Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHMA NotesFewContents
Uploaded by
Sayyan ShaikhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHMA NotesFewContents
Uploaded by
Sayyan ShaikhCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
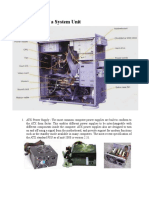
The computer cases are a visible part of our computers called PC towers and Computer towers.
Its function is to serve as a protective structure for the rest of the internal components where
they will be assembled.
There are many different types of cases. The main feature of each of them is its form and size
factor. This is due to the motherboard, whose form factor must be compatible with that of the
tower to fit perfectly.
The cooling system is one of the main components of any PC case. There should be enough
space inside for air circulation and large radiators that a powerful PC needs.
It must be understood that a PC case is an essential component for protecting the internal
equipment from external influences.
Along with characteristics, it is necessary to highlight their size and type of execution, which can
be either vertical or horizontal. The following are the computer case sizes and models available
in the market.
4 Different Types of Computer Case
1. Full tower
Firstly, Full Tower is used to accommodate an E-ATX or CEB motherboard. This is very
useful for high-performance servers that can use two processors and massive RAM and other
storage units at once.
The full tower ranges between 55- 75 cm tall and 22 – 32 cm in width. It can have from 4 to 9
5.25-inch bays (for additional optical drive). Allows you to install up to seven expansion cards,
such as a sound card or a receiver.
Department of Computer Science 1
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
This type of computer case comes with proper size and weight, which usually has better internal
cooling. Of course, their prices are a little high. That’s why enthusiasts, administrators have
always used full Tower cases, and hardcore streaming gamers.
If you want to build your separate uncompromising, powerful gaming PC and wanted to
use three monitors and play in 4K togetherly? Then such a case will provide your future
computer with the necessary space.
Such a case provides better cooling for two top-end graphics cards and a processor like the Intel
Core i9-9900K and allows you to create a custom cooling system with 230mm fans.
Buying a Full Tower is worth it, but only if you need space for a large number of components or
need a lot of airflows to cool the powerful processors and cards.
Full Tower Gaming ⬇ Chassis
Department of Computer Science 2
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
One big drawback to having a Full Tower is that it takes up a lot of space and is difficult to
hide. But if you have free space available, then it is not essential for you, then Full Tower can be
the best choice for your PC.
2. Mid Tower
Mid-tower or ATX format is the most popular and widely used computer case that allows you to
use many drives and almost all types of motherboards with acceptable overall dimensions in it.
The average full tower ranges between 35- 55 cm tall and 15 – 25 cm in width.
Inside the mid-tower case, there is more enough space for installing full-size components, such
as most extensive video cards over 300 mm long, and this case is capable of using 120, 140, or
even 200 mm fans for a positive effect on cooling the air.
Department of Computer Science 3
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
If you want to build a regular gaming PC, not as hardcore gaming, then Mid Tower is most likely
your right choice. This case is about 31 cm long, which is easy to install a full-size video card
and two to three expansion slots thick.
Besides, the components inside the Mid Tower will receive adequate cold airflow. With proper
use of fans (and regular cleaning from dust), the video card and processor temperatures will
never exceed 70-80 degrees Celsius, even in the most stressful conditions.
Using these types of computer cases, you can build a productive PC with a sound ventilation
system. It is considered a universal option for desktop users because you can assemble a wide
range of designs, a low-power office computer, a home media center, and a gaming computer.
Department of Computer Science 4
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
This type of format includes both those developed for the mini ITX standard and those designed
for the micro ATX standard. Therefore, you will find all the small computer cases in this
segment, including many cube-shaped or oriented for HTPC.
Recommended: Full Tower vs. Mid Tower – Which is Suitable? (Comparison)
Related: 3 Pin vs. 4 Pin Fans for PC Case – Which is Best? (Comparison)
3. Mini Tower
These types of computer cases are designed to take up as little physical space and without
installing decent-sized graphics cards. The average mini-tower length ranges between 30 – 45
cm tall and 15 – 25 cm in width (they can sometimes be smaller).
Their thermal enclosures are not the best on the market, so it is more convenient for you to install
low-consumption components rather than high-consumption ones.
The Mini Tower chassis is the smallest in size and not very popular among computer assemblers
due to the limited volume, which does not allow assembly of a more or less productive computer
and low airflow. A small body limits the choice of types of accessories too.
You can install only a microATX motherboard and a low power supply in these types of
computer cases. Typically, Mini Tower computers are shipped in the most basic configuration
for back-office machines or network terminals.
Department of Computer Science 5
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Mini Towers are an increasingly common choice for regular home PCs – both budget and
enough for standard video games. Regarding their possible uses, given their limited size and
expansion capabilities, their benefits are quite limited.
However, during assembly, only a specialist or experienced can beautifully arrange everything in
its place as there is not much space inside.
4. HTPC and SFF
HTPC stands ‘Home theatre PC’ for and SFF stands for ‘Small Form Factor‘. These types of
cases were considered very niche, but in recent years they have gained popularity due to the
miniaturization of powerful components that can fit in them.
HTPC is the perfect choice for the computer at your home multimedia entertainment. You can
place it under the TV table, or even you can hang on the wall. And the computing power of this
is more enough to play music and video in any modern format.
Department of Computer Science 6
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Also, such a PC will not make a sound – often, you can have passive cooling.
SFF takes little space. Due to their small size and lightweight, they can be an excellent
alternative to laptops. Some SFFs are handy to come with handles or unique bags to make them
easier to transport. Also, the SFF has a significant advantage over a laptop since it has more
power at less cost.
Many SFFs come with motherboards by offering cooling options that differ from the standard
fans found in other types of computer cases.
This happens because the video and sound on such motherboards are built-in, leading to
generating heat in a very tiny amount. As a result, they do not need powerful cooling. Also, this
arrangement reduces the size.
Department of Computer Science 7
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
SFF cases with Mini-ITX motherboard suits perfectly the people who work or play in tight
spaces. These are specially for small living rooms and small offices. It will also be much easier
to repair and improve such a PC than a laptop with the feature of portability.
It has one drawback that they are most often limited to only one CD drive.
==== * ====
Department of Computer Science 8
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Back side connectors of PC
SMPS. Switch Mode Power Supply uses electronics circuitry that converts the AC input
voltage to different values of regulated DC supply which is fed into various color-coded
wires fixed to connectors.
SMPS FAN. The fan is fixed inside the SMPS and is used to radiate the internal heat of
SMPS to outside.
Power In Socket. This socket is used to input 220V AC to the PC from mains supply
when the computer switch on the front side is pressed.
PS-2 Port. You can see two different colored 6-pin round shaped connectors. These
connectors are used to connect input devices, keyboard and mouse. Color Coding defines
the connector type. The purple connector is dedicated to connect Keyboard and Green
color is used for Mouse.
USB Port. The full form is Universal Serial Bus and is used to connect various input and
output devices like Mouse,Keyboard, Printers, Webcams etc. USB 3.0 is the latest
version which offers high data transfer speed.
Department of Computer Science 9
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
DVI Port. Digital Video Interface is a high-speed serial link for connecting output
display Devices.
HDMI Port.HDMI stands for high definition multimedia interface. This is a latest
interface that helps to get high definition video and multi channel sound. You can
connect HDMI enabled blue ray devices, LED’s etc.
15-pin Female VGA Port. This is used to connect display devices like Monitor / LCD /
LED Display.
LAN Port. The LAN or network port is used to connect to other devices and computers
in a network.
Audio Ports.Generally there are 3 number of audio ports on the back side of a PC. These
parts are either aligned vertically or in horizontal position. Green color port is dedicated
for headphones or speakers, a blue colored port is marked as Line-in and Mic can be
inserted in a pink port.
Expansion Slots: These expansion slots are used to connect add-on cards to increase the
capabilities of the motherboard.
Front Side buttons on PC
DVD-Writer. Top slot of the cabinet is reserved to fix CD-ROM or DVD-writer.
Power-LED: The LED glows and indicates that the Input Power is ON
Department of Computer Science 10
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
HDD LED: When we are working on the computer, the hard disk is in use , this LED
glows and is the indication that the hard disk drive is in use.
Reset Switch: This computer switch is quite handy when the computer is stuck-up and
you are not able to work on the computer . Just press this switch, the computer will Re-
Boot.
Front USB. Cabinet provides a facility for you to connect USB devices from front-side
as it is quite awkward to get to the back side of the computer again and again.
Front Audio Ports: The ports for MIC and HeadPhone at the front are for user quite easy
to approach.
Power Switch. It is used to switch-ON the computer.
=== * ===
Identify and understand different cables and connectors:
Video cables-
Mini-HDMI, Display port,
DVI;
VGA Cable for Computer and Projector
HDMI Cable
Department of Computer Science 11
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Mini HDMI
DVI Port
Department of Computer Science 12
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Peripheral cables:
Serial
Department of Computer Science 13
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Hard drive cables
There are three main types of cables: IDE/PATA, SATA and SCSI. IDE (Integrated Drive
Electronics) drives, also known as PATA (Parallel AT Attachment) drives, are commonly found
in personal computers.
There are several types of hard drives, and they all require different data cables. To connect a
hard drive to a computer, one must have the proper cables and plug the cables into the
appropriate places.
IDE/PATA Cable:
IDE/PATA data cable.
An IDE/PATA hard drive cable is a ribbon cable containing 40 pins. Either one or two devices
may be connected to an IDE/PATA cable, and the devices need not be of the same type. For
example, an IDE/PATA DVD-R drive may be connected along with an IDE/PATA hard drive on
the same cable.
SATA Cable:
SATA data cable.
Department of Computer Science 14
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
A SATA hard drive cable has seven conductors and is smaller than an IDE/PATA cable. A
SATA cable connects a single hard drive to a single connector on the SATA controller, which is
usually found on the computer's motherboard.
SCSI Cable:
SCSI 50-pin cable - by Smial on Wikimedia, Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 2.0
Germany.
SCSI cables look similar to IDE/PATA cables in that both drives use ribbon cables. However,
SCSI cables have more pins than IDE cables. Depending on the SCSI interface, a SCSI cable
may have 50 or 68 pins (IDE/PATA drives have 40). Like IDE, multiple SCSI devices can be
connected to a single channel through "daisy chaining." Depending on the SCSI interface, as
many as 7 or 15 devices may be connected to a single SCSI channel.
Adapters:
DVI to HDMI,
Usage: Computers and Laptops and Projectors
USB to ethernet,
Department of Computer Science 15
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Usage: Network Connection
DVI to VGA
Usage: Multimedia, DVD Player, Computer, Monitor, Game Player
=== * ===
I/O devices and Interfaces
Input/Output Device:
Input Devices are devices which send information to a computer system for processing.
Example: keyboard, mouse, webcam, microphone, etc.
Output devices accept the output after processing of data from other devices. Example: Monitor,
Printer, Speaker, etc.
Department of Computer Science 16
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Input devices:
An input device can receive instructions from users or forward information to another device.
After receiving input, it translates these data into the electrical signals in binary code, which
cannot be understandable by humans, and only a digital computer can understand it.
Keyboard and Mouse: These are the input devices that are used by the users to give
input to the computer. They send the received input (Data) from users to the system.
Microphone: This accepts sound generated by an input source and allows users to send
audio into their computers. In the microphone, the accepted signal may be converted into
a digital signal or can be amplified as an analog signal.
Webcam: A webcam is a video camera that connects to a computer and faces the user,
which is used to capture pictures, make a video by a computer system. It takes images as
input from where it is pointed and used for calling and taking selfies. However, most
modern webcams have a microphone, which offers users a better sound quality while
making videos. Webcams are attached to the monitor of a desktop computer and also
built into laptops.
Output devices
Output devices that receives data from another device and produces output with the information.
It functions to take data from input devices and translate the digitized signals into a form that can
be understandable by users.
Monitor: A monitor is a piece of computer hardware that accepts data from a computer
(output) and displays it on the system screen through the computer's video card. Monitors
have the ability to display information at a much higher resolution.
Speakers: Speakers accept sound data from a computer and play the sounds for users to
hear. Some speakers are manufactured in such a way that it cannot receive sound
generated by users as well as refer that sound to another device. The main objective of the
speakers is to produce sound or audio output for the listener.
Projector: A projector is an output device that accepts data from a computer (output) and
projects that data or information as a picture onto a wall or screen or any large surface. It
does not have the ability to receive data from a user and also not capable of sending that
data to another device. When you are showing video or images to a large group of people,
Department of Computer Science 17
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
a projector is more beneficial to use instead of a monitor because it displays data on a
large surface that can be visible to a large number of people clearly.
Input/output devices
An input/output device has the ability to accept data from users or another device (input), as well
as forward data to another device (output). Some examples of input/output devices are discussed
below:
CD-RW drive and DVD-RW drive: These drives functions for accepting data from a
computer as an input to copy onto a writable CD or DVD. And, this data contained on a
CD or DVD is sent by the drive to the computer.
USB flash drive: It is also referred to as a keychain drive, data stick, USB flash drive,
thumb drive, memory unit, pen drive. It is a portable storage device that saves or accepts
data from a computer (input). It connects to a computer via a USB port and forwards data
to a computer or another device (output).
Difference between Input and Output devices.
The below table contains major key points of the difference between both Input and Output
devices.
Input device Output device
An output device displays data on the screen for
The input device receives data from users.
users.
It works for translating user-friendly It works for translating the machine's instructions to
instructions into a machine friendly. user intelligible.
An input device can be commanded by the
Processor commands output device.
user.
The data, which is processed by the processor, is sent
It accepts data from the user as an input and
to the output device for sending it back to the user; it
forwards it to the processor for further
means that the output device takes the processed data
processing.
from the processor.
As compared to input devices, its design is less
Its design is more complex.
complex.
Department of Computer Science 18
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Input device helps the computer to receive The output device helps the computer to produce or
instructions from users. display the information to the users.
There are various input devices available
There are several output devices available such as
like Microphone, Joystick, Keyboard,
Speakers, Printers, Plotters, Projector, Monitor and
Pointing device, Image Scanner, Graphics
more.
tablet, and more.
Ports :
It is the connection point which acts as an interface between the computer and the external
devices like: Printer, Modem, Scanner, etc.
There are two types of ports :
1. Internal Port: It connects the system’s motherboard to internal devices like hard-disk,
CD drive, internal Bluetooth etc.
2. External Port: It connects the system’s motherboard to internal devices like mouse,
printer, USB etc.
Department of Computer Science 19
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Some important types of ports are as per follows:
1. Serial Port:
Used for external modems and older computer mouse
Two versions-9pin,25pin
Data travels at 115 kilobits per second
2. Parallel Port:
Used for scanners and printers
25 pin model
3. Universal Serial Bus (or USB) Port:
It can connect all kinds of external USB devices such as external hard disk, printer,
scanner, mouse, keyboard, etc.
Data travels at 12 megabits per seconds.
4. Firewire Port:
Department of Computer Science 20
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Connects camcorders and video equipment to the computer.
Transfers large amount of data at very fast speed.
Data travels at 400 to 800 megabits per seconds.
5. Ethernet Port:
Connects to a network and high speed Internet.
Data travels at 10 megabits to 1000 megabits per seconds depending upon the network
bandwidth.
Computer Ports
A port is a connection or a jack provided on a computer to connect external or peripheral devices
to the computer, for example, a port needed to connect a keyboard, mouse, pen-drives, etc.
It acts as an interface or a point of attachment between computer and external devices.
It is also called a communication port, as it is the point where a peripheral device is plugged to
allow data transfer or communication between the device and computer.
Generally, they are four to six in number and present on the back or sides of the computer.
Based on the type of protocol used for communication, computer ports can be of two types:
Serial Ports and Parallel Ports.
Serial Port:
In this port, the rate of transmission of data is one bit at a time through a single communication
line.
For example, D-Subminiature or D-sub connector is a commonly used serial port, which carries
RS-232 signals.
Department of Computer Science 21
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Parallel Port:
A parallel port is an interface that allows communication or data transfer between a computer
and a device in a parallel manner through more than one communication line.
For example, a printer port is a parallel port.
Examples of Computer Ports:
1) PS/2:
As the name suggests, it was introduced with IBM's Personal Systems/2 series of computers.
These connectors are colour coded, e.g., green was for mouse, and purple was for the keyboard.
Besides this, it is a DIN connector with six pins. At present, it is superseded by USB ports.
2) VGA Port:
This port is commonly found in computers, projectors, and high definition TVs. It is a D-sub
connector called DR-15 as it has 15 pins, which are arranged in 3 rows with five pins in each
row. It was most often used to connect CPU with CRT monitors. Still, most of the LCD and LED
monitors come with VGA ports.
Department of Computer Science 22
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
As the demand and emphasis on video quality kept growing, the VGA ports were gradually
replaced by more advanced ports that can assure high video quality such as HDMI and Display
Ports.
3) Digital Video Interface (DVI):
It is another interface between a CPU and a monitor.
It is a high-speed interface that is developed to transmit the lossless digital video signals and to
replace analogue digital video signal transmission through VGA technology.
The DVI interface can be of three types based on the signals transmitted by it: DVI-I, DVI-D,
and DVI-A. The DVI-I supports combined digital and analogue signals, whereas DVI-A supports
only analogue signals, and DVI-D supports only digital signals.
Mini-DVI: As the name suggests, it is smaller than a commonly used DVI port. It is a 32 pin
port developed by Apple as a substitute to Mini-VGA port. It can transmit various types of
signals such as S-Video, VGA, and composite signals using respective adapters.
4) Display Port:
This interface allows transmitting a video and audio from a device to a display screen. It is an
advanced display technology that is developed as a substitute for older interfaces such as DVI
and VGA. A display port can be seen on laptops, desktops computers, tablets, monitors, etc. It
has a 20-pin connector and offers a better resolution than DVI port.
Department of Computer Science 23
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
5) RCA Connector:
It is designed to accept composite video and stereo signals transmitted by three cables called
RCA cable. A RAC cable has three color-coded plugs that are connected to the three
corresponding coloured jacks of an RCA connector. Each of the coloured jack is ringed with
metal. The red jack supports the right stereo channel, and the white one supports the left stereo
channel, while the yellow is used for composite video.
6) Component Video:
This interface allows splitting video signals into three channels. The component video generally
has three color-coded slots; Red, Blue, and Green. Each slot receives and then transmits a
particular component of the video signal. It offers high-quality videos than composite video and
can carry both analogue and digital video signals.
7) HDMI port:
Department of Computer Science 24
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
HDMI (High Definition Media Interface) is a digital interface developed to connect high
definition devices such as digital cameras, gaming consoles, etc., to computers and TVs with
HDMI ports. Besides this, it can carry uncompressed video and uncompressed or compressed
audio signals. The advanced version of HDMI, such as 2.0, can transfer video signals of up to a
resolution of 4096x2160.
