imaging. February 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2017.
- ^ "Press Release: The smc Pentax-D FA Macro 100mm F2.8 WR". Hoya Corporation. 9 December 2009. Retrieved 16 March 2015 – via dpreview.
- ^ a b Tokina#History
- ^ "Press Release: The smc Pentax-D FA Macro 100mm F2.8 WR". Pentax Ricoh Imaging Company. 4 February 2015. Retrieved 16 March 2015 – via dpreview.
- ^ "Ricoh announces development of long-awaited full-frame Pentax DSLR". dpreview. 4 February 2015. Retrieved 16 March 2015.
- ^ Keppler, Herbert (2007). "The Name Game – Just who made your favourite lens?". Popular Photography (January 2007): 46 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Ricoh announces 'HD' update to Pentax DA Limited primes".
- ^ "Press Release: HD Pentax-DA 20-40mm F2.8-4ED Limited DC WR". Pentax Ricoh Imaging Company. 6 November 2013. Retrieved 12 February 2015 – via dpreview.
- ^ "All Current K-Mount Lenses - Pentax Lens Reviews & Lens Database". pentaxforums.com. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ^ "Product page of Pentax K-50 - RICOH IMAGING EUROPE S.A.S".
- ^ Hoya Corporation: smc Pentax-DA Interchangeable Lens Operating Manual (available online from Ricoh Archived 2015-02-13 at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ "PENTAX Lens Technology". Ricoh Imaging. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ Pentax (2011). "Pentax Lens Compatibility". Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 26 December 2011.
- ^ Pentax (2010). "smc Pentax DA Star 300mm F4 ED(IF) SDM". Archived from the original on 5 December 2010. Retrieved 2 December 2010.
- ^ "Samsung and Pentax to co-develop DSLRs".
External links[edit]
- Pentax lenses, Ricoh Imaging
- Pentax lens technology, Ricoh Imaging
- Pentax K-Mount Page, KMP (formerly Bojidar Dimitrov)
- Pentax K Lens Database, Aperturepedia
- The Pentax K-mount Camera Lens Compatibility Chart, MosPhotos.com
- Pentax Lens Reviews & Lens Database, PentaxForums.com
- Pentax Lens Performance Survey, OpticalLimits
- database of Pentax K compatible lenses, PhotoPentax.com
