Abstract
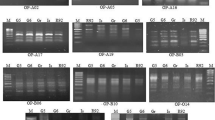
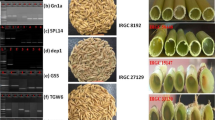
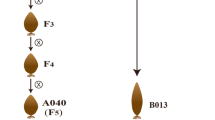
Garden stock [Matthiola incana (L.) R. Br.] is a commercially important horticultural crop owing to its ornamental effect. There are different stock cultivars varied in color and shape, especially flowered phenotype is an essential index evaluating its commercial value, because double flowered individuals have more brilliant flowers compared to single flowered one. The present work aimed: (1) to make superior cultivars with different colors, high fertility, being capable of early selecting only double flowered seedlings by leaf color and to investigate morphological characteristics and (2) to select RAPD and ISSR primers for the cultivar certification and identification to culture and produce good commercial stock cultivars. Here, in this study new stock cultivars were obtained with different colors including pink, pale pink and white, through outcrossing between “white” cultivar (high fertile but unable to select double flower phenotype) and “pink” cultivar (vice. versa). Among newly obtained stock cultivars, single and double flowered seedlings are distinguishable from single ones by leaf color, having about 70% of fertility. Moreover RAPD and ISSR markers selected in this study can be applied to identify different stock cultivars in seed production, culture and to establish cultivar certification system.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- ISSR:
-
Inter simple sequence repeat
References
Baruah J, Pandey SK, Begum T, Sarma N, Paw M, Lal M (2019) Molecualr diversity assessed amongst high dry rhizome recovery Ginger germplasm (Zinger officinale Roscoe) from NE-India using RAPD and ISSR markers. Ind Crops Prod 129:463–471
Chen D, Liu Y, Pan Q, Li F, Zhang Q, Ge X, Li Z (2018) De novo transcriptome assembly, gene expressions and metabolites for flower color variation of two garden species in Brassicaceae. Sci Hortic 240:592–602
Chowdhury T, Mandal A, Roy SC, De Sarker D (2016) Diversity of the genus Ocimum (Lamiaceae) through morpho-molecular (RAPD) and chemical (GC–MS) analysis. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 15(1):275–286
Chroboková E, Raddová J, Vachůn M, Krška B, Pidra M (2011) An analysis of apricot cultivars by random amplified polymorphic DNA and microsatellite primers. Hort Sci (prague) 38(4):125–133
Dogan B, Duran A, Hakki EE (2007) Phylogenetic analysis of Jurinea (Asteraceae) species from Turkey based on ISSR amplifiation. Ann Bot Fenn 44:353–358
Doğan B, Çelik M, Ünal M, Sefali A, Martin E, Kaya A (2016) Study of phylogenetic relationship of Turkish species of Matthiola (Brassicaceae) based on ISSR amplification. Turk J Bot 40:130–136
Domenyuk VP, Verbitskaya TG, Belousov AA, Sivolap YM (2002) Marker analysis of quantitative traits in maize by ISSR-PCR. Russ J Genet 38:1161–1168
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Ecker R, Barzilay A, Osherenko E (1993) Linkage relationships of genes for leaf morphology and double flowering in Matthiola incana. Euphytica 74:133–136
Elmeer K, Elkhgkheg A (2019) Genetic diversity of Artemisia herba-alba in Libyan Green Mountain. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 43(4):1507–1512
Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567
Galvan MZ, Bornet B, Balatti PA, Branchard M (2003) Inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers as a tool for the assessment of both genetic diversity and gene pool origin in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Euphytica 132:297–301
Ho U-H, Kye J-S, Choe S-I, Kim J-H, Kim MH (2021) Molecular distinction among mulberry (Morus spp.) species and varieties cultivated in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Genet Resour Crop Evol 68:3103–3114
Jafari S, Garmdareh SHE (2019) Effects of salinity on morpho-physiological, and biochemical characteristics of stock plant (Matthiola incana L.). Sci Hortic 257:108731
Jafari S, Garmdareh SEH, Azadegan B (2019) Effects of drought stress on morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of stock plant (Matthiola incana L.). Sci Hortic 253:128–133
Kaur P, Pandey DK, Gupta RC, Dey A (2019) Assessment of genetic diversity among different population of five Swertia species by using molecular and phytochemical markers. Ind Crop Prod 138:111569
Kimura M, Crow JF (1964) The number of alleles that can be maintained in a finite population. Genetics 49:725–738
Lewontin RC (1972) The apportionment of human diversity. Evol Biol 6:381–398