8) USB:
USB (Universal Serial Bus) port is very versatile in use; It can be used for various purposes, such
as to transfer data, to connect peripheral devices, and even as an interface for charging devices
such as smartphones, digital cameras, etc. Today, it has replaced PS/2 connectors, game ports,
serial and parallel ports, etc.
Types of USB ports:
USB Type A:
It is a four-pin connector and has many versions that include USB 1.1, USB 2.0 and USB 3.0,
and USB 3.1. Version 3.0 is a common standard that supports a data transfer rate of upto 400
MBps. Version 3.1 allows a data rate of upto 10 Gbps.
USB Type C:
It is the latest design of the USB that comes with 24 pins and can handle a current of 3A. As it
can handle high current, it is also used in devices for fast charging. This port was developed by
Department of Computer Science 25
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF). One of the distinguishing features of this port is that it
has no up or down orientation, which means you don't need to flip the male connecter over to
plug it in the USB port. For example, a USB-C plug is symmetrical, so that it can be inserted or
plugged in either way.
9) RJ-45:
It is an Ethernet style network port found on the computer and other devices such as routers,
switches, etc. This port allows your computer to interact or communicate with other computers
and networking devices where Ethernet networking is required.
Its full form is Registered Jack 45. It is also known as Ethernet port, network jack, or RJ45 jack.
It has eight pins; accordingly, the RJ45 cable comprises eight separate wires of different colours.
Besides this, it looks like a telephone jack; however, it is slightly wider than that.
10) RJ11:
It is also a registered jack, which is often used as an interface for modem, ADSL, and telephone
and for terminating the telephone wires. Although it looks like RJ45, it is different from that as it
is smaller and has only six pins; it is a 6P4C connector that shows it has six pins with four
contacts. This port is mainly used to connect to dial-up modems and is also known as a phone
connector, modem port, phone jack, etc.
Department of Computer Science 26
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
11) 3.5 mm Audio Jack:
It is a small round connector, port, or an audio jack commonly found on laptops, computers,
phones, etc. It is designed to connect to wired headphones and speakers. In other words, it
accepts a pin-shaped plug from a headphone, earphone, etc. The measurement "3.5 mm" denotes
the diameter of the connector.
However, in older devices, there were two audio jacks, one for mic and another one for
headphone. Besides this, they have a 2.5 mm jack or port for phone headphones.
=== * ===
In data communication terminology, a Transmission Medium
is a physical path between the transmitter and the receiver OR
it is the channel through which data is sent from one place to another.
Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types:
1. Guided Media:
It is also referred to as Wired or Bounded transmission media. Signals being transmitted
are directed and confined in a narrow pathway by using physical links.
Features:
High Speed
Secure
Department of Computer Science 27
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Used for comparatively shorter distances
There are 3 major types of Guided Media:
(i) Twisted Pair Cable: It consists of 2 separately insulated conductor wires wound about
each other. Generally, several such pairs are bundled together in a protective sheath. They
are the most widely used Transmission Media. Twisted Pair is of two types:
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): This type of cable has the ability to block
interference and does not depend on a physical shield for this purpose. It is used for
telephonic applications.
Advantages:
Least expensive
Easy to install
High-speed capacity
Susceptible to external interference
Lower capacity and performance in comparison to STP
Short distance transmission due to attenuation
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): This type of cable consists of a special jacket to
block external interference. It is used in fast-data-rate Ethernet and in voice and data
channels of telephone lines.
Advantages:
Better performance at a higher data rate in comparison to UTP
Eliminates crosstalk
Comparatively faster
Department of Computer Science 28
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Comparatively difficult to install and manufacture
More expensive
Bulky
(ii) Coaxial Cable: It has an outer plastic covering containing 2 parallel conductors each
having a separate insulated protection cover.
The coaxial cable transmits information in two modes:
Baseband mode(dedicated cable bandwidth)
Broadband mode(cable bandwidth is split into separate ranges).
Cable TVs and analog television networks widely use Coaxial cables.
Advantages:
High Bandwidth
Better noise Immunity
Easy to install and expand
Inexpensive
Disadvantages:
Single cable failure can disrupt the entire network
(iii) Optical Fibre Cable: It uses the concept of reflection of light through a core made up
of glass or plastic. The core is surrounded by a less dense glass or plastic covering
called the cladding. It is used for the transmission of large volumes of data.
The cable can be unidirectional or bidirectional. The WDM (Wavelength Division
Multiplexer) supports two modes, namely unidirectional and bidirectional mode.
Department of Computer Science 29
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Advantages:
Increased capacity and bandwidth
Lightweight
Less signal attenuation
Immunity to electromagnetic interference
Resistance to corrosive materials
Disadvantages:
Difficult to install and maintain
High cost
Fragile
(iv) Stripline:
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium Stripline is the
earliest form of the planar transmission line.
It uses a conducting material to transmit high-frequency waves it is also called a
waveguide.
This conducting material is sandwiched between two layers of the ground plane which
are usually shorted to provide EMI immunity.
(v) Microstripline
Here the conducting material is separated from the ground plane by a layer of dielectric.
2. Unguided Media: It is also referred to as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media. No
physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic signals.
Features:
The signal is broadcasted through air
Less Secure
Used for larger distances
There are 3 types of Signals transmitted through unguided media:
Department of Computer Science 30
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
(i) Radiowaves:
These are easy to generate and can penetrate through buildings. The sending and
receiving antennas need not be aligned.
Frequency Range: 3KHz – 1GHz. AM and FM radios and cordless phones use
Radiowaves for transmission.
Further Categorized as (i) Terrestrial and (ii) Satellite.
(ii) Microwaves:
It is a line of sight transmission i.e. the sending and receiving antennas need to be
properly aligned with each other.
The distance covered by the signal is directly proportional to the height of the antenna.
Frequency Range:1GHz – 300GHz.
These are majorly used for mobile phone communication and television distribution.
(iii) Infrared:
Infrared waves are used for very short distance communication.
They cannot penetrate through obstacles.
This prevents interference between systems.
Frequency Range:300GHz – 400THz.
It is used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, keyboard, printer, etc.
Department of Computer Science 31
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
HDMI stands for High Definition Multimedia Interface:
HDMI works as an interface between any multimedia devices to transfer audio and video
signals.
It is mainly a port in which cables (known as HDMI cables) are connected to transfer
audio and video together.
HDMI can transmit high-definition video and audio signals over up to 8-channels.
HDMI standard was developed by multiple companies, such as Hitachi, Silicon Image,
Thomson, Philips, Sony, Panasonic and Toshiba
Advantages
HDMI support high resolution at high refresh rate.
HDMI supports audio and video together with one port and one cable.
Also HDMI supports HDCP and 3D transmission.
HDMI has comes with nowadays TVs, monitor, laptops, in many devices.
HDMI has Simple connection to connect devices.
It has integrated audio. video and content protection.
HDMI uses digital interface instead of an analog interface.
In HDMI high definition signal is not compressed at all.
Disadvantages
While using HDMI sometimes authentication delay can be happen which causes
blanks screen, which is irritating thing.
Department of Computer Science 32
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
HDMI cables as well as HDMI supported devices are costlier than others.
There are limitations to field terminations of HDMI cables
CEC(Consumer Electronics Control) causes confusion when the devices themselves
change their configuration as they might get undetected by the control systems.
HDMI use DVI interfacing so its need a HDMI-DVI adapter to connect the audio,
otherwise the audio cannot be connected.
Multiple applications are difficult to run simultaneously via HDMI.
Universal Serial Bus (USB):
It is used as a device for communication between connectors and cables.
Data transfer and electricity supply between peripheral devices such like keyboard,
mouse, printer, portable media players, disk drive etc was the main motive behind
designing a USB.
It is also used for connection and power supply between computers, laptops, and
electronic devices.
Characteristics of USB:
A maximum of 127 peripherals can be connected to a single USB host controller.
USB device has a maximum speed up to 480 Mbps (for USB 2.0).
Length of the individual USB cable can reach up to 5 meters without a hub and 40 meters
with hub.
USB acts as a “plug and play” device.
USB can draw power by its own supply or from a computer.
If a computer turns into power-saving mode, some USB devices will automatically
convert themselves into “sleep” mode.
Advantages:
Ease of use
Acceptable data rate for many applications
Robust connector system
Variety of connector types/sizes available
Low cost
Disadvantages:
Department of Computer Science 33
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
USB cables are limited in length.
Some very high-speed peripheral devices require sustained speeds not available in the
USB standard.
Use of the USB logos on the product require annual fees and membership in the
organization.
=== * ===
Speaker:
Speakers are used to connect to a computer to generate sound. With the computer speaker, the
computer's sound card creates a signal that is used to produce sound. The primary objective of
speakers is to offer audio output for the listener. The electromagnetic waves are converted into
sound waves through the speaker as they are transducers. The devices, like an audio receiver or
computer, give audio input to speakers, which may be in the form of analog or digital. The
function of the analog speaker is simply to magnify the analog electromagnetic waves into sound
waves.
The sound waves are produced in analog form, but first, the digital input is converted into an
analog signal by digital speakers then the sound waves are generated. The amplitude and
frequency define the sound produced by speakers. The frequency determines the pitch of the
sound of how high or low it is. The sound quality, how clear it will be, depends upon the speaker
system's ability; if it is able to accurately reproduce sound frequencies, it can be the best
indicator to determine audio quality.
There are numerous speakers that consist of different speaker cones, which make them capable
of offering more accurate sounds for different ranges. The three-way speakers generally contain
a subwoofer, mid-range speaker, and a tweeter, whereas the two-way speakers have a mid-range
speaker and a tweeter. The air pressure created by the speakers' sound waves determines the
loudness or amplitude.
Department of Computer Science 34
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Speakers that have the ability to increase the sound input are commonly known as active
speakers. If a speaker can be plugged into an electrical outlet or consists of volume control, you
can easily determine if the speaker is active. The passive speakers are those that do not have any
internal amplification; these speakers need a high level of audio input as they do not increase the
audio signal.
Usually, speakers come in pairs that led to producing stereo sound. It means, on two separate
channels, the left and right speakers produce audio. Music sounds much more natural when you
use two speakers, as in this condition, our ears hear sounds from the left and right at one time,
which makes sounds much more natural. Furthermore, surround systems can produce more
realistic sound as they may include four to seven speakers, including a subwoofer.
Rating a Speaker:
Speakers are rated in distortion, watts, frequency response, and total harmonic.
Frequency response: It is produced by speakers, which is the rate of the lows and highs
of the sound.
Watts: For the speakers, it is the amount of amplification.
Total harmonic distortion (THD): It is the amount of distortion created with the help of
amplifying the signal.
=== * ===
Keyboard
A keyboard is an input devices that allows users to input text into a computer or any other
electronic machinery. It consists of multiple buttons, which create numbers, symbols, and letters,
and special keys like the Windows and Alt key, including performing other functions. The design
of the keyboard comes from the typewriter keyboards, and numbers and letters are arranged on
the keyboard in that way, which helps to type quickly.
The above keyboard design is called QWERTY design because of its first six letters across in the
upper-left-hand corner of the keyboard. Keyboards have function keys (F1 to F12 or F16) at the
Department of Computer Science 35
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
top of the keyboard and arranged arrow keys in the downside used to perform numerous
functions.
Types of keyboards
Most computer users use the standard keyboard, which connects to the computer. Although there
are many types of a computer keyboard, such are as follows:
1. Flexible keyboard: It is a type of keyboard that is made of soft silicone with highly portable.
It is water and dust-resistant and does not require constant cleaning. It acts the same as a standard
keyboard and connects to the computer via a USB connection serial port.
The flexible keyboard is made of soft silicone that saves it from a number of different
substances. It does not make a sound when being used; that's why it is also called a silent
keyboard. These keyboards are useful for traveling time because they can be rolled up into a bag
and flexible in outdoorsy situations.
2. Ergonomic Keyboard: This type of keyboard is beneficial for your body posture. Instead of
adjusting yourself to fit the keyboard, it is designed to fit you easily, ease of use, and reduce
strain. It is designed in that way; instead of bending their hands, it allows users to straight their
hands. Generally, the space-bar is bigger as compared to a regular keyboard, which allows for
fast typing.
Department of Computer Science 36
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
3. Wireless Keyboard: It is a computer keyboard that is connected to computers, laptops, or
tablets without any cables. It uses radio frequency (RF), infrared (IR), or Bluetooth technology to
connect with devices. Users can move the wireless keyboard around without having to put it on a
desk as it provides portability and flexibility to the users. It is designed by stainless steel material
that increases its life for a long time. It can set up very easily by plugging the USB receiver into
the computer.
It utilizes light waves to transmit signals to other infrared-enabled devices as it is based on
infrared technology. Some wireless keyboards use radio frequency technology, which
communicates via signals with a range from 27 MHz to up to 2.4 GHz.
4. Mechanical Keyboard: It is made with high quality that commonly used in both home and
office. It is designed for long life with high durability and responsiveness. It provides crisp click
sound, medium resistance, and better feedback for gaming performance and ultimate typing. It
offers framing, switches, type print methods, functionality, PCB board, key construction, LED
lighting, or more other better features as compared to traditional rubber dome keyboards.
Department of Computer Science 37
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
5. Virtual Keyboard: It is a software-based keyboard that enables users to type without the need
for physical keys. It is an alternative for a physical keyboard or a digital representation of a
QWERTY keyboard. These types of keyboards commonly have many pages of characters,
including numbers, letters, punctuation, and symbols. Some virtual
keyboards also include options to insert emojis, stickers, or animated GIFs on the basis of the
device's operating system.
Examples of virtual keyboards
6. Projection Keyboard: It is a form of computer input device that can be connected via
Bluetooth to the mini PC, tablet computer, or even smartphone. In projection keyboard, the
image of a virtual keyboard is projected onto a surface. The device records the corresponding
keystroke when a user touches any key from the shown keyboard on the surface. Some devices
are connected via Bluetooth devices such as tablets, smartphones, mini-PC with Android,
Windows operating system or iOS, etc.
Department of Computer Science 38
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
7. Gaming Keyboard: A keyboard that contains a few specific keys used for gamers is known
as a gaming keyboard. The W, S, D, A, and arrow keys are widely used for games on the
standard QWERTY keyboard. Gaming keyboards (mostly mechanical keyboard), the key
switches needless depression that provides faster action for games.
=== * ===
Monitor:
A monitor is an electronic output device that is also known as a video display terminal (VDT)
or a video display unit (VDU). It is used to display images, text, video, and graphics
information generated by a connected computer via a computer's video card.
Department of Computer Science 39
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Older monitors were built by using a fluorescent screen and Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), which
made them heavy and large in size and thus causing them to cover more space on the desk.
Nowadays, all monitors are made up by using flat-panel display technology, commonly backlit
with LEDs. These modern monitors take less space on the desk as compared to older CRT
displays.
Types of Monitors
There are several types of monitors; some are as follows:
1. Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Monitors
It is a technology used in early monitors. It uses a beam of electrons to create an image on the
screen. It comprises the guns that fire a beam of electrons inside the screen. The electron beams
repeatedly hit the surface of the screen. These guns are responsible for generating RGB (Red,
Green, Blue) colors, and more other colors can be generated with the help of combining these
three colors.
2. Flat Panel Monitors
These types of monitors are lightweight and take less space. They consume less power as
compared to CRT monitors. These monitors are more effective as they do not provide harmful
radiation. These monitors are more expensive than CRTs. The flat-panel monitors are used in
PDA, notebook computers, and cellular phones. These monitors are available in various sizes
like 15", 17", 18" & 19" and more. The display of a flat-panel monitor is made with the help of
two plates of glass. These plates contain a substance, which is activated in many ways.
Department of Computer Science 40
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Flat-panel monitor screens use two types of technologies, which are given below:
Liquid Crystal Display: LCD (Liquid crystal display) screen contains a substance
known as liquid crystal. The particles of this substance are aligned in a way that the light
located backside on the screens, which allow to generate an image or block. Liquid
crystal display offers a clear picture as compared to CRT display and emits less radiation.
Furthermore, it consumes less power and takes less space than a CRT display.
Gas Plasma Display: This display uses gas plasma technology, which uses a layer of gas
between 2 plates of glass. When voltage is applied, the gas releases ultraviolet light. By
this ultraviolet light, the pixels on the screen glow and form an image. These displays are
available in different sizes of up to 150 inches. Although it offers effective colors as
compared to the LCD monitor, it is more expensive. That's why it is less used.
3. Touch Screen Monitors
These monitors are also known as an input device. It enables users to interact with the computer
by using a finger or stylus instead of using a mouse or keyboard. When users touch the screen by
their finger, it occurs an event and forward it to the controller for processing. These types of
screens include pictures or words that help users to interact with the computer. It takes input
from the users by touching menus or icons presented on the screen.
Department of Computer Science 41
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
There are different types of touch screen monitors; three common types are given below:
Resistive Touch Screen: Generally, this screen includes a thin electrically conductive
and resistive layer of metal. When the touch is pressed, a change in the electrical current
occurs that is sent to the controller. These screens are widely in use. These monitors are
more reliable as they cannot be affected by liquids or dust.
Surface Wave Touch Screens: These monitors process the input through ultrasonic
waves. When a user touches the screen, the wave is processed and absorbed by the
computer. It is less reliable as they can be damaged by water or dust.
Capacitive Touch Screen: This screen includes a cover with an electrically-charged
material. This material continuously flows the current over the screen. It is mainly used
by the finger rather than a stylus. These monitors contain better clarity and do not damage
by dust. Nowadays, capacitive touch screen is mostly used in smartphones.
4. LED Monitors
It is a flat screen computer monitor, which stands for light-emitting diode display. It is
lightweight in terms of weight and has a short depth. As the source of light, it uses a panel of
LEDs. Nowadays, a wide number of electronic devices, both large and small devices such as
laptop screens, mobile phones, TVs, computer monitors, tablets, and more, use LED displays.
Department of Computer Science 42
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Advantages of LED Monitor:
It includes a broader dimming range.
It is a more reliable monitor.
It is often less expensive.
It consumes less power (20 watts), and run on a lower temperature.
It has a more dynamic contrast ratio.
Comparison between LCD and LED monitors:
Resolution 1920 x 1080 LCD Monitors Led Monitors
Brightness 250 cd / m2 250 cd / m2
Energy Star Certified No Yes
Weight 2.4 kg 2.4 kg
Contrast Ratio 12,000,000: 1 100,000,000: 1
5. OLED Monitors
It is a new flat light-emitting display technology, which is more efficient, brighter, thinner, and
better refresh rates feature and contrast as compared to the LCD display. It is made up of locating
a series of organic thin films between two conductors. These displays do not need a backlight as
they are emissive displays. Furthermore, it provides better image quality ever and used in tablets
and high-end smartphones.
Department of Computer Science 43
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Nowadays, it is widely used in laptops, TVs, mobile phones, digital cameras, tablets, VR
headsets. The Samsung, Apple, iPhone X uses AMOLED display.
6. DLP Monitors
DLP stands for Digital Light Processing, developed by Texas Instruments. It is a technology,
which is used for presentations by projecting images from a monitor onto a big screen. Before
developing the DLP, most of the computer projection systems produced faded and blurry images
as they were based on LCD technology. DLP technology utilizes a digital micromirror device,
which is a tiny mirror housed on a special kind of microchip. Furthermore, it offers better quality
pictures that can also be visible in a lit room normally.
7. TFT Monitors
It is a type of LCD flat panel display, which stands for a thin-film transistor. In TFT monitors, all
pixels are controlled with the help of one to four transistors. The high-quality flat-panel LCDs
use these transistors. Although the TFT-based monitors provide better resolution of all the flat-
panel techniques, these are highly expensive. The LCDs, which use thin-film transistor (TFT)
technology, are known as active-matrix displays. The active-matrix displays offer higher quality
as compared to older passive-matrix displays.
Department of Computer Science 44
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
8. Plasma Screen Monitors
A plasma screen is a thin, flat-panel, and capable of hanging on a wall like LCD and LED
televisions. It is a brighter screen as compared to LCD displays and thinner than CRT displays. It
can be used to either display modes of digital computer input or analog video signals, and
sometimes, it is marketed as 'thin-panel' displays. Plasma displays have wide viewing angles,
high contrast ratios, and high refresh rates, which is used to reduce a blur video. Additionally, it
provides better quality pictures as it supports high resolutions of up to 1920 x 1080.
The plasma screen also includes some disadvantages such as the chance of screen burn-in,
consumes more power, loss of brightness with time, can be heavier in weight.
=== * ===
Installation of a Local printer:
Department of Computer Science 45
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Steps:
If you DO NOT have the installation CD that came with your printer: proceed to Manual
Installation and follow remaining directions (as mentioned in Manual Installation).
If you DO have the installation disk that came with your printer: Insert the CD into your
computer, and follow the installation wizard using all defaults.
Installing Manually
Click the START button and select DEVICES AND PRINTERS.
Select "Add a Printer"
Select "Add a Local Printer"
Department of Computer Science 46
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Choose to "Use an Existing Port", and leave as default "LPT1: (Printer Port)"
If you already have another printer connected to this PC, you may need to change to
LPT2
Select "Windows Update" to populate the list of known printers. This may take several
minutes.
Then choose your printer from the list. If multiple drivers are listed for your printer,
select the one that say PCL. For instance: Dell 5130PCL
Choose a name for your printer. The default name is fine, unless you have multiples of
the same printer.
Department of Computer Science 47
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
If you wish to test your printer to make sure it was installed correctly, select "Print a test
page"
When you're all done, press "Finish"
=== * ===
Installation of Shared Printer through Wired and Wireless Means
Share the printer on the primary PC
There are two ways to share your printer: using Settings or Control Panel.
Share your printer using Settings
1. Select the Start button, then select Settings > Devices > Printers & scanners.
2. Choose the printer you want to share, then select Manage.
3. Select Printer Properties, then choose the Sharing tab.
4. On the Sharing tab, select Share this printer.
5. If you want, edit the share name of the printer. You'll use this name to connect to
the printer from a secondary PC.
Department of Computer Science 48
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Connect the shared printer to another PC
There are two ways to connect a shared printer to another PC: using Settings or Control Panel.
1. Select the Start button, then select Settings > Devices > Printers & scanners.
2. Under Add printers & scanners, select Add a printer or scanner.
3. Choose the printer you want, and then select Add Device.
4. If you don’t see the printer you want, select The printer that I want isn’t listed.
5. In the Add printer dialog box, select Select a shared printer by name, and then enter the
computer or device name of the primary PC and the share name of the printer using one
of these formats:
o \\computername\printername
6. When prompted to install the printer driver, select Next to complete the installation.
=== * ===
Department of Computer Science 49
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Installing Cloud Printer:
Download PrinterShare Software (full Version) from
http://download.printershare.com/files/PrinterShare2308.exe
Install PrinterShare in Personal Computer (Windows OS)
Launch the PriterShare Software at the end of Installation
Login to PrinterShare Software with valid Gmail Account by Clicking icon at Taskbar (or
Search for PrinterShare Console) at TaskBar. Provide password of your own choice.
Select the Printer which is to be shared (From Share Local Printer Lists)
Click Share (Which will appear in Remote Printers List after Success)
Download and Install "PrinterShare" Software Application in Mobile (Another Device)
using Google Play Store.
In Mobile, Login PrinterShare App with Username and Password (Which is available in
message sent to gmail account, in case of Forgot Password)
Select the File to be printed remotely From Mobile Gallery and Click on Print, Select the
Shared Printer Name which is Shared in Personal Computer.
And Click Print.
Go to Personal Computer, the New Printing job is now available at Personal Computer
PrinterShare Application and automatically Prints the file which is sent remotely (through
Mobile).
PrinterShare Software GUI at Desktop and Android Mobile.
Department of Computer Science 50
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
Power Suppy
=== * ===
Inside a computer, a PSU is the device that converts alternate electricity (the electricity from
your outlet, normally 220V) to direct current to the components inside the case. Looking from
the outside, it's the three-prong plug that plugs into your socket. Laptops' are much the same,
except they're external: A block and cord that attaches to the back and plugs into the wall.
Every power supply is different. Some (typically for laptops) may have a low output of 65 watts,
while others might output 1,000 watts or more. Some may only have 10 amps, while others
output 65 amps.
Department of Computer Science 51
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Computer power supplies (PSU) convert AC to low-voltage regulated DC power. Most modern
desktop computers conform to the ATX standard, which supplies three positive rails: +3.3V,
+5V and +12V.
Wires coming out of an ATX PSU are color-coded as follows:
Yellow: +12V
Red: +5V
Orange: +3.3V
Black: Ground
Purple: 5V SB (standby voltage)
Green: /PS_ON (it can be shorted to ground to start PSU)
Grey: PWR_OK (status signal generated by PSU to indicate voltages are OK)
White: -5V (optional on newer ATX-2 PSUs)
Blue: -12V
Working of Switch Mode Power Supply
Initially, the unregulated AC input signal from the source is provided to the input rectifier
and filter circuit. Here the ac input signal is rectified to generate a DC signal and further
smoothened to remove high-frequency noise component from it. The DC output (still in
unregulated form) is fed to the power transistor that acts as a high-frequency switch.
According to the switching action of the power transistor (High Frequency Switch) DC
voltage will be obtained at its output side. The chopping frequency plays a crucial role in
maintaining the desired DC voltage level.
Department of Computer Science 52
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
The obtained DC signal at the output of the chopper circuit is then fed to the primary
winding of the high-frequency power transformer. Here the step-down transformer converts
the high voltage signal into a low voltage level which is further provided as input to the output
rectifier and filter unit. This simply filters out the unwanted residuals from the signal in order to
provide a regulated DC signal as the output.
The control circuitry present here acts as the feedback circuit for the complete unit.
This involves a comparator along with a pulse width modulator (PWM). The DC output from
the rectifier and filter is fed to the control circuit where the error amplifier which acts as a
comparator, compares the obtained DC voltage with the reference value.
If the DC output is greater than the reference value then the chopping frequency is to be
decreased. The decrease in chopping frequency will reduce the output power and so the dc output
voltage. However, if the DC output is less than the reference value then the chopping frequency
is increased. When chopping frequency is raised then the DC output voltage will get increased.
Applications of SMPS found in various power amplifiers, personal computers, security
and railway systems, television sets, motor drives, etc.
=== * ===
+5 Volts: This voltage is used to drive motors present in drives of form factors 2.5 inch
and 3.5 inches. Also a 5 Volts green wiring is used to connect the power button to the rest
of the circuitry.
+12 Volts: This voltage is used by the cooling systems and cooling fans of the
computer. Also, this supply may be used to drive motors which can’t run on a +5V DC
Supply.
-12 Volts: This voltage is used in the ISA bus slots. Now mostly the work which was
carried out earlier by a -12 volts supply, is being taken care of by the +/- 5 Volt supply.
+ 3.3 Volts: The +3.3 Volts orange line is the most basic supply line. Most of the CPUs
and RAM use 3.3 volts. The PCI Bus is powered with this supply voltage and hence any
components attached to it use this voltage line. In addition, a 3.3 Volts line powers up the
motherboard and is used to compensate any line losses since every device needs a
constant supply voltage.
The Power-Good signal prevents the computer from attempting to operate on improper
voltages and damaging itself.
Department of Computer Science 53
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
Experiment Conducted on SMPS Voltage Checking:
Wire Color with Theoretical Voltage Voltage Reading in Lab
Value
Yellow: +12V
Red: +5V
Orange: +3.3V
Black: Ground
Purple: 5V SB (standby voltage)
Green: /PS_ON (it can be shorted
to ground to start PSU)
Grey: PWR_OK (status signal
generated by PSU to indicate
voltages are OK) – Power Good
Signal
White: -5V (optional on newer
ATX-2 PSUs)
Blue: -12V
Department of Computer Science 54
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) Power Supply
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is a motherboard and power supply configuration
specification developed by Intel
Department of Computer Science 55
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
ATX is the most common motherboard design.[1] Other standards for smaller boards (including
microATX, FlexATX, nano-ITX, and mini-ITX)
Dimensions of a full-size ATX board are 12 × 9.6 in (305 × 244 mm), which allows many ATX
chassis to accept microATX boards.
Heat Sink
A heat sink is a component that increases the heat flow away from a hot device. It accomplishes
this task by increasing the device's working surface area and the amount of low-temperature fluid
that moves across its enlarged surface area. Based on each device's configuration, we find a
multitude of heat sink aesthetics, design, and ultimate capabilities.
A heat sink works by moving heat away from a critical component.
Department of Computer Science 56
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Active Heat Sinks and Passive Heat Sinks
Heat sinks are most commonly utilized in Active, Passive or hybrid configurations.
- Passive heat sinks
rely on natural convection, meaning the buoyancy of hot air alone causes the airflow
generated across the heat sink system.
These systems are advantageous as they do not require secondary power or control
systems to remove heat from the system.
passive heat sinks are less effective at transferring heat from a system than active heat
sinks.
- Active heat sinks
utilize forced air to increase fluid flow across the hot area.
Forced air is most commonly generated by a fan, blower, or even movement of the entire object
One example of a fan producing forced air across a heat sink is the fan in your personal computer
turning on after your computer gets warm.
- Hybrid heat sinks combine some aspects of passive and active heat sinks. These
configurations are less common
Department of Computer Science 57
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
How to test your PSU to see if it is dead or alive
Testing for a faulty power supply is a process of elimination. The process isn’t exhaustive, but
should give you a good idea of whether your PSU is working properly or not.
If you have performed software troubleshooting and think the issue may be hardware, follow
these steps. Retest after each step.
1. Make sure any external switch on the rear of the power supply hasn’t accidentally been
turned off.
2. Check the power cable is secure in the wall socket and rear of the computer.
3. Try a different power cable and wall socket to make sure neither is dead.
4. Check all internal connections inside your PC, especially power connectors to
peripherals.
5. Remove all peripherals and hardware from your computer except your boot drive and
graphics card if you don’t have onboard graphics. If your CPU does have built-in
graphics, remove the graphics card also.
Symptoms of a Failing Power Supply
System failures during the boot-up process.
The PC doesn’t power on at all
Spontaneous restarts or lockouts when trying to use the machine
Case fans and hard drives that do not spin
An overheating system due to heatsink and fan failure
Errors related to system memory
Recurring Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
Department of Computer Science 58
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
Active and Passive Components on Motherboard:
As a computer professional, you should be familiar with the more common types of electronic
components within a power supply.
Fuse
Before the advent of the circuit breaker, fuses were common in the home and office. A fuse
serves one purpose-to fail-and thus cut the flow of power in the event of a current load that has
exceeded the safe capacity of the system components to absorb.
Capacitors
A capacitor is an electrical component used to hold an electrical charge.
In PCs, they are often used to regulate the flow of current to areas of the system circuits for a
short period of time. Some are fixed-capacity models, whereas others can absorb or hold variable
Department of Computer Science 59
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
amounts of power. The amount of electrical current a capacitor can control is called capacitance,
measured in microfarads
Rectifiers and Diodes
Rectifiers are devices that convert AC power into a DC form (rectification). A diode is a device
that lets current flow in only one direction (see Figure 13.12). Two or more diodes connected to
an AC supply will convert the AC voltage to DC voltage.
Transistors
Transistors are basically a pair of diodes connected in series with an "on-off" switch. Varying the
voltage sent to a transistor turns the switch on or off.
Transformers
The most common forms of electrical transformers are step-down or step-up devices. A step-
down transformer decreases the transformer's voltage on the output side; a step-up model
increases it.
Department of Computer Science 60
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Inductors (Coils)
Inductors, commonly called coils because of their shape, are loops of conductive wire (see
Figure 13.16). Current passing through the inductor sets up a magnetic field. This field reduces
any rapid change in current intensity. Inductors can also be used to distinguish between rapidly
and slowly changing signals in a circuit.
Types of Electronic Components
These are of 2 types: Passive and Active Components. Both these types of components can be
either Through-Hole or SMD.
1. Passive Components
These components are those that do not have gain or directionality. They are also called
Electrical elements or electrical components.
Example: Resistors, Capacitors, Diodes, Inductors.
Department of Computer Science 61
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
2. Active Components
These components are those that have gain or directionality.
Example: Transistors, Integrated Circuits or ICs, Logic Gates.
Function of Basic Electronic Components
1. Terminals and Connectors: Components to make electrical connection.
2. Resistors: Components used to resist current.
3. Switches: Components that may be made to either conduct (closed) or not (open).
4. Capacitors: Components that store electrical charge in an electrical field.
5. Magnetic or Inductive Components: These are Electrical components that use
magnetism.
6. Network Components: Components that use more than 1 type of Passive Component.
7. Piezoelectric devices, crystals, resonators: Passive components that use piezoelectric.
effect.
8. Semiconductors: Electronic control parts with no moving parts.
9. Diodes: Components that conduct electricity in only one direction.
10. Transistors: A semiconductor device capable of amplification.
11. Integrated Circuits or ICs: A microelectronic computer circuit incorporated into a chip
or semiconductor; a whole system rather than a single component.
Department of Computer Science 62
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Circuit Symbols of Electronic Components
Output Values Output Values
Measured Measured
Components Or Components Or
Status of the Device Status of the Device
Observed Observed
=== * ===
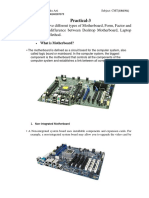
Motherboard:
The motherboard is generally a thin circuit board that holds together almost all parts of a
computer except input and output devices. All crucial hardware like CPU, memory, hard drive,
Department of Computer Science 63
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
and ports for input and output devices are located on the motherboard. It is the biggest circuit
board in a computer chassis.
It allocates power to all hardware located on it and enables them to communicate with each
other. It is meant to hold the computer's microprocessor chip and let other components connect
to it. Each component that runs the computer or improves its performance is a part of the
motherboard or connected to it through a slot or port.
There can be different types of motherboards based on the type and size of the computers. So, a
specific motherboard can work only with specific types of processors and memory.
Components of a Motherboard:
CPU Slot: It is provided to install the CPU. It is a link between a microprocessor and a
motherboard. It facilitates the use of CPU and prevents the damage when it is installed or
removed. Furthermore, it is provided with a lock to prevent CPU movement and a heat
sink to dissipate the extra heat.
RAM Slot: It is a memory slot or socket provided in the motherboard to insert or install
the RAM (Random Access Memory). There can be two or more memory slots in a
computer.
Expansion Slot: It is also called the bus slot or expansion port. It is a connection or port
on the motherboard, which provides an installation point to connect a hardware
expansion card, for example, you can purchase a video expansion card and install it into
the expansion slot and then can install a new video card in the computer. Some of the
common expansion slots in a computer are AGP, AMR, CNR, PCI, etc.
Capacitor: It is made of two conductive plates, and a thin insulator sandwiched between
them. These parts are wrapped in a plastic container.
Inductor (Coil): It is an electromagnetic coil made of a conducting wire wrapped around
an iron core. It acts as an inductor or electromagnet to store magnetic energy.
Northbridge: It is an integrated circuit that allows communications between the CPU
interface, AGP, and memory. Furthermore, it also allows the southbridge chip to
communicate with the RAM, CPU, and graphics controller.
USB Port: It allows you to connect hardware devices like mouse, keyboard to your
computer.
PCI Slot: It stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect slot. It allows you to connect
the PCI devices like modems, network hardware, sound, and video cards.
Department of Computer Science 64
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
AGP Slot: It stands for Accelerated Graphics Port. It provides the slot to connect
graphics cards.
Heat Sink: It absorbs and disperses the heat generated in the computer processor.
Power Connector: It is designed to supply power to the motherboard.
CMOS battery: It stands for complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor. It is a memory
that stores the BIOS settings such as time, date, and hardware settings.
Motherboard form factors
A motherboard form factor is a specification for its general shape and size. It helps to prevent
incompatibilities between many hardware manufactures. It also determines the types of power
supply, supported case, the physical layout and organization of the board, and the placement of
mounting holes. Furthermore, if you construct your own computer system, a form factor is much
important as it specifies the correct case and components of the computer system. Nowadays,
ATX is the most common form factor for desktop computers. There are different types of form
factors of the motherboard, which are as follows:
1. AT & Baby AT: The size of AT is 12" wide x 13.8" deep, which is rarely used, and its
replaced by ATX and Baby AT.
Baby AT motherboard was introduced by IBM that is a replacement for the AT
motherboard, which is also known as BAT. The width of Baby AT is 8.57" and 13.04"
deep, which is more similar to the original IBM XT motherboard. It was mainly designed
for peripheral devices such as a keyboard and mouse.
2. ATX: It stands for Advanced Technology eXtended, which was first released by Intel.
The size of Standard ATX or Full-ATX is 12" wide x 9.6" deep. There were some
improvements in the ATX form factor as well as a single 20-pin connector for power
supply, less overlap between the drive bays and motherboard, and integrated I/O Port
connectors soldered directly onto the motherboard.