Maciel FL, Gerald LTS, Echeverrigaray S (2001) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers variability among cultivars and landraces of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) of south-Brazil. Euphytica 120:257–263
Masvodza DR, Mazhude N, Mugabe J, Musango R (2014) Preliminary genetic diversity analysis of introduced and local Zimbabwe cowpea landraces. Afr J Agric Res 9(49):3571–3580
Mei Z, Xianqin Zhang Md, Khan A, Imani S, Liu X, Zou H, Wei C, Junjiang Fu (2017) Genetic analysis of Penthorum chinense Pursh by improved RAPD and ISSR in China. Electron J Biotechn 30:6–11
Mohamed AH (2009) Molecular systematic of some Brassicaceae Taxa in Egypt based on electrophoretic isoenzymes pattern and RAPD markers. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3(3):1499–1511
Nakatsukaa T, Koishi K (2018) Molecular characterization of a double-flower mutation in Matthiola incana. Plant Sci 268:39–46
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590
Palai SK, Rout GR (2007) Identification and genetic variation among eight varieties of ginger by using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Plant Biotechnol 24:417–420
Palaiyur N, Sivalingam Dilip K, Singh SD, Chauhan S (2016) Molecular markers to distinguish ‘Thar Shoba’, a variety of khejri [Prosopis cineraria (L.) Druce], from trees in natural populations. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 91(4):353–361
Prasad B, Khan RG, Radha T, Ravi C, Venkataiah P, Subhash K, Reuben TC (2013) DNA profiling of commercial chilli pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) varieties using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Afr J Biotechnol 12(30)
Rameshkumar R, Pandian S, Rathinapriya P, Selvi CT, Satish L, Gowrishankar S, Leung DWM, Ramesh M (2019) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship of Nilgirianthus ciliatus populations using ISSR and RAPD markers: Implications for conservation of an endemic and vulnerable medicinal plant. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 18:101072
Rohela GK, Bylla P, Pendli S, Rajender K, Dharavath B, Thammidala CR (2018) ISSR marker based DNA profiling studies in Rauwolfia species. Ann Plant Sci 7(5):2289
Rohlf FJ (2008) NTSYSpc: numerical taxonomy system, ver. 2.20. Exerter Publishing Ltd., Setauket, New York
Rozhmina TA, Fu Y-B, Diederichsen A, Richards KW, Pavelek M, Vrbova M (2016) Research of genetic polymorphism species Linumu sitatissimum L. on a basis a RAPD-method. J Nat Fibers 15(2):155–161
Saunders ES (1911) Further experiments on the inheritance of doubleness and other characters in stock. J Genet 1:303–376
Saunders ES (1915) A suggested explanation of the abnormally high records of doubles quoted by growers of stocks (Matthiola). J Genet 5:137–143
Saunders ES (1921) Note on the evolution of the double stock (Matthiola incana). J Genet 11:69–74
Saunders ES (1928) Further studies on inheritance in Matthiola incana. II. Plastid Colour Doubing J Genet 20:53–77
Sharma S, Kumar P, Gambhir G, Kumar R, Srivastava DK (2018) Assessment of genetic diversity in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) germplasm using RAPD markers. 3 Biotech 8:9
Tasaki K, Higuchi A, Fujita K, Watanabe A, Sasaki N, Fujiwara K, Abe H, Naito Z, Takahashi R, Hikage T, Nishihara M (2017) Development of molecular markers for breeding of double flowers in Japanese gentian. Mol Breed 37
Tatsuzawa F, Saito N, Toki K, Shinoda K, Honda T (2012) Flower colors and their anthocyanins in Matthiola incana cultivars (Brassicaceae). J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 81:91–100
Verma KS, ul Haq S, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2017) RAPD and ISSR marker assessment of genetic diversity in Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: a unique source of germplasm highly adapted to drought and high-temperature stress. 3 Biotech 7:288
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:653l–6535
Yeh FC, Boyle T, Yang R-C, Ye ZMJX (2000) POPGENE, version 1.32. Department of Renewable Resources, University of Alberta, Edmonton
Acknowledgements
All the authors thank all horticulturists of Pyongyang floriculture institute who helped culturation during stock breeding.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, UH., Ri, JH. & Ri, CJ. Identification of new stock [Matthiola incana (L.) R. Br] cultivars with high fertility through morphological and molecular markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 69, 2719–2730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-022-01392-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-022-01392-9