3. BTX (Balanced Technology Extended): The BTX includes features such as a more
efficient layout to facilitate cooling, low profile, support for high-mass motherboard
components, and a scalable board to accommodate several system sizes. BTX was
developed to offer advantages like PCI Express, ATA, and USB 2.0.
Furthermore, it uses in-line airflow and allows to switch the places of memory slots and
expansion slots. Its main components, such as chipset, graphics controller, and processor,
Department of Computer Science 65
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
use the same airflow, which decrease the required fans in the system; that's why
unnecessary noise reduces. The industry considers the ATX form factor in terms of
standard, although legacy AT systems are mainly still used today. The BTX form factor is
incompatible with the design of ATX. Thus, it is not a standard for the industry.
4. DTX: In telecommunications, it stands for discontinuous transmission. It is a method
that is used to improve the efficiency of two-way wireless voice communication.
In the computer, it is a form factor for motherboards, which is a variation of ATX
specification. It was designed for small form factor computers such as home theater PCs
with dimensions of 8 × 9.6 inches. It is an open standard declared by AMD and is lower
compatible with ATX form factor cases. Furthermore, the Mini-DTX, a smaller version,
was also developed that had 8.0-inches by 6.7-inches dimensions. It uses fewer layers of
printed circuit board wiring through which it offers a lower cost of manufacturing.
5. LPX (Low Profile eXtension): The size of an LPX motherboard is 9" wide and 13"
deep. As compared to other motherboards, it has several placements of the video, serial,
parallel, and PS/2 ports. It is known as low profile as it contains a big slot for a riser card
that gives the permission to the expansion cards to be installed parallel to the
motherboard. The computers using low profile motherboards are much slimmer as
compared to use a Baby-AT motherboard computer.
6. microATX: It is a smaller motherboard that is designed by following the ATX form
factor, having the same benefits. But it improved the overall design cost by reducing the
physical size of the motherboard. Intel developed the first mATX motherboard. The size
of mATX is 9.6" wide x 9.6" deep, which can be reduced to size as 6.75" wide x 6.75"
deep. It provides more I/O space at the rear, and with the help of integrated Input/Output,
connectors help to reduce the emissions.
7. NLX: It is based on the boards, stands for New Low Profile Extended. These
motherboards can be removed easily, and it was developed to replace the nonstandard
LPX design. The size of the NLX motherboard is 9" wide x 13.6" deep maximum to 8" x
10" deep minimum. It includes various features such as provide support for AGP, DIMM,
USB, Pentium II, larger memory modules, lower cases, and can reduce cable length.
Additionally, it is an actual standard (unlike NLX form factor) that has more component
options for repairing and upgrading.
=== * ===
Department of Computer Science 66
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Mother Board Example: ASUS P5AD2-E motherboard LGA 775 (Socket T) ATX
Department of Computer Science 67
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Department of Computer Science 68
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Department of Computer Science 69
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Department of Computer Science 70
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Department of Computer Science 71
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Department of Computer Science 72
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
CPUID CPU-Z Tool
The CPU-Z utility displays detailed information about the memory modules installed in a
computer using a feature called Serial Presence Detect. The "SPD" tab in CPU-Z displays this
information, helping you learn more about the computer's configuration and confirm that
memory module makes and models are as expected.
Information Displayed in CPU-Z
Size, Maximum Speed, Manufacturer, Model Number and Production Date of each
memory module in the computer.
CPU-Z detects whether a module is Registered, Buffered or Error-Correcting.
CPU-Z displays the Latency Timings that a memory module is compatible with at all
supported speeds.
CPU-Z displays an overview of the Hardware Installed in a computer.
CPU-Z displays the Brand, Model and Speed of the Processor, the Manufacturer, Model
and Chipset of the Motherboard and the Manufacturer and Model of the Video Adapter.
Department of Computer Science 73
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Department of Computer Science 74
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Output Observed in CPU-Z Tool for CPU
Processor Name
Core Speed
Number of Cores
Bus Speed
Cache L1 Data
Cache L1 Inst.
Level-2 Cache
Few Terms Found in CPU-Z Report:
Concurrency or Single Core: In Operating Systems, concurrency is defined as the
ability of a system to run two or more programs in overlapping time phases.
Department of Computer Science 75
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Parallel Execution or (Multi-Core): In parallel execution, the tasks to be performed by
a process are broken down into sub-parts, and multiple CPUs (or multiple cores) process
each sub-task at precisely the same time.
Thread:
o A thread is a unit of execution on concurrent programming. Multithreading is a
technique which allows a CPU to execute many tasks of one process at the same
time.
CPU Core:
o A CPU core is the part of something central to its existence or character. In the
same way in the computer system, the CPU is also referred to as the core.
o The number of threads you have depends on the number of cores in your CPU.
Each CPU core can have two threads. So a processor with two cores will have
four threads. A processor with eight cores will have 16 threads.
MMX: The MMX instructions enable x86 processors to perform single-instruction,
multiple-data(SIMD) operations on packed byte, word, doubleword, or quadword integer
operands contained in memory, in MMX registers, or in general-purpose registers.
Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE). Older processors only process a single data
element per instruction. SSE enables the instruction to handle multiple data elements.
A cache is a reserved storage location that collects temporary data to help websites,
browsers, and apps load faster.
Recently used Instructions or upcoming instructions will be made available in
Instruction Cache
Recently used Data or upcoming data will be made available in Data Cache
Department of Computer Science 76
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
VID/FID – Voltage Identification / Frequency Identification
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a publicly available specification
that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware.
The RAS to CAS delay determines the time between memory accessing RAS (Row
Address Strobe) and CAS (Column Address Strobe). The lower the number, the better
Serial Presence Detect (SPD) is a standardized way to automatically access information
about a memory module.
EHCI PCI: The Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI) is a register-level
interface that enables a host controller for USB or FireWire hardware to communicate
with a host controller driver in software.
eXtensible Host Controller Interface (xHCI) is a computer interface specification that
defines a register-level description of a host controller for Universal Serial Bus (USB),
which is capable of interfacing with USB 1.x, 2.0, and 3.x compatible devices.
Universal Host Controller Interface (UHCI) was created by Intel as an implementation
of the USB 1.0 host controller interface. The UHCI specification defines a set of I/O
mapped registers that allow communication between the controller and the operating
system.
High Definition Audio (HDA): High Definition Audio Specification includes
architecture, register and electrical interface, programming model, link protocol, and
codec features.
The DMI (Desktop Management Interface) is an abstraction layer provided by your
system management BIOS that provides information about your computer's hardware to
your operating system.
Desktop Management Interface (DMI) is an industry framework for managing and
keeping track of hardware and software components in a system of personal computers
from a central location.
=== * ===
Windows Resource Monitor:
When Windows slows down or freezes, we usually turn to the Task Manager to figure out
what is going on. If you need a better understanding of the way Windows and its apps use
Department of Computer Science 77
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
the resources of your computer, Resource Monitor (resmon.exe) is the right tool for the
task.
The information is concise and real-time with graphs and grouping by resources.
You can monitor the use of the CPU, memory, disk, and network. This tutorial shows
what you need to know about Resource Monitor and how to use it:
How to start the Resource Monitor in Windows
An easy way to start Resource Monitor that works in all Windows versions is to search
for the name of its executable file resmon or for Resource Monitor, and click or tap the
search result with the same name.
=== * ===
Chipset:
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components in an integrated circuit
known as a “Data Flow Management System” that manages the data flow between the processor,
memory and peripherals. It is usually found on the motherboard. Chipsets are usually designed to
Department of Computer Science 78
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the
processor and external devices.
The term chipset often refers to a specific pair of chips on the motherboard: the
northbridge and the southbridge. The northbridge links the CPU to very high-speed devices,
especially RAM and graphics controllers, and the southbridge connects to lower-speed peripheral
buses (such as PCI or ISA).
Department of Computer Science 79
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
System Bus Architecture:
System bus contains 3 categories of lines used to provide the communication between the CPU,
memory and IO named as:
1. Address lines (AL)
2. Data lines (DL)
Department of Computer Science 80
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
3. Control lines (CL)
1. Address Lines:
Used to carry the address to memory and IO.
Unidirectional.
Based on width of a address bus we can determine the capacity of a main memory
2. Data Lines:
Used to carry the binary data between the CPU, memory and IO.
Bidirectional.
Based on the width of a data bus we can determine the word length of a CPU.
Based on the word length we can determine the performance of a CPU.
3. Control Lines:
Used to carry the control signals and timing signals
Control signals indicates type of operation.
Timing Signals used to synchronize the memory and IO operations with a CPU clock.
=== * ===
Identify system faults using POST diagnostics card.
Whenever you power on your computer, the ROM BIOS runs a diagnostic test of the
hardware, called the Power On Self Test (POST).
Each stage of testing generates a two-digit hex code. By tracking these codes, you can
view a progress report of the boot-up process and diagnose computer problems.
By monitoring POST codes using a POST diagnostic card, which plugs into a machine's
ISA or PCI port, one can troubleshoot a computer right on the bench, without needing to
hook up a monitor, keyboard, or even a disk drive.
These cards allow you to make quick work of fixing components and avoid the usual
time-consuming method of swapping them out one at a time and retesting.
POST codes vs. BIOS beep codes
Beep codes use audible signals to alert users to computer problems—an especially useful
feature if a hardware failure occurs before the video card is initialized.
While some sets of beep codes, such as those generated by the latest Phoenix BIOSs, can
provide extensive troubleshooting information, others are less revealing.
Department of Computer Science 81
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
There may be only 10 beep codes—a tiny subset of the up to 255 two-digit POST codes
that can be displayed right on a POST diagnostic card, via digital readouts (Figure A).
This POST diagnostic card, called POSTmortem, plugs into an ISA port. In addition to
digital readouts, the POSTmortem also includes four LEDs to diagnose power-supply
voltage problems.
POST card quick facts
POST codes are most often sent to port 80h (although some manufacturers use different
ports, Compaq, for example, uses port 84h.) POST cards either automatically detect the
port or contain jumpers for setting it manually.
In addition to providing digital readouts of POST codes, these cards typically include
LEDs for troubleshooting power-supply voltages. For example, the POSTmortem ISA
card pictured above contains four LEDs for testing +5V, +12V, -12V, and -5V power
supplies, as well as five contacts for testing these voltages with a probe.
For a more complete troubleshooting solution, get an ISA card if possible. (Your
motherboard will likely have an ISA legacy port.)
Sometimes PCI ports do not show all the available codes, for two reasons.
o 1. ISA busses are initialized before PCIs—the PCI bus will only receive the codes
that are generated after it is initialized.
Department of Computer Science 82
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
o 2. ISA busses connect to the South Bridge chip; motherboards with damaged
North Bridge chips may not be able to send codes to the PCI bus at all.
Before using a POST diagnostic card, you'll need a code manual.
POST card usage
As simple as POST cards are to use, they do require some care. Not all models, the
POSTmortem included, have protection circuits built in. Therefore, be careful not to
install these cards in reverse or upside down. Doing so could burn out the card. A marker
shows which way to orient the card. After you plug in the card, power up the machine
and follow the progress of the POST test.
The code you'll see is sent to the card just prior to the start of each test.
In above Figure, the code displayed (53) indicates the start of a video display ROM test.
The four lit LEDs indicate normal power from the power supply.
Should the computer fail during the POST, the failing test number will be the last one
displayed. Consider the failed test as only a possible indicator of the real problem at
hand—another component may, in fact, be the culprit. For example, a failed memory test
could indicate a badly seated chip or a motherboard problem.
Department of Computer Science 83
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
POST Codes:
Table A: AMIBIOS POST codes (sample selection)
=== * ===
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a publicly available specification
that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware.
Department of Computer Science 84
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface
originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI
firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services.
UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating
system installed.
Intel developed the original Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) specifications. Some
of the EFI's practices and data formats mirror those of Microsoft Windows.
The Unified EFI Forum is the industry body that manages the UEFI specifications
throughout.
EFI Services:
EFI defines two types of services: boot services and runtime services.
Boot services are available only while the firmware owns the platform (i.e., before the
ExitBootServices() call), and they include text and graphical consoles on various devices,
and bus, block and file services.
Runtime services are still accessible while the operating system is running; they include
services such as date, time and NVRAM access.
UEFI booting
Unlike the legacy PC BIOS, UEFI does not rely on boot sectors, defining instead a boot
manager as part of the UEFI specification.
When a computer is powered on, the boot manager checks the boot configuration and
based on its settings, then executes the specified OS boot loader or operating system
kernel (usually boot loader).
The boot configuration is defined by variables stored in NVRAM, including variables
that indicate the file system paths to OS loaders or OS kernels.
OS boot loaders can be automatically detected by UEFI, which enables easy booting from
removable devices such as USB flash drives.
=== * ===
BIOS Settings:
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, is the built-in core processor software responsible
for booting up your system.
Department of Computer Science 85
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Typically embedded into your computer as a motherboard chip.
Programmed on an erasable, programmable, read-only memory (EPROM) chip, BIOS is
stored on this memory chip which retains data when the power source is switched off.
The BIOS system is also responsible for managing data flow between your computer’s
operating system and any attached devices including a hard drive, keyboard, video
adapter, printer, or mouse.
Each time you power your PC on, BIOS runs through a process called Power-On Self
Test, or POST, that determines whether your attached devices are operating correctly and
are in their proper place.
Once all attachments are allocated and given the OK, your computer startup continues as
usual and takes you to your load screen in a matter of seconds.
If BIOS detects any problems, an error screen will appear or a series of beep codes will
sound, effectively indicating to you that something has gone wrong.
In order to access BIOS on a Windows PC, you must press your BIOS key set by your
manufacturer which could be F10, F2, F12, F1, or DEL.
Basic functions of BIOS:
BIOS’s functionality can be broken down into four key responsibilities.
1. POST
o POST (Power-On Self Test) that your PC runs through the moment you turn it on.
POST tests the hardware of your PC and ensures that there is nothing out of order
and no errors present with your operating system.
o If No Problem found, POST will continue as usual and allow your PC to boot
normally.
o If there is a detected error, BIOS will issue an error message that may come in the
form of displayed text or a series of error-indicating beeps.
2. CMOS setup
o Your PC stores all low-level settings like system time and hardware configuration within
its CMOS. This means that every change you make to your BIOS structure is saved on
this special memory chip called the Complementary
o Metal-Oxide Semiconductor, or CMOS. The CMOS setup is responsible for setting your
password, time, and date.
Department of Computer Science 86
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
3. Bootstrap loader
o The program that lives within your computer’s EPROM or ROM, the bootstrap loader is
tasked with reading your PC’s hard drive boot sector to move along the complete
operating system load.
o When you restart your PC, the bootstrap loader activates the POST, then loads Windows-
10 into memory.
o Newer PCs have replaced the bootstrap loader with an EFI, or Extensible Firmware
Interface.
4. BIOS drivers
o BIOS drivers are the many programs stored in your computer’s many memory chips.
o These low-level drivers are used to boot your system and prompt basic operational
controls on your PC.
Working with Settings:
Change the boot order
Create a BIOS password
Change your date and time
Change Keyboard Typing Speed
=== * ===
When to replace CMOS battery?
Computer is losing its time or date settings.
An error or alert message, like the following, is displayed when the computer boots.
o CMOS Read Error
o CMOS Checksum Error
o CMOS Battery Failure
o System battery voltage is low
Department of Computer Science 87
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Steps:
Locate CMOS battery
Open the computer case and find the battery on the motherboard.
Verify it is accessible and can be removed. Today, most computers use a coin cell CMOS
battery (like the CR2032 battery shown in the picture.
Note:
o Some CMOS batteries may be held down by a metal clip or bar. The battery can be
removed by sliding it out from under the clip. Do not bend this clip to get the battery out,
as a bent clip can result in the new battery not staying in the socket.
o With some computers, you may need to disconnect cables, remove drives, or remove
other parts of the computer to get full access to the CMOS battery.
Obtain battery information
Once the battery is located, it is recommend writing down its specifications (voltage,
chemistry, wiring). If possible, remove the battery and take it to a retail location.
Removing the battery
If a computer uses a coin cell battery, removing the battery is relatively simple. Use
fingers to grab the edge of the battery and pull it up and out of the socket holding it in
place.
o Some motherboards have a clip holding the battery down. If computer's motherboard
has this clip, it is necessary to use one hand to move the clip up and the other hand to
pull the battery out.
o Unfortunately, not all CMOS batteries are removable. Some manufacturers only
allow a replacement battery to be added.
Department of Computer Science 88
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
o If computer's motherboard does not have a removable battery, you need to set a
jumper on the motherboard to install the new battery.
Insert the new battery
After purchasing a new battery, remove the old battery and replace it with the new
battery.
o Some computers may not have a removable battery, for these computers insert the
new battery into the secondary battery socket on the motherboard.
Enter CMOS values
Once the battery has been replaced, turn on the computer and reset the CMOS values to
the defaults.
After the values have all been entered, make sure to save the settings before exiting.
Many CMOS setups allow you to press a key, such as F10, to save values and exit with
one action.
Bad hardware
If you continue to receive the error after following all the steps above, this is a sign of a
more serious issue. The most likely causes are a bad power supply or bad motherboard.
=== * ===
Nonvolatile BIOS memory refers to a small memory on PC motherboards that is used to store
BIOS settings.
It is traditionally called CMOS RAM because it uses a volatile, low-power
complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) SRAM powered by a small
"CMOS" battery when system and standby power is off.
o It is referred to as non-volatile memory or NVRAM because, after the system
loses power, it does retain state by virtue of the CMOS battery.
o The typical NVRAM capacity is 256 bytes.
The CMOS RAM and the real-time clock have been integrated as a part of the
southbridge chipset and it may not be a standalone chip on modern motherboards.
In turn, the southbridge have been integrated into a single Platform Controller Hub
=== * ===
CMOS battery
Department of Computer Science 89
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Type CR2032 button cell, the most common CMOS battery.
The memory battery (CMOS, real-time clock (RTC), clock battery) is generally a
CR2032 lithium coin cell.
This cell battery has an estimated life of 3 years when power supply unit (PSU) is
unplugged or when the PSU power switch is turned off. This battery type, unlike the
Lithium-ion battery, is not rechargeable and trying to do so may result in an explosion.
Motherboards have circuitry preventing batteries from being charged and discharged
when a motherboard is powered on. Other common battery cell types can last
significantly longer or shorter periods, such as the smaller CR2016 which will generally
last about 40% less time than CR2032.
Higher temperatures and longer power-off time will shorten battery cell life. When
replacing the battery cell, the system time and CMOS BIOS settings may revert to default
values.
=== * ===
Memory
Computer memory is any physical device capable of storing information temporarily like
RAM (random access memory), or permanently, like ROM (read-only memory). Memory
devices utilize integrated circuits and are used by operating systems, software, and hardware.
Department of Computer Science 90
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Types of Memory
Primary Memory
RAM (Random access memory) – Random Access Memory (RAM) is a type of data storage
used in computers that is generally located on the motherboard. This type of memory is volatile
and all information that was stored in RAM is lost when the computer is turned off
There are two types of Random access memory
Dynamic RAM – dynamic indicates that the memory must be constantly refreshed
(reenergized) or it will lose its contents.
Static Memory – A computer memory that contains fixed information and retains its
programmed state as long as the power is on.
Virtual memory is a feature of an operating system (OS) that allows a computer to compensate
for shortages of physical memory by temporarily transferring pages of data from random access
memory(RAM) to disk storage.
ROM (Read only memory) – Once data has been written onto a ROM chip, it cannot be
removed and can only be read. Unlike main memory (RAM), ROM retains its contents even
when the computer is turned off.ROM is referred to as being nonvolatile.
There are three types of Read only memory (ROM)
PROM – PROM stands for Programmable Read Only Memory. This form of ROM is
initially blank. The user or manufacturer can write data/program on it by using special
devices. However, once the program or data is written in PROM chip, it cannot be
Department of Computer Science 91
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
changed. If there is an error in writing instructions or data in PROM, the error cannot be
erased. PROM chip becomes unusable.
EPROM – EPROM stands for Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. This form of
ROM is also initially blank. The user or manufacturer can write program or data on it by
using special devices. Unlike PROM, the data written in EPROM chip can be erased by
using special devices and ultraviolet rays. So program or data written in EPROM chip
can be changed and new data can also be added. When EPROM is in use, its contents can
only be read.
EEPROM – EEPROM stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory. This kind of ROM can be written or changed with the help of electrical devices.
So data stored in this type of ROM chip can be easily modified.
Cache:
A cache is a place to store something temporarily in a computing environment. Cache memory,
also called CPU memory, is random access memory (RAM).
Secondary memory
Secondary memory – Secondary memory is a computer memory that is not directly accessed by
the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer and is usually available as non-volatile memory.
One of the most common forms of this memory is the hard drive of a computer, which is used to
store the operating system (OS) and other programs. Example: DVD, CDs, Floppy Disk etc.
Hard Drive – a rigid non-removable magnetic disk with a large data storage capacity.
Floppy disk- A floppy disk, also called a diskette or just disk, is a type of disk storage
composed of a disk of thin and flexible magnetic storage medium, sealed in a rectangular
Department of Computer Science 92
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
plastic carrier lined with fabric that removes dust particles. Floppy disks are read and
written by a floppy disk drive (FDD).
Magnetic Tape – Magnetic tape used in recording sound, pictures, or computer data.
Flash memory – a kind of memory that retains data in the absence of a power supply.
Optical disk – an electronic data storage medium that can be written to and read using a
low-powered laser beam.
CD-ROM: “Read Only” (used for distribution of commercial software, for example)Standard
storage capacity is 640MB.
CD-R (or CD-WORM): “Write Once, Read Many” times
CD-RW: rewritable multiple times
DVD: similar to CD, but with significantly larger storage capacity (4.7GB)
Mother board – A motherboard is the main circuit board inside a computer that connects the
different parts of a computer together. It has sockets for the CPU, RAM and expansion cards
(e.g. discrete graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, storage cards etc)… and it also hooks
up to hard drives, disc drives and front panel ports with cables and wires. Also Called as
mainboard, system board.
=== * ===
=== * ===
Memory Units
Memory units are used to measure and represent data. Some of the commonly used memory
units are:
o Bit: The computer memory units start from bit. A bit is the smallest memory unit
to measure data stored in main memory and storage devices. A bit can have only
one binary value out of 0 and 1.
Department of Computer Science 93
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
o Byte: It is the fundamental unit to measure data. It contains 8 bits or is equal to 8
bits. Thus a byte can represent 28 or 256 values.
o Kilobyte: A kilobyte contains 1024 bytes.
o Megabyte: A megabyte contains 1024 kilobytes.
o Gigabyte: A gigabyte contains 1024 megabyte.
o Terabyte: A terabyte contains 1024 gigabytes.
o Peta Byte: A Petabyte contains 1024 Terabytes
o Exa Byte: A Exabyte contains 1024 Petabytes
o Zetta Byte: A Zettabyte contains 1024 Exabytes
o Yotta Byte: A Yottabyte contains 1024 Zettabytes
Memory Locations:
=== * ===
HDD (Hard Disk Drive):
The hard drive is the component that stores your data. Several reasons to buy HDD:
Shortage of space on your current HDD and need a bigger one
Takes a long time to open documents or export large files like videos
Setting up a new PC from scratch
SATA (or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) Drives
Department of Computer Science 94
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
SATA (or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is the default interface for most
desktop and laptop hard drives.
They are referred to as SATA hard drives, but they are actually rotary hard drives with
spinning platters and a moving needle that writes data to consecutive sectors on each
platter.
SATA hard drives are incredibly fast compared to their predecessor, the PATA hard
drive, and can write to the disk with an interface rate of 6 Gb/s with a throughput of 600
MB/s.
A single drive can range from 500 GB to 16 TB and are available at a lower cost than any
of the other drive types discussed here.
Since data is physically written to a disk, it can also become fragmented, meaning that
different sectors can be spread across different areas of the disk, slowing down the drive.
Department of Computer Science 95
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
They also are vulnerable to shock and sudden movement since there are moving parts in
each drive, which makes them a poor choice for laptops.
Pros:
Low cost
High disk sizes
Cons:
Not good for laptops
Requires regular de-fragmentation
SSD hard drives
Department of Computer Science 96
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
SSD stands for Solid State Drive.
These disks don't have any moving parts.
That means that there isn't a needle that has to move to read or write data and that they
are significantly faster than SATA drives.
It's difficult to find an exact speed because it varies by manufacturer and form factor, but
even the lower-performing drives are comparable to SATA drives.
Data is stored on a series of NAND chips, which can retain their charge without a power
source.
The downside is that these drives are significantly more expensive and don't come in as
many sizes.
SSD drives range from about 120 GB to 2 TB, and are about 2-4 times the price of a
SATA hard drive of the same size.
Since there are no moving parts, these drives are also a lot more durable, and there are
form factors built specifically for laptops, making them ideal for storage on the go.
Pros:
Fast
More durable, especially for laptops
Cons:
More expensive than SATA drives
Lower disk sizes
NVMe
Department of Computer Science 97
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Non-Volatile Memory Express, or NVMe, is a type of SSD that's attached to a PCI
Express (PCIe) slot on a main board.
These slots were originally designed for graphics cards, so they are incredibly fast.
Speeds on NVMe drives can reach an interface rate of 32 Gb/s with a throughput of 3.9
GB/s.
That can be very useful if you are doing something that needs a lot of disk throughput,
like gaming or high-resolution video editing.
For starters, they are only available on desktop PCs and are very expensive.
Most BIOS don't support booting from NVMe at this time.
It's still possible to get one that does, but it might mean replacing your entire main board.
Pros:
Fastest disk type on the market
Cons:
Extremely expensive
Available for desktop PCs only
May require replacing main board to get full benefit
=== * ===
Department of Computer Science 98
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
=== * ===
Optical Disc Drive
Department of Computer Science 99
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
An optical drive is a piece of computer hardware about the size of a thick softcover book. The
front has a small Open/Close button that ejects and retracts the drive bay door. This is how media
like CDs, DVDs, and BDs are inserted into and removed from the drive.
Most optical drives also have jumper settings on the back end that define how the motherboard is
to recognize the drive when more than one is present. Alternatively, an external optical drive
may be a self-contained unit that connects to a computer via a USB cable.
Optical Disc Drive Media Formats
Most optical drives can play and/or record a large number of different disc formats.
Popular formats include CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD, DVD-RAM, DVD-R, DVD+R,
DVD-RW, DVD+RW, DVD-R DL, DVD+R DL, BD-R, BD-R DL & TL, BD-RE, BD-RE DL
& TL, and BDXL.
Recordable and Rewritable Discs
The "R" in these formats means "recordable" and the "RW" means "rewritable." For example,
DVD-R discs can be written to just once, after which the data on them cannot be changed, only
read. DVD-RW is similar but since it's a rewritable format, one can erase the contents and write
new information to it at a later time.
Recordable discs are ideal if someone is borrowing a CD of photos and don't want them to
accidentally delete the files. A rewritable disc may be handy if data in the storage required to be
deleted and make a room for newer backups.
CD and Blu-Ray Discs
Department of Computer Science 100
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Discs that have the "CD" prefix can store around 700 MB of data, while DVDs can keep around
4.7 GB (nearly seven times as much). Blu-ray discs hold 25 GB per layer, dual-layer BD discs
can store 50 GB, and triple and quadruple layers in the BDXL format can store 100 GB and 128
GB, respectively.
Logical BlockAddressing (LBA)
A disc or disk is divided into blocks. Each block with a unique address. There are however
different addressing methods. The Logical address does not necessary match with the Physical
address. A block is also referred to as a frame or sector.
Logical block addressing (LBA) is a common scheme used for specifying the location of blocks
of data stored on computer storage devices, generally secondary storage systems such as hard
disk drives. LBA is a particularly simple linear addressing scheme; blocks are located by an
integer index, with the first block being LBA 0, the second LBA 1, and so on.
A 28 -bit LBA address allows addressing of 228 blocks and each block of size 512 bytes (29),
which is equal to the 128 GB (237). As an extension of a 48 -bit addressallows addressing of 248
blocks and each block of size 512 bytes (29), which is equal to the 128 PB (257).
Memory Capacity:
The total memory (RAM) that can be added to a computer depends on the address registers built
into the CPU. For example, most 32-bit CPUs can address only up to 4 GigaBytes (GB) of
memory.
The reason the maximum capacity in a 64-bit computer is limitless for all intents and purposes is
that 64-bit hardware manipulates (calculates, compares and copies) 64 bits, or 8 bytes, of data at
a time. However, the actual memory is addressed with far fewer bits. A 64 bit register could
address 16 exabytes (EB) of memory (which is 16 million Terabytes).
Physical and Logical Addressing
Logical Address is generated by CPU while a program is running. The logical address is virtual
address as it does not exist physically, therefore, it is also known as Virtual Address. This
address is used as a reference to access the physical memory location by CPU. The term Logical
Address Space is used for the set of all logical addresses generated by a program’s perspective.
Department of Computer Science 101
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
The hardware device called Memory-Management Unit is used for mapping logical address to its
corresponding physical address.
Physical Address identifies a physical location of required data in a memory. The user never
directly deals with the physical address but can access by its corresponding logical address. The
user program generates the logical address and thinks that the program is running in this logical
address but the program needs physical memory for its execution, therefore, the logical address
must be mapped to the physical address by MMU before they are used. The term Physical
Address Space is used for all physical addresses corresponding to the logical addresses in a
Logical address space.
Basis for
Logical Address Physical Address
Comparison
It is the virtual address generated by The physical address is a location in a
Basic
CPU memory unit.
Set of all logical addresses generated Set of all physical addresses mapped to
Address Space by CPU in reference to a program is the corresponding logical addresses is
referred as Logical Address Space. referred as Physical Address.
The user can view the logical address The user can never view physical
Visibility
of a program. address of program
The user uses the logical address to The user can not directly access physical
Access
access the physical address. address.
Generation The Logical Address is generated by Physical Address is Computed by MMU
Department of Computer Science 102
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Basis for
Logical Address Physical Address
Comparison
the CPU
=== * ===
Causes of Hard drive failure:
Department of Computer Science 103
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Department of Computer Science 104
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Signs of Hard Disk Failure:
Computer Crashes Or Blue Screen Of Death
Error Messages While Copying Or Moving Files –
Hard Drive Doesn’t Boot
Hard Drive Is Making A Beeping Sound: When a hard drive makes a beeping sound,
this is usually because the platters may be physically blocked by something. The beeping
noises are made by the spindle motor inside the drive as it attempts to get the platters
spinning. This generally happens when the read/write headstack clamps down on the
platter surfaces instead of floating above them.
Hard Drive Is Not Spinning – A hard drive will fail to spin up if there is no electricity
that flows through its PCB (or Printed Control Board). This generally happens when the
circuit board experiences a short or it has worn out over time.
Hard Drive Is Smoking – It is a warning sign that the PCB of the hard drive has burned.
This is mainly due to an electrical surge which may cause the PCB to short or burn.
Hard Drive Is Clicking Or Buzzing -When the hard drive makes a clicking or other
strange sounds, this is mainly due to the read write heads being unable to perform their
key functions. This may be what’s know as a head crash. Also referred to as the “click of
death”, this happens when the hard drive has been severely damaged or has failed
completely. It is never a good idea to keep running a hard drive that’s making some kind
of physical sound.
Losing Files Without Notice – This can sometimes mean that drive is having issues.
Department of Computer Science 105
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
File Access Takes A Long Time
Noise – Most recently manufactured hard drives are whisper quiet. Any noise at all,
particularly a clicking hard drive noise, can mean the drive may be on its last legs.
Try the best to backupthe contents, or shut down the system and call an expert.
=== * ===
SSD Common Specifications:
The common specs include
Form Factor
The Interface
Read Speed
Write Speed
Endurance Rating TBW - Overall Lifespan
IOPS
Storage Capacity
Memory Cell Type - SLC, MLC, TLC, QLC, PLC
1. Form Factors
Common Form factors include:
2.5" SSD Drive (or 7mm SSD Drive)
M.2 Drive (half the size of a single RAM stick)
Portable SSD
2. SSD Interface
Uses the traditional SATA connection, which is also used by hard drives.
To give you a better understanding of how these transport interfaces perform, following are the
speeds:
SATA II - Maximum bandwidth of 3Gb/s or 384 MB per second.
SATA III - Maximum bandwidth of 6Gb/s or 768 MB per second.
PCI-E Gen 3 - Maximum bandwidth of 8GT/s or 8 GB per second.
3. Read Speed - Sequential and Random
Up to 560 MB per second which is three times the performance of a traditional hard
drive (HDD 80-160MB per Second).
M.2 drives, its sequential read speed could vary between 2.4 GB per second up to 3.4
GB per second.
Department of Computer Science 106
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
4. Write Speed - Sequential and Random
Up to 530MB per Second ((HDD 80-160MB per Second).
5. Endurance Rating (TBW - Terabytes Written)
While SSDs are more durable compared to hard drives, they can still break down in time.
In this case, you should look out for solid-state drives with a decent TBW (Total Bytes
Written) rating. TBW indicates how much data you can write on an SSD over its lifespan.
A good SSD like the Western Digital Blue has a 600 TWB rating for the 4 terabyte
model.
For better understanding, a 250 GB SSD would usually have a 70 TWB rating which
you can max out for a year if you store 190 GB of new data every day, which is
impossible for a typical user.
In this case, it is safe to say that most SSDs would have a lifespan of double or even triple
compared to an ordinary hard drive in normal usage.
5. IOPS
IOPS or Input/Output Operations Per Second determines how fast an SSD can read
and write random packets of data like browser files, cookies, saved game data, and
documents.
For example, the Western Digital Blue SSD has a 4KB sequential read speed of 97,000
IOPS.
In order to convert these to MB per second, we would use the formula:
MBps = (IOPS * 4)/1024
So, our Western Digital Blue solid-state drive would have 378.90 MB per second 4KB
sequential read speed.
6. Capacity
Most SSD manufacturers offer solid-state drives with a capacity of 80 GB up to 4 TB or
even higher. However, SSDs get even more expensive as you increase its capacity.
A 500 GB variant of Western Digital Blue SSD is priced around $60 while its 4 TB
model would cost you over $500 on Amazon. For that price, you can already build a
decent desktop PC.
Department of Computer Science 107
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
7. Memory Cell Type - SLC, MLC, TLC, QLC
Solid-state drives use NAND flash memory that consists of cells that can hold bits of
memory.
These bits are controlled by an electric charge that either turns it off or on.
7.1 Single Level Cell (SLC)
Typically found on server-grade drives, single-level cell flash is known to be the most
accurate when it comes to reading and writing data.
7.2 Multi-Level Cell (MLC/eMLC)
Based on its name, multi-level cell memory stores multiple bits of data in one cell,
which makes manufacturing cost a lot cheaper compared to SLC drives.
7.3 Triple Level Cell (TLC)
TLC solid-state drives can write three bits to each of its cells, which allows it to
have higher storage capacities compared to MLC and SLC memories.
However, packing three bits on one cell has a few drawbacks like slower
performance, decreased reliability, and endurance.
7.4 Quad and Penta Level Cell (QLC/PLC)
Similar to how TLC flash memory works, Quad and Penta level cell NAND flash can
store multiple bits in a single cell (four bits for QLC and five bits for PLC) but with a
few compromises.
7.5 3D NAND Flash
Compared to traditional 2D planar NAND memory, 3D NAND stacks cells on top of
each other, utilizing both vertical and horizontal space that resulted in better
performance and increased reliability without needing to shrink single cells to its
limits.
=== * ===
Difference between SIMM and DIMM
S.NO SIMM DIMM
In SIMM, Pins present in either facet are
1. DIMM pins are freelance.
connected.
SIMM supports 32 bit channel for data DIMM supports 64 bit channel for data
2.
transferring. transferring.
Department of Computer Science 108
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
S.NO SIMM DIMM
3. SIMM consumes 5 volts of power. DIMM consumes 3.3 volts of power.
SIMM provides the storage 4 MB to 64 DIMM provides the storage 32 MB to 1
4.
MB. GB.
The classic or most common pin
The foremost common pin configuration
5. configuration of the SIMM module is 72
of the DIMM module is 168 pins.
pins.
DIMMs are the replacement of the
6. SIMMs are the older technology.
SIMMs.
7. SIMMs are installed in pairs at a time. DIMMs are installed one at a time.
SIMMs are used by 486 CPU as well as DIMMs are used by modern Pentium
8.
early Pentium computers. computers.
The length and width of DIMM are
The length and width of SIMM are
9. respectively 1.67 to 5.25 inches and 1 to
respectively 4.25 inches and 1 inch.
1.75 inches.
10. There are single notches in SIMMs. There are two notches in DIMMs.
Department of Computer Science 109
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
DIMM
Department of Computer Science 110
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
How to Install RAM:
Make sure to use a static-free work area when beginning any component change in your
computer, and make sure the computer is unplugged.
Clear away any paper, tape, and electrical devices (including your smartphone) from the area.
Always touch the metal chassis of your computer to ground yourself and draw away any static
electricity
Department of Computer Science 111
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
.
The RAM slots, at the right, are red and yellow.
Find out how much memory your computer can handle, and how much you want to add.
Step 1: right-click on My Computer (or go to Control Panel > System and Security and
under System, click on View Amount of RAM and processor speed))
Step 2: use some Tool that will scan your system and return a report that tells you how
much RAM your system can take, how much RAM you currently have, how many slots
you have—both available and occupied—and even suggest which RAM to buy to
upgrade.
Department of Computer Science 112
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
There are four RAM slots here.
If using unbalanced RAM (a 2GB and a 4GB module, for instance) pair up RAM in slots 1 and 3
or 2 and 4. If there is old RAM here and you are going to use it, pair the new RAM correctly. Try
not to put three modules in a 4 module slot. It will be less effective
Unhinge the clips (on some motherboards, there is one clip, on others there are two—one on
each end). Unseat the old RAM by pulling on each end, wiggling it up and down just a bit. Do
not wiggle it from side to side.
Department of Computer Science 113
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Make sure that the pins and cutout on the RAM match the slot before placing the new RAM (if
you purchased it according to the steps above, they should match). Never force a RAM module
into a slot that doesn’t match the notch on the module.
Make sure the RAM is seated securely; it takes a slight amount of force. If positioned properly, it
usually snaps the retaining hinge into place. Unseated RAM is the major cause of the RAM not
being recognized by the computer OS.
Department of Computer Science 114
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Plug the computer back in and start it up. On Windows 7 computers, click on the Windows tab,
and right-click on My Computer (or go to Control Panel > System and Security > and under
System, click on View Amount of RAM and processor speed), on Windows 8.1, right-click on
the Windows tab, click System. Your new RAM should be seen immediately.
===*===
Serial presence detect (SPD)
Serial presence detect (SPD) is information stored on an EEPROM chip when a computer
is booted. It is located on an SDRAM memory module and communicates to the BIOS the
module size, data width, speed and voltage, which are used to configure the module memory
controller for maximum reliability and performance.
The manufacturer of the memory module will put the SPD information on the EEPROM
chip. When a computer is turned on, if the BIOS is not provided with SPD, it will assume the
memory module information, which presents no problem to some memory modules.
Parallel presence detect (PPD) data was used in earlier 72-pin SIMMs. However, the
standard changed to SPD with the later model 168-pin DIMM. SPD encodes much more
information.
Department of Computer Science 115
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
Installation: Windows 10
1. Check your device meets the Windows 10 system requirements. The minimum specs
needed to run Windows 10, so check your device is capable:
CPU: 1GHz or faster processor
RAM: 1GB for Windows 10 32-bit or 2GB for Windows 10 64-bit
Storage: 32GB of space or more
GPU: DirectX 9 compatible or later with WDDM 1.0 driver
Display: 800x600 resolution or higher
2. Create USB installation media. Visit Microsoft's Windows 10 download page and select
“Download tool now” under the “create Windows 10 installation media” section. Transfer the
downloaded installer tool to a USB drive.
3. Run the installer tool. Open the installer tool by clicking on it. Accept Microsoft’s terms, and
then select “Create installation media for another PC” on the “What do you want to do?”
page. After selecting which language you want Windows 10 to run in, and which edition you
want as well (32-bit or 62-bit), you’ll be asked what type of media you want to use.
Department of Computer Science 116
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Installing from a USB drive is definitely the preferred option but you can also install from a CD
or ISO file. Once you choose your device, the installer tool will download the required files and
put them onto your drive.
4. Use your installation media. Insert your installation media into your device and then access
the computer’s BIOS or UEFI. These are the systems that allow you to control your
computer’s core hardware.
The process of accessing these systems is unique to each device, but the manufacturer’s website
should be able to give you a helping hand here. Generally, you'll need to press the F2, F12 or
Delete keys as your computer boots up.
5. Change your computer's boot order. Once you have access to your computer’s BIOS/UEFI
you’ll need to locate the settings for boot order. You need the Windows 10 installation tool to be
higher up on the list than the device’s current current boot drive: this is the SSD or HDD that
your existing OS is stored on. You should move the drive with the installer files to the very
top of the boot order menu. Now, when you restart your device the Windows 10 installer
should load up first.
6. Restart your device. Save your settings in the BIOS/UEFI and reboot your device.
7. Complete the installation. Your device should now load up the Windows 10 installation tool
on restart. This will guide you through the rest of the installation process.
=== * ===
=== * ===
Installation - Upgrading to Windows 10: Upgrading from an older version of Windows
If you’re upgrading to Windows 10 from Windows 7 or Windows 8, the process is much easier.
1. Download the installer tool. Visit Microsoft's Windows 10 download page and select
“Download tool now” under the “create Windows 10 installation media” section.
2. Run installer tool. You can just upgrade your version of Windows directly from the installer
tool, without creating separate installation media. When you reach the “what do you want to
do?” section, select “Upgrade this PC now.”
3. Complete Windows 10 installation. Now the installer tool will guide you through the rest of
the process. Just follow the steps to complete the installation process and you'll have Windows
10 installed on your device at the end of it.
Department of Computer Science 117
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
Preparing the System for Dual-Booting:
Different operating systems have different uses and advantages. Having more than one
operating system installed allows you to quickly switch between two and have the best tool for
the job. It also makes it easier to dabble and experiment with different operating systems.
If Separate Disk space is allocated for the installation of another Operating System, use
that space during second Operating System.
If separate space is NOT allocated, then go to the existing operating system Device
Manager, Select the Drive and Right Click and Apply Shrink Volume, it will ask the amount of
Disk Space required for the new Operating System. Set the correct space for new operating
system and restart the PC for loading new operating system as usual like loading from DVD/Pen
Drive.
Department of Computer Science 118
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
After Successful installation, the system will ask for choosing operating system to get load
=== * ===
Working on Recovery Partition:
Department of Computer Science 119
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
A recovery partition is a partition on the disk that helps to restore the factory settings of the OS
(operating system) if there is some kind of system failure. This partition has no drive letter, and
you can use only Help in Disk Management.
The recovery partition has two varieties:
The first of the varieties is the most widespread and installed with the Windows
operating system on a GPT disk and occupies a negligible amount of disk space.
The second is set by the computer manufacturer (like Lenovo, Dell or HP). It
occupies a significant amount of disk space since it is this part of the recovery
partition that contains the manufacturer settings for application drivers and other
things that allow you to restore these default settings. This partition is also called the
OEM section.
New Recovery Partitions get created after every Windows Upgrade.
A curious thing is that every time you update Windows, a new recovery partition is
created. This happens due to a lack of free space in your recovery partition or in
system reserved partition. As a result, you will get as many recovery partitions as you
update your system.
When you get a new recovery partition on your disk, the old recovery partition can be
removed without worries, as it is nonfunctional. That’s how you can get a bit of free
space.
Deleting Recovery Partitions:
Use Disk Manager, and select Old recovery Disk Partitions and delete (if sure)
Use Diskpart utility to remove old recovery Disk Partitions with suitable commands
o Diskpart list disk Select disk 0 (Assume Disk 0 is Listed) list volume
select volume 1 (Assume Volume 1 is Recovery Partition) Delete Volume 1
=== * ===
Ten Windows Registry Tweeks:
Start the Settings of Windows Registry opening the Registry Editor
Department of Computer Science 120
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Hit Win+R
Type regedit
Click OK.
1. Add “Open with Notepad” to the context menu
When you right-click on your desktop the appeared list is called the Context menu. There are a
few options available in the context menu but if you want you can even customize it accordingly
and one such customization adding the Open with Notepad option.
Navigate using the following route:-
o Computer\HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\*\shell
Right-click on Shell> New> Key. Then rename it to Open With Notepad.
Right-click on Open with Notepad> New> Key. Then rename it to Command.
Double-click on Default from the right panel of the Window, in the Value data section
type “notepad.exe %1” and click OK.
Now, close the Registry Editor, right-click on the file that you want to open with
Notepad, and select the “Open with Notepad” option.
=== * ===
2. Change your Logon Screen Background
Changing the wallpaper on your desktop is one of the easiest things to do in Windows. But if you
can have that display any image you want, why not do the same with your logon screen?
Go to the Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Authent
ication\LogonUI\Background
Double click on “OEMBackground” to open it.
Change the value in the “Value data” field to 1.
Click OK.
Using Windows Explorer, navigate to your Windows directory and go to the path
C:\Windows\System32\oobe
If there’s a folder in here called “info,” go into it; if there’s a folder inside of that one
called “backgrounds,” go into that. If neither exists, you’ll need to create them both first.
Department of Computer Science 121
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Copy the image (it must be a JPEG, and smaller than 256KB in size) you want to use as
your logon screen background into the info\backgrounds folder.
Rename the image backgroundDefault.jpg
The next time you restart your computer, or log out, see this image as the new logon screen.
If you chose an image that prevents the buttons and text from looking their best on the
logon screen, you can adjust their appearance as well.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Authent
ication\LogonUI (Now NOT going into Background this time).
Add a DWORD value called “ButtonSet.”
Change its value to either 1 (darker text shadows and lighter buttons, intended for lighter
backgrounds) or 2 (no text shadows and opaque buttons, for darker backgrounds); 0 is
the Windows default.
=== * ===
3. Adding Applications to the Desktop Context Menu: Adding Notepad
Go to the Key:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\Background\shell
Right-click on Shell New Key. Then rename it to Notepad
Right Click on Notepad New Key. Then rename it to Command
Select the Command. Double Click on Default on Right Pane. Set the Value data to
“notepad.exe”
Go to the Desktop Right Click. Popup Menu will display Notepad
=== * ===
4. Remove the “- Shortcut” Text by Editing the Registry Manually
Go to the Key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer
Department of Computer Science 122
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
On the right-hand side, scroll down and locate a value named link. (If it is not there,
create it by right-clicking the Explorer key, choosing New Binary Value, and then
Renaming the New value “link”
Double click on link. In the “Value data” box, replace the current value with “00 00 00
00”. (Note that the current value will depend on what version and edition of Windows
running. It doesn’t matter what’s there already. Just replace it with all zeroes.)
Old values in Value data New values in Value data
Sign out and back in (or Restart your computer) to complete the change.
Test it out by creating a new shortcut. Windows should no longer add the “- Shortcut”
text.
If you want to reverse the changes, just head back into the Registry and delete the link
value.
o This will work whether the value was already there or you created it yourself.
Windows will recreate the value with the default setting when it needs to.
Output Before and After Registry Settings
=== * ===
5. Change the Width of Window
Navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop\WindowMetrics
Scroll to find the “BorderWidth” entry. (If it’s not there, create it. Right click in the
right pane, select New, then Select “String Value,” and name the object BorderWidth.
Double click BorderWidth to open it. (Note down the number in that for recovery)
Department of Computer Science 123
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Change the number in the “Value Data” field to the width you want to allot to the
window (say -150).
Click OK.
Sign out and back in (or Restart your computer) to complete the change.
Output Before and After Registry Settings
=== * ===
6. Disable Short cut Key Win-X (Test Win+D for Desktop, and Win+E for Explorer)
Navigate to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explo
rer
Right Click on Explorer New Key Create a 32-bit DWORD. Rename it to value
called NoWinKeys.
Double Click on NoWinKeys and set the Value data to 1.
Click Ok
Sign out and back in (or Restart your computer) to complete the change.
Try Win+D (by opening many application) and Win+E to go to Explorer – See the
Changes.
To reverse the changes, go to the Registry key, and delete NoWinKeys and Sign
out/Restart
=== * ===
7. Make " Open Command Window Here" Always Display for Folders or Drives
Navigate to HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\cmd
Select cmd. On Right Pane, Rename Key “Extended” to “Extended-Orig”
Go to any Folder and Right Click on Folder, will get “Open Command Window Here”,
with this one can work with Command Prompt.
Do the Same thing for Drive by Navigating to
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Drive\shell\cmd
Department of Computer Science 124
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Select cmd. On Right Pane, Rename Key “Extended” to “Extended-Orig”
Go to any Drive in My Computer and Right Click on Drive, will get “Open Command
Window Here”, with this one can work with Command Prompt.
=== * ===
8. Remove “Send To” from Menu in Windows
Navigate to
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\AllFilesystemObjects\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers\Send To
Select SendTo, in Right Pane Double Click on Default
Note down the data (numbers) in Value data (Required for Value Recovery).
Clear the Contents of Value data
Click OK.
To Test, Go to Desktop, Right on any File, “Send To” will not be visible.
To reverse, the task, just head back into the Registry and Restore the “SendTo” Value
data to Original Value i.e. {7BA4C740-9E81-11CF-99D3-00AA004AE837}
To Test, Go to Desktop, Right on any File, “Send To” will be visible now.
Department of Computer Science 125
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Output Before and After Registry Settings
=== * ===
9. Enable and Disable Task Manager in Windows
Navigate to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies
If System is not found Create New Key System
Right-click on Policies New Key. Then rename it to System
Right Click on System New DWORD (32bit). Then rename it to DisableTaskMgr
Double Click on DisableTaskMgr, Set the Value data to 1 (For Disabling Task
Manager)
Click OK,
Test it by right Click on Task bar.
If you want to reverse the changes, just head back into the Registry and set the Value
data of DisableTaskMgr to 0.
Output Before and After Registry Settings
Department of Computer Science 126
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
10. Change the Title Bar Text Color and Button Text Colors
Navigate to
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Colors
Select Colors, and on Right Pane Select TitleText
o Set the Value data for TitleText to Color of your Choice in RGB format (Original
Value is 255 255 255, it means Text appeared in Title bar is in pure White Color).
o Set the color to 0 0 0 (means Title bar Text appears in Black Color)
Select Colors, and on Right Pane Select ButtonText
o Set the Value data for ButtonText to Color of your Choice in RGB format
(Original Value is 0 0 0, it means Text appeared in Buttons is in pure Black Color).
o Set the color to 0 0 255 (means Button Text appears in Blue Color)
Click OK,
Sign out and back in (or Restart computer) to complete the change.
=== * ===
Disk Management Utilities:
Disk Management is a system utility in Windows that enables you to perform advanced
storage tasks. Here are some of the things Disk Management is good for:
To setup a new drive.
To extend a volume into space that's not already part of a volume on the same drive
To shrink a partition, usually extend a neighboring partition
To change a drive letter or assign a new drive letter.
Department of Computer Science 127
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Here are some common tasks but that use other tools in Windows:
To free up disk space
To defragment your drives.
To take multiple hard drives and pool them together, similar to a RAID
=== * ===
What is a File System?
A file system is a process of managing how and where data on a storage disk, which is
also referred to as file management or FS.
It is a logical disk component that compresses files separated into groups, which is
known as directories.
The file system enables you to view a file in the current directory as files are often
managed in a hierarchy.
It is abstract to a human user and related to a computer; hence, it manages a disk's
internal operations.
NTFS is the most common in modern times (Windows OS).
It would be impossible for a file with the same name to exist and also impossible to
remove installed programs and recover specific files without file management, as well as
files would have no organization without a file structure.
Department of Computer Science 128
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
A disk (e.g., Hard disk drive) has a file system, even with type and usage.
Also, it contains information about file size, file name, file location fragment information,
and where disk data is stored and also describes how a user or application may access the
data.
The operations like metadata, file naming, storage management, and directories/folders
are all managed by the file system.
On a storage device, files are stored in sectors in which data is stored in groups of sectors
called blocks.
The size and location of the files are identified by the file system, and it also helps to
recognize which sectors are ready to be used.
Other than Windows, there are some other operating systems that contain FAT and NTFS
file system.
Apple product (like iOS and macOS) uses HFS+ as operating system is horizon by many
different kinds of file systems.
Different partitions of the same disk may use different file systems. That is, C Drive may
use NTFS and D Drive may use FAT. But it means two separate partitions are there that
use the same physical disk.
Department of Computer Science 129
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Examples of File Systems:
The examples of file systems are given below:
FAT: FAT is a type of file system, which is developed for hard drives. It stands for File
Allocation Table. On hard drives and other computer systems, it helps to manage files on
Microsoft operating systems. In devices like digital cameras, flash memory, and other
portable devices, it is also often found that is used to store file information. It also helps
to extend the life of a hard drive as it minimizes the wear and tears on the hard disc. Now
a days later versions of Microsoft Windows like Windows XP, Vista, 7, and 10 as use
NTFS.
o The FAT8, FAT12, FAT32, FAT16 are all the different types of FAT (for file
allocation table).
GFS: A GFS is a file system, which stands for Global File System. It has the ability to
make enable multiple computers to act as an integrated machine. When the physical
distance of two or more computers is high, and they are unable to send files directly with
each other, a GFS file system makes them capable of sharing a group of files directly. A
computer can organize its I/O to preserve file systems with the help of a global file
system.
HFS: HFS (Hierarchical file system) is the file system that is used on a Macintosh
computer for creating a directory at the time a hard disk is formatted. Generally, its basic
function is to organize or hold the files on a Macintosh hard disk. Apple is not capable of
supporting to write to or format HFS disks since when OS X came on the market. Also,
HFS-formatted drives are not recognized by Windows computers as HFS is a Macintosh
format. With the help of WIN32 or NTFS file systems, Windows hard drives are
formatted.
NTFS: NTFS is the file system, which stands for NT file system and stores and retrieves
files on Windows NT operating system and other versions of Windows like Windows
2000, Windows XP, Windows 7, and Windows 10. Sometimes, it is known as the New
Technology File System. As compared to the FAT and HFS file system, it provides
better methods of file recovery and data protection and offers a number of improvements
in terms of extendibility, security, and performance.
Department of Computer Science 130
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
UDF: A UDF is a file system, stands for Universal Disk Format and used first
developed by OSTA (Optical Storage Technology Association) for ensuring consistency
among data written to several optical media. It is used with CD-ROMs and DVD-ROMs
and is supported on all operating systems. Now, it is used in the process of CD-R's and
CD-RW's, called packet writing.
=== * ===
How a file is located in FAT32/NTFS:
=== * ===
Support on Large File
FAT32 uses a 32-bit area to record file size in bytes, so a single file can only be up to 232
bytes i.e. 22 x 230 = 4GB.
FAT32 can store file of size in the range 4G – 1byte, because we cannot have files of 0
length.
To save a file which is larger than 4G NTFS is used.
Maximum file size on a NTFS partition can be 264 bytes i.e. 24 x 260 = 16 EB.
=== * ==
Types of file systems
There are various kinds of File Systems, which are as follows:
1. Disk file systems
On the disk storage medium, a disk file system has the ability to randomly address data within a
few amounts of time. Also, it includes the anticipation that led to the speed of accessing data.
Department of Computer Science 131
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Without regard to the sequential location of the data, multiple users can access several data on
the disk with the help of a disk file system.
2. Flash file systems
A flash file system is responsible for restrictions, performance, and special abilities of flash
memory. It is superior to utilize a file system that is designed for a flash device; however, a disk
file system is the basic storage media, which can use a flash memory device.
3. Tape file systems
A tape file system is used to hold files on the tape as it is a tape format and file system. As
compared to disks, magnetic tapes are more powerful to access data for a long time, which are
the challenges for a general-purpose file system in terms of creation and efficient management.
4. Database file systems
A database-based file system is another method for file management. Files are recognized by
their characteristics (like a type of file, author, topic, etc.) rather than hierarchical structured
management.
5. Transactional file systems
Some programs require one or more changes to fail for any reason or need several file systems
changes but do not make any changes. For instance, a program may write configuration files or
libraries and executables at the time of installing or updating the software. The software may be
unusable or broken if the software is stopped while updating or installing. Also, the entire system
may leave in an unusable state if the process of installing or updating the software is incomplete.
6. Network file systems
A network file system offers access to files on a server..
7. Shared disk file systems
A shared-disk file system allows the same external disk subsystem to be accessed by multiple
machines, but when the number of machines accesses the same external disk subsystem, there
may be occurred collisions in this condition; so, to prevent the collision, the file system decides
which subsystem to be accessed.
8. Minimal file system
Early, to record and read the data in to cheaper Cassette Tape, a minimal file system is used (It is
designed as an alternative to expensive microcomputer, disk and digital tape devices). On the
cassette recorder, the user was informed about pressing "RECORD" when there was required to
write data by system. And, to notify the system, press "RETURN" on the keyboard. Also, on the
Department of Computer Science 132
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
cassette recorder, the user was needed to press the "PLAY" button when the system required to
read data.
9. Flat file systems
The subdirectories are not available in the flat system. It contains the only directory, and all files
are held in a single directory. Due to the relatively small amount of data space available, this
type of file system was adequate when floppy disk media was available for the first time.
=== * ===
When a computer crashes, it can result in data loss. This can be loss of small files, or in the case
of a large company, it can cause a company to lose a ton of money. There are many different
types of Data Recovery Services that can be offered to recover data depending on the type of
crash. Below are some of the services that are offered at many data recovery companies:
Hard Drive recovery: Recovering data from Hard Disk Drives (Random Access
Storage).
RAID Recovery: Recovering data from extremely complex storage structure RAID
systems.
Tape Recovery: Recovering data from Tape Drives (Sequential Access Storage).
Optical Recovery: Recovering data from Optical media. (Please do not attempt to fix.
This will only make things worse.)
Removable Recovery: Recovering data from Removable media like, floppy disks, zip
drives, and other related storage media.
Digital Recovery: Recovering data from Digital media devices like cameras, portable
storage devices, and other flash media.
=== * ===
Department of Computer Science 133
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Recuva: Data Recovery Software
Superior file recovery: Recuva can recover pictures, music, documents, videos, emails
or any other file type you’ve lost. And it can recover from any rewriteable media you
have: memory cards, external hard drives, USB sticks and more!
Recovery from damaged disks: Unlike most file recovery tools, Recuva can recover
files from damaged or newly formatted drives. Greater flexibility means greater chance
of recovery.
Deep scan for buried files: For those hard to find files, Recuva has an advanced deep
scan mode that scours your drives to find any traces of files you have deleted.
Securely delete files: Sometimes you want a file gone for good. Recuva’s secure
overwrite feature uses industry- and military-standard deletion techniques to make sure
your files stay erased.
=== * ===
Working with Task Manager:
Task Manager displays the programs, processes, and services that are currently running
on your computer.
Task Manager can be used to monitor your computer’s performance or to close a program
that's not responding.
Department of Computer Science 134
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Way to Open Task Manager:
Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open the Task Manager with a keyboard shortcut
Right-Click the Windows taskbar and select “Task Manager.”
The Task Manager includes the following tabs:
Processes: A list of running applications and background processes on your system along
with CPU, memory, disk, network, GPU, and other resource usage information.
Performance: Real-time graphs showing total CPU, memory, disk, network, and GPU
resource usage for your system. Many other details like computer’s IP address, model
names of your computer’s CPU and GPU etc. can be obtained here.
App History: Information about how much CPU and network resources apps have used
for your current user account. This only applies to new Universal Windows Platform
(UWP) apps—in other words, Store apps—and not traditional Windows desktop apps
(Win32 applications.)
Startup: A list of your startup programs, which are the applications Windows
automatically starts when you sign into your user account. You can disable startup
programs from here, although you can also do that from Settings > Apps > Startup.
Users: The user accounts currently signed into your PC, how much resources they’re
using, and what applications they’re running.
Details: More detailed information about the processes running on your system. This is
basically the traditional “Processes” tab from the Task Manager on Windows 7.
Department of Computer Science 135
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Services: Management of system services. This is the same information you’ll find in
services.msc, the Services management console.
Performance Information in Task Manager:
The Performance tab shows real-time graphs displaying the usage of system resources
like CPU, memory, disk, network, and GPU.
If multiple disks, network devices, or GPUs are present that could be viewed all of them
separately.
The small graphs in the left pane shows resource usage over the last 60 seconds.
In addition to resource information, the Performance page shows information about system’s
hardware. Some different panes are:
CPU: The name and model number of CPU, its speed, the number of cores it has, and
whether hardware virtualization features are enabled and available. It also shows
system’s “uptime,” which is how long system has been running since it last booted up.
Memory: How much RAM the system has, its speed, and how many of the RAM slots on
motherboard are used. It also shows how much of memory is currently filled with cached
data.
Department of Computer Science 136
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Disk: The name and model number of disk drive, its size, and its current read and write
speeds.
Wi-Fi or Ethernet: Windows shows a network adapter’s name and its IP addresses (both
IPv4 and IPv6 addresses) here. For Wi-Fi connections, it also shows the Wi-Fi standard
in use on the current connection—for example, 802.11ac.
GPU: The GPU pane shows separate graphs for different types of activity—for example,
3D vs. video encoding or decoding. The GPU has its own built-in memory, so it also
shows GPU memory usage. It shows the name and model number of GPU here and the
graphics driver version it’s using.
=== * ===
Working with Task Scheduler:
Task Scheduler is a tool that allows you to create and run virtually any task
automatically.
Task Scheduler works by keeping tabs of the time and events on your computer and
executes the task as soon as the condition is met.
How to create a basic task using Task Scheduler
To create a task using basic settings on Windows 10, use these steps:
1. Open Start.
2. Search for Task Scheduler, and click the top result to open the experience.
3. Right-click the "Task Scheduler Library" branch, and select the New Folder option.
4. Type a name for the folder. For example, MyTasks. (This step isn't a requirement, but it's
a recommended step to keep your tasks separate from the system and apps tasks.)
5. Click the OK button.
6. Expand the "Task Scheduler Library" branch, and select the MyTasks folder.
Department of Computer Science 137
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
7. Click the Action menu.
8. Select the Create Basic Task option.
9. In the "Name" field, type a short descriptive name for the task. For example, Notepad
Launcher.
10. (Optional) In the "Description" field, create a description for the task.
11. Click the Next button.
12. Select the Monthly option.
Department of Computer Science 138
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Task Scheduler allows you to select from a number of triggers, including on a specific
date, during startup, or when you or a particular user signs in. Depending on your
requirements, you'll need to configure additional parameters. In this case, we'll be
selecting the option to run a task every month.
13. Click the Next button.
14. Using the "Start" settings, specify when the task should start running and the time (very
important).
15. Use the "Monthly" drop-down menu to the months of the year that you want to run the
task.
16. Use the "Days" or "On" drop-down menu to specify the days that the task will run.
Department of Computer Science 139
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Quick Tip: Using the "On" setting may be your best option if you're planning to run a
task during a specific day of the week.
17. Click the Next button.
18. Select the Start a program option to launch an app, run a command, or execute a script
file.
You can select the Send an e-mail or Display a message option, but these are deprecated
features, which means that they may or may not work because Microsoft is no longer
maintaining them.
o Send an e-mail: Triggers an email notification with a custom message on
schedule, but it requires to specify an email server to work.
o Display a message: Allows to display a text message on the screen on schedule.
19. In the "Program/script" field, specify the path for the application.
Department of Computer Science 140
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Quick Tip: If you don't know the path of the app, click the Browse button to find it.
20. (Optional) In the "Add arguments" field, you can specify arguments to run the task with
special instructions.
21. (Optional) In the "Start in" field, specify the folder in which the program will start.
(Usually, you can leave this setting empty.)
22. Click the Finish button.
Once you've completed the steps, the task will be saved, and it'll run automatically on the
schedule you specified.
=== * ===
Customize Windows Desktop
1. Change the Welcome Screen
Department of Computer Science 141
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
There are two basic things you can change that will affect the welcome screen. First of all, you
can change your profile picture. Secondly, you can apply a hack or software to change the
background image.
To change your profile picture, go to > Start and type > User Accounts into the bar that says >
Search programs and files, then open the respective entry under > Control Panel. Next, select >
Change your picture. You can now choose a default image or click > Browse for more pictures...
at the bottom of the list to access your own files.
Once you have selected an image click the > Change Picture button and you're done.
2. Add Desktop Gadgets
Gadgets are tiny tools that sit on your desktop. They add functionality and quickly let you
complete tasks without launching a large program. Some of my three favorite Windows gadgets
are:
Clipboard Manager - Manage your clipboard history, search entries, store favorite clips,
and more.
Skype Gadget - Keep a minimized Skype interface on your desktop and save space.
The Magic Folder - Automatically sort files into pre-defined folders based on their file
extension.
Department of Computer Science 142
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
To browse, discover, and install gadgets, visit the Windows Live Gadget Gallery. To launch
existing gadgets, go to > Start and type > Desktop Gadgets into the bar that says > Search
programs and files, then open the respective entry under > Control Panel.
3. Change the Windows Theme
Changing the theme will have the greatest impact on your system in terms of look and feel. And
you'll be surprised how easy it is. > Right-click desktop and select > Personalize..
4. Create a Custom Desktop Slideshow
To add some variety to your desktop or showcase your own photos, you can create a custom
desktop slideshow that will regularly change your wallpaper.
> Right-click desktop, select > Personalize, and click on > Desktop Background. To create a
slideshow, you need to select any entry from the > Picture location drop-down menu other than
the default 'Solid Colors'. Now > Browse for the folder that holds your pictures, > Select the ones
Department of Computer Science 143
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
you like, choose a > Picture position and time interval to > Change picture. Finally click the >
Save changes button and enjoy.
Like the > Desktop Background you can also customize > Window Color and > Sounds and so
create your own custom theme. Don't forget to > Save theme!
5. Add Toolbars to Taskbar & Enable Quick Launch Bar
A toolbar located in your taskbar can provide instant access to often used programs, for
example iTunes. Simply > right click Taskbar, expand > Toolbars, and check the ones you
would like to see.
Follow the same steps outlined above and select > New toolbar..., enter the following path >
%userprofile%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Quick Launch and click > Select
Folder. The Quick Launch bar will appear, but it needs more customization. > Right-click Quick
Launch and uncheck > Show title and > Show Text to make it more compact. You can also
uncheck > Lock the taskbar and then > drag and drop Quick Launch into place.
=== * ===
PowerShell ISE
Department of Computer Science 144
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
The Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) is a host application
for Windows PowerShell.
In Windows PowerShell ISE, one can run commands and write, test, and debug scripts in
a single Windows-based graphic user interface with multiline editing, tab completion,
syntax coloring, selective execution, context-sensitive help, and support for right-to-left
languages.
One can use menu items and keyboard shortcuts to perform many of the same tasks that
you would perform in the Windows PowerShell console. For example, when you debug a
script in the Windows PowerShell ISE, to set a line breakpoint in a script, right-click the
line of code, and then click Toggle Breakpoint.
To open it you just go to Start - Search and then Type - PowerShell
Command-line shell and scripting language built on the .NET Framework Designed
specifically for system administration
o Automate tasks on local and remote Windows machines
o Originally designed as a replacement for the current command environment and
BATCH files
=== * ===
Start PowerShell by typing powershell
Department of Computer Science 145
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
• Looks like command prompt, but with PS in front
• For help use:
get-help <cmdlet name>
• For help on all the possible get commands use:
get-help –Name get-*
=== * ===
Execute basic commands in Windows using command prompt and PowerShell like listing
the drives in a system, creating a new file, removing a file or directory, retrieving the list of
processes and services
Basic Commands in Windows using Command Prompt:
Command to be Practiced Description
dir Listing Files and Folders
md FloderName To make the Directory
rd FloderName To remove Directory
cd NextFloderName Change Directory to successor Directory
cd .. Change Directory to Previous Directory
cd Display Current Working Directory
del FileName Deleting File
ren OldFilename NewFilename Renaming Old File with New Name
Create New file and Adding Contents, Copying
copy con FileName
Contents on the Console to File
echo Text to be Displayed To Display the typed Text
tasklist List of Processes running
taskkill –pid Taskid End particular Process
prompt UserPromptText To display the Prompt with user Defined Text
cls Clear the contents in Console
type FileName Display the Contents of the File
exit Close the Command Prompt
Department of Computer Science 146
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
copy OriginalFile CopyofFile Copies the Contents of OriginalFile to CopyofFile
move FileWithPath1 File which is one path will be moved to another path
FilewithAnotherPath with same or different name.
attrib [+h] [-h] [+r][-r] Attach the attributes to the File like, add hidden,
FileName remove hidden, add Read Only, Remove Read only
=== * ===
Simple DOS Command based Example:
Create Folder named DTE
Create Four Folders inside DTE as, Engineering, Diploma, Office, Polytechnic
Create file named diplomafile.txt with initial Content “Hardware Lab” inside Diploma
Folder
Create file named enggfile.txt with initial Content “Hello, ” inside Engineering Folder
Create file named officefile.txt with initial Content “Welcome to ” inside Office Folder
Create file named polytechnicfile.txt inside the Polytechnic Folder in such a way that,
the Final Content of the diplomafile.txt should be “Hello, Welcome to Hardware Lab”,
which is obtained by placing of contents of respective files inside the Folders inside the
DTE Folder.
Create one Command.cmd and execution of this file should create above task
automatically in Current Directory in one go.
Contents of file Command.cmd
set path=%cd%
md %path%\DTE %path%\DTE\Engineering %path%\DTE\Diploma
%path%\DTE\Office %path%\DTE\Polytechnic
echo Welcome to > %path%\DTE\Office\officefile.txt
echo Hello, > %path%\DTE\Engineering\enggfile.txt
echo Hardware Lab > %path%\DTE\Diploma\diplomafile.txt
type %path%\DTE\Engineering\enggfile.txt %path%\DTE\Office\officefile.txt
%path%\DTE\Diploma\diplomafile.txt >
%path%\DTE\Polytechnic\polytechnicfile.txt
=== * ===
Department of Computer Science 147
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Experiments on Command Prompt Commands Executed:
Commands List Command Issued
Department of Computer Science 148
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
=== * ===
Basic Commands in Windows using PowerShell Prompt
Listing Drives in System
Get-PSDrive
Get Preset Working Directory
pwd
List all the Files and Folders in Drive
ls
New-Item cmdlet is used to create a text file and Set-Content cmdlet to put content into it.
Creating a new text file named test.txt
New-Item D:\temp\test\test.txt
Adding content to test.txt.
Set-Content D:\temp\test\test.txt 'Welcome to Hardware Lab'
Reading content of test.txt.
Get-Content D:\temp\test\test.txt
Output
Welcome to Hardware Lab
Adding content to the file test.txt.
Add-Content D:\temp\test\test.txt 'Good Lab'
Reading content of test.txt.
Get-Content D:\temp\test\test.txt
Department of Computer Science 149
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Output
Welcome to Hardware Lab
Good Lab
Display Number of Characters, Words and Lines in a File
Get-Content test.txt | measure-object -character -line -word
Output
Lines Words Characters
--------------------------------
2 6 31
Erasing content of test.txt.
Clear-Content D:\temp\test\test.txt
Create New Folder
Create Folder using New-Item cmdlet by passing the path using -Path as path of the
directory and -ItemType as Directory.
New-Item -Path 'D:\temp\Test Folder' -ItemType Directory
Delete Folder
Remove-Item 'D:\temp\Test Folder1'
Remove the folder D:\Temp\Test Folder1 recursively. PowerShell confirms if directory is
not empty.
Remove-Item 'D:\temp\Test Folder' -Recurse
You can see the content of temp folder in Windows Explorer where its folders are now
removed.
Encrypt & Decrypt Using Cipher:
Using the cipher command to securely encrypt a single file is extremely easy, simply
type the cipher command along with the /e parameter followed by the name of the file. The /e
parameter stands for encrypt.
Department of Computer Science 150
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Cipher /e File.txt
To undo the operation and decrypt the file simply replace the /e parameter with /d, which
stands for decrypt.
Cipher /d File.txt
To check whether or not your file was indeed encrypted/decrypted use the cipher
command without any parameters followed by the name of your file or folder:
Cipher File.txt
The encryption status of your file or folder should appear at once.
If the result is U it means that the file is unencrypted.
If the result is E it means that the file is encrypted.
The command for encrypting and decrypting a folder is exactly the same.
Cipher /e Folder
Replace the /e parameter with /d to decrypt the folder instead.
This operation however will only perform the operation on the folder itself and not any of
the contents inside it.
To encrypt/decrypt every item within the folder you need to use the /s parameter.
Cipher /e /s:Folder
The specified operation will now be performed on all the contents inside your folder as
well.
To get list of Processes
Get-Process
To get list of Services
Get-Service
=== * ===
Experiments on Power Shell: Commands Executed:
Department of Computer Science 151
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Commands List Command Issued
=== * ===
What is E-waste and E-waste Recycling?
E-waste is short for electronic waste. That is, trash generated from broken, obsolete, and surplus
electronic devices.
Typically, these electronics often contain toxic chemicals and hazardous materials. And
improper disposing of these electronics can cause the release of toxic substances into our
environment.
E-waste recycling then refers to the reprocessing and re-use of these electronic wastes. It is
simple. It is a process that seeks to recover material from electronic waste.
Department of Computer Science 152
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
These electronic wastes may be in the form of home appliances like your air conditioners,
televisions, electric cookers, air condoners, heater, DVDs, fans, microwaves, and radios.
They may also be in the form of information tech equipment like your computers,
laptops, mobile phones, batteries, hard disks, circuit boards, monitors.
E-waste is quite crucial because electronics have a short useful life. As such, they become
electronic waste at a swift pace.
E-waste recycling is important to reduce environmental hazards and pollution. There is
also the fact that it can protect our lives as humans and other life forms existing in our
world. E-waste recycling is the reuse and reprocessing of electrical and electronic
equipment of any type that has been discarded or regarded as obsolete.
Recycling of e-waste is a growing trend and was initiated to protect human and
environmental health mainly due to the widespread environmental pollution impacts of e-
waste.
Only 12.5% of e-waste is recycled.
Components of E-waste that Can be Recycled
Plastic
Plastic materials may be retrieved and sent for recycling. The recyclers can then use the plastic
materials to manufacture items like plastic sleepers and vineyard stakes. You can also get fence
posts, plastic trays, insulators, equipment holders, and much more.
Metal
Metals can also be retrieved and recycled to manufacture newer steel products and metals.
Glass
Extract glass from CRTs (Cathode Ray Tubes) of computer monitors and televisions. As CRT’s
contains several hazardous substances, such as lead a care must be taken while recycling CRT’s.
First, separate the CRT from the monitor or television. Then shred the CRT into small
pieces. Remove the metals with over-band magnets. This helps you remove ferrous and
even non-ferrous objects from that glass.
Department of Computer Science 153
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
After this, use washing lines to clear phosphors and oxides from that glass. The last step
is called glass sorting. This is where you separate non-leaded from leaded gas. You can
then use the extract to make newer screens.
Mercury
Devices containing mercury may be sent to recycling facilities using specialized technology to
eliminate mercury. The end product of this elimination includes metric instruments, dental
amalgams, and fluorescent lighting.
Circuit Boards
There are accredited and specialized companies smelting and recovering resources like tin, gold,
silver, copper, palladium, and valuable metals.
Hard Disk
When shredded and processed, you can recover aluminum ingots from hard disks. These are
particularly useful for automobiles.
Toner and Ink Cartridges
Recyclers in various manufacturing industries that remanufacture them take these toners and ink
cartridges for recycling. They then use retrieved plastic and metals as raw materials for other
products.
Batteries
One can take your scrap batteries to specialist recyclers to recover cadmium, steel, nickel, and
cobalt for re-use in new batteries. They are also useful for fabricating stainless steel.
Apart from the listed objects, there is an endless list of other objects. But, overall, there’s kind of
hack to recycling any item or component. And no, e-waste recycling is not a one size fits all
approach. However, there is a general way to go about it.
=== * ===
Step-by-Step Process of E-waste Recycling
This is because e-scraps are typically sophisticated and manufactured from diverse elements such
as metals, plastics, and glass. While this process often varies, there is a general process.
Department of Computer Science 154
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Step 1: Collecting and Transporting
This is the first stage of recycling e-waste. Here, recyclers place take-back booths or collection
bins in specific places. When these bins get filled, the recyclers then transport the e-wastes to
recycling facilities and plants.
Step 2: Shredding and Sorting
After collecting and transporting, the next step is to shred and sort the e-waste. The success of
subsequent separation relies on shredding. And this is why efficiency is essential at this stage.
Shredding involves breaking e-waste into smaller pieces for proper sorting. With the use of
hands, these tiny prices get sorted and then manually dismantled. This is typically labor-intensive
as waste items are, at this stage, separated to retrieve different parts.
After this, the materials get categorized into core materials and components. Then, these items
get sorted into various categories. Typically, these category includes items that you can re-use as
they are and those that require further recycling processes.
In any case, e-wastes are often manually sorted, while compounds such as fluorescent light,
batteries, UPS batteries, and toner cartridges should not be crushed or shredded by hand.
Step 3: Dust Extraction
The tiny waste particles get smoothly spread via a shaking process on the conveyor belt. The
smoothly spread e-waste pieces then get broken down even further. At this point, the dust gets
extracted and discarded in an environmentally compliant manner. This way, there is no
environmental degradation.
Step 4: Magnetic Separation
After this, a strong overhead magnet helps you separate steel and iron from other wastes. This
way, you have successfully recycled the steel from the waste stream.
However, some mechanical processes may sometimes be required to separate circuit board,
copper, and aluminum from other wastes particles. And this is especially where they are mostly
plastic.
Department of Computer Science 155
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
Step 5: Water Separation
After this, water separation tech becomes relevant to separate the glass from the plastic. You can
then send leads that contain glass to smelters to use in the production of batteries, x-ray tubes,
and new CRTs.
Step 6: Purification of Waste Stream
The next thing is locating and extracting leftover metals from plastics to purify the waste stream
further.
Step 7: Preparing Recycled Materials For Sale
The final stage is preparing recycled materials for sale. Here, the materials separated during SSS
get prepared for sale as raw materials to produce new electronics.
Benefits of E-waste Recycling
1. E-waste Recycling Helps to Conserve Available Natural Resources
E-waste recycling helps recover valuable materials from electronic products that are either old or
no longer used. In turn, this saves and conserves natural resources.
This is because manufacturers can now obtain raw materials from recycled waste. Consequently,
there is less need to go to earth for raw materials.
Department of Computer Science 156
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
So, yes, there is less need to get copper or lead or metal from mother nature. You will need to
remember that these materials are not inexhaustible to realize how much good this represents.
2. It Prioritizes Environmental Protection
As you may have observed from the processes explained above, e-waste recycling prioritizes
environmental protection. It seeks to prioritize properly handling, processing and managing
hazardous and toxic substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium. All substances you may
find in your e-waste stream.
As you have read, as one of the sub-steps of e-waste processing, any dust sorted from shredded
particles must be disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner. This way, the hazards that
these elements usually pose to our environment get substantially reduced, thanks to e-waste
recycling.
3. Creates Jobs
E-waste recycling is creating new jobs for persons such as professional recyclers. What’s more is
that, by so doing, it has created a secondary market where recycled materials are the primary
commodity.
The Environmental Protection Agency released findings that show the magnitude of economic
benefits that comes from e-waste recycling. Guess what. This even beats the results derived at
the REI Study earlier in 2016.
In a year, the US’s recycling activities provided 757,000 jobs, $6.7 billion tax revenues, and
$36.6 billion as wages.
By implication, for every thousand tons you recycle, there’s 1.57 job created, $ 76,000 wages
paid, and $ 14,101 tax revenues. It seems like a lot of benefit coming from trash, right? But
there’s more.
For a million laptops you recycle, you will have saved the equivalent of electric power capable
of running 3657 households for one year. More, for a million cell phones, you can recover gold
weighing 75 pounds, silver of 772 pounds, copper of 35,274 pounds, and palladium of 33
pounds. Amazing, right?
Department of Computer Science 157
Computer Hardware, Maintenance and Administration – 20CS32P
4. Saves Landfills and Reduces Global Warming
Usually, uncollected e-wastes get dumped at incinerators and landfills. By recycling e-waste, we
are reducing the amount of e-wastes pilling up at these places.
This is because two-thirds of waste on landfills are biodegradable and capable of breaking down
and returning to their natural elements. As these wastes break down and decompose, they
produce harmful gases (Methane and CO2) – greenhouse gases – which heavily contribute to
global warming.
Since landfills also pollute the water and soil in our local environment, activities like e-waste
recycling, which seek to reduce these environmental concerns are not merely beneficial, but also
life-saving.
Summary:
E-waste recycling is a serious global concern for a lot of reasons. It has a strong bearing on our
immediate environment as humans and life on earth generally. It even promises significant
economic returns for persons, communities, and even nations.
Many people have begun to tap from the floodgate of opportunities provided by e-waste
recycling. In developing nations, entrepreneurs are taking advantage of e-recycling as a steady
revenue stream and advancing environmental goals.
Although the steps involved might be labor-intensive, they are easy to follow. From collecting
and separating to preparation for sale, there are several steps involved which you can easily flow
with. And of course, you too can directly benefit from e-waste recycling and also help to save
our planet.
=== * ===
Department of Computer Science 158
You might also like
- Modern Patterns Warm Ups For Jazz For Trumpet and All InstrumentsDocument117 pagesModern Patterns Warm Ups For Jazz For Trumpet and All InstrumentsJosé López Droguett67% (6)
- Bad Guy - Sheet MusicDocument1 pageBad Guy - Sheet MusicKristof Van ReckNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument27 pagesMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்No ratings yet
- Components of LaptopDocument7 pagesComponents of LaptopMa Michelle Nica DmNo ratings yet
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Document54 pagesOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- Motherboard Form FactorsDocument5 pagesMotherboard Form FactorsShe Real LeanNo ratings yet
- Dav Institute of Engineering & Technology, JalandharDocument35 pagesDav Institute of Engineering & Technology, JalandharKaran GuptaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Computer and Their FunctionsDocument33 pagesParts of A Computer and Their FunctionsMia Dess Angawa Ananayo100% (1)
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- What Is A Motherboard ?Document13 pagesWhat Is A Motherboard ?Ian OffemariaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Electromagnetic WaveDocument10 pagesPhysics - Electromagnetic WaveEuw Chaiwanont100% (1)
- Ludovico Einaudi - FlyDocument8 pagesLudovico Einaudi - FlyTim BonninNo ratings yet
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System UnitIvan Louie Cruto100% (1)
- 40 Essential Scale Patterns and Exercises PDF FreeDocument27 pages40 Essential Scale Patterns and Exercises PDF FreeRubén Ruiz100% (1)
- Electronics Technician ReviewerDocument10 pagesElectronics Technician ReviewerAlpyn100% (3)
- Nursing InformaticsDocument13 pagesNursing InformaticsNursidar Pascual MukattilNo ratings yet
- LTE Paging Performance Monitoring Guideline Rev PA2 PDFDocument15 pagesLTE Paging Performance Monitoring Guideline Rev PA2 PDFRud's Simanullang100% (1)
- Interference L900 TroubleshootDocument5 pagesInterference L900 TroubleshootAhmadArwani88No ratings yet
- Chma Unit - ViDocument19 pagesChma Unit - ViSayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Bongoman - New Cool Collective - LeadsheetDocument1 pageBongoman - New Cool Collective - LeadsheetQuinten PietersNo ratings yet
- Computer CaseDocument16 pagesComputer CaseSnehal TembhurkarNo ratings yet
- Tower Type ComputerDocument20 pagesTower Type ComputerLouie RazalasNo ratings yet
- Types of MotherboardDocument6 pagesTypes of MotherboardmarianneNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-4: 1) AT (Advanced Technology)Document4 pagesExperiment:-4: 1) AT (Advanced Technology)Vishv PatelNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Maintenance and AdministrationDocument138 pagesComputer Hardware Maintenance and AdministrationSayyan Shaikh100% (2)
- Motherboard ComponentsDocument24 pagesMotherboard ComponentsCarol MutugiNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardDocument7 pagesMotherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardMustafa MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDocument22 pagesLesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument18 pagesHandoutHenock TadesseNo ratings yet
- CP and I AssigenmentDocument59 pagesCP and I Assigenmentfagixa3491No ratings yet
- Summary Report in TRDocument9 pagesSummary Report in TREllie KimNo ratings yet
- And Its Form FactorsDocument13 pagesAnd Its Form FactorsLong Live TauNo ratings yet
- What Is Motherboard:-: 1 Integrated 2 Non IntegratedDocument5 pagesWhat Is Motherboard:-: 1 Integrated 2 Non IntegratedHitesh SinglaNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard PresentationDocument21 pagesComputer Motherboard PresentationKoushal JainNo ratings yet
- Cassy AssignmentDocument8 pagesCassy AssignmentrickNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Mother Board Form FactorsDocument10 pagesLesson 2 Mother Board Form FactorsagwonadavidNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lesson 5 CSSDocument4 pagesWeek 5 Lesson 5 CSSShe SheNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsDocument17 pagesParts of A Computer With Their FunctionsREZA TAGLENo ratings yet
- Lecture On WebsiteDocument5 pagesLecture On WebsitePythiusNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Mastering Lan and Trouble ShootingDocument17 pagesUnit 1-Mastering Lan and Trouble Shootingbala smileyNo ratings yet
- Bing MotherboardDocument3 pagesBing Motherboards4tr10.d1m4sNo ratings yet
- TESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Document77 pagesTESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Sharalyn P. SiaNo ratings yet
- Computer MotherboardDocument15 pagesComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNo ratings yet
- Inggris MotherboardDocument4 pagesInggris Motherboards4tr10.d1m4sNo ratings yet
- A Brief Computer HistoryDocument6 pagesA Brief Computer HistoryMalachi LamaNo ratings yet
- Practical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodDocument7 pagesPractical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodAarunain PandavdraNo ratings yet
- International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) Is An AmericanDocument9 pagesInternational Business Machines Corporation (IBM) Is An AmericanClash ClansNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in SomeDocument20 pages1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in Somekadilobari100% (3)
- How Motherboards WorkDocument5 pagesHow Motherboards Workapi-19737301No ratings yet
- The Parts of The ComputerDocument18 pagesThe Parts of The ComputerJuan Diego Moncaleano LópezNo ratings yet
- Motherboard - Wikipedia PDFDocument46 pagesMotherboard - Wikipedia PDFLorien Lolong LamanNo ratings yet
- Cycle 1Document106 pagesCycle 1Srinivas KanakalaNo ratings yet
- Amarpreet Singh Bhawanpreet Singh Kulwinder Singh Manjeet SinghDocument10 pagesAmarpreet Singh Bhawanpreet Singh Kulwinder Singh Manjeet Singhmanjeetsinghnavab100% (1)
- Computer PartsDocument9 pagesComputer PartsAlexis Dhave AlgireNo ratings yet
- CSS PrintDocument6 pagesCSS Printjhazmineiloveyou123No ratings yet
- CSS G11 Module 3Document8 pagesCSS G11 Module 3Shendelzare Silkwood Quinto AronNo ratings yet
- Components of MotherboardDocument4 pagesComponents of MotherboardMayur GoreNo ratings yet
- Motherboard - Wikipedia PDFDocument41 pagesMotherboard - Wikipedia PDFDance plus 3No ratings yet
- Chip Insider June 2011Document52 pagesChip Insider June 2011Trisa KaapoorNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument9 pagesMotherboardAhmed AbuNasserNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Group 6 Devices of ComputerDocument22 pagesPresentation of Group 6 Devices of Computerkliz TanNo ratings yet
- CPH Microproject PDFDocument12 pagesCPH Microproject PDFRohanNo ratings yet
- A Typical Desktop Computer Consists of A Computer System UnitDocument17 pagesA Typical Desktop Computer Consists of A Computer System UnitHary BertNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4Document12 pagesExperiment No.4Kshitij DudheNo ratings yet
- Technical Dictionary: Computer PartsDocument11 pagesTechnical Dictionary: Computer PartsDiego AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: 6 September 2008Document11 pagesMotherboard: 6 September 2008aaron-ryan-3857No ratings yet
- Building The New PCDocument11 pagesBuilding The New PCthesingh_0No ratings yet
- To Make Comparative Study On MotherboardsDocument13 pagesTo Make Comparative Study On MotherboardsPankaj GillNo ratings yet
- CHMA Unit - IDocument29 pagesCHMA Unit - ISayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CHMA Unit - IIDocument14 pagesCHMA Unit - IISayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- CHMA Unit - VDocument25 pagesCHMA Unit - VSayyan Shaikh100% (1)
- CHMA Unit - IIIDocument6 pagesCHMA Unit - IIISayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Maintenance and AdministrationDocument138 pagesComputer Hardware Maintenance and AdministrationSayyan Shaikh100% (2)
- FLESH AND THE POWER IT HOLDS OFFICIAL by Death @ PDFDocument19 pagesFLESH AND THE POWER IT HOLDS OFFICIAL by Death @ PDFLevan LomidzeNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - KundimanDocument2 pagesModule 6 - KundimanPixie DoggieNo ratings yet
- ILMEA District I Wind and Percussion - Junior Level Audition Etudes Set IDocument1 pageILMEA District I Wind and Percussion - Junior Level Audition Etudes Set IMark RandolphNo ratings yet
- KD nx5000Document357 pagesKD nx5000Uri DjNo ratings yet
- Physiological Effects of MusicDocument3 pagesPhysiological Effects of MusicFedepant100% (1)
- Aguirre Op17 5 Tristes No4Document3 pagesAguirre Op17 5 Tristes No4eduardo carreroNo ratings yet
- De Thi HK1 Tieng Anh 10 Nam 22 23Document7 pagesDe Thi HK1 Tieng Anh 10 Nam 22 23Anh Nguyễn HảiNo ratings yet
- Forbidden Attraction (Watson, S R) (Z-Library)Document174 pagesForbidden Attraction (Watson, S R) (Z-Library)KanikaNo ratings yet
- Calculating PIM 2018Document16 pagesCalculating PIM 2018Владан ДакићNo ratings yet
- Playlist Recomandat SM!Document11 pagesPlaylist Recomandat SM!Codruța ȚocaNo ratings yet
- Core 12 Physical-Education-And-Health Q1 CLAS5-6 Week5-6 POPdance V5Document13 pagesCore 12 Physical-Education-And-Health Q1 CLAS5-6 Week5-6 POPdance V5Kristine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BITX20 - A Bidirectional SSB Transceiver: Ham News June - July 2004Document9 pagesBITX20 - A Bidirectional SSB Transceiver: Ham News June - July 2004dayaaolNo ratings yet
- Digital Issue 115Document78 pagesDigital Issue 115Melita ArifiNo ratings yet
- Muppets ShowDocument1 pageMuppets Showbach34No ratings yet
- Tonal Harmony - Stefan Kostka - Chapter 4 - Diatonic Chords in Major and Minor KeysDocument12 pagesTonal Harmony - Stefan Kostka - Chapter 4 - Diatonic Chords in Major and Minor KeysYayi Wira PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Amy Beach-Four SketchesDocument18 pagesAmy Beach-Four Sketchesjcpiano100% (2)
- Vaselina : Violin 2 (You're The One That I Want)Document1 pageVaselina : Violin 2 (You're The One That I Want)Arturo Gabriel Hernandez GarciaNo ratings yet
- TDJ 709015 172717DE 65Fv01Document4 pagesTDJ 709015 172717DE 65Fv01Maksim PatrushevNo ratings yet
- College of Arts, Sciences, & Education Teaching Music in The Elementary GradesDocument9 pagesCollege of Arts, Sciences, & Education Teaching Music in The Elementary GradesangelNo ratings yet
- Caps Ip Life Skills GR 4-6 WebDocument66 pagesCaps Ip Life Skills GR 4-6 WebPortia MudalahotheNo ratings yet
- Idol-YOASOBI - Flute 1&2Document3 pagesIdol-YOASOBI - Flute 1&2kendralam227No ratings yet