Variations: Kephalokroustes, Sklerokephalon
Nicander classified the Kranokolaptes, the “Head Striker”, as a phalangion or spider. This is all the more puzzling because the description has nothing arachnoid about it. No doubt its deadly bites were seen as reason enough to list it after wolf spiders and malmignattes.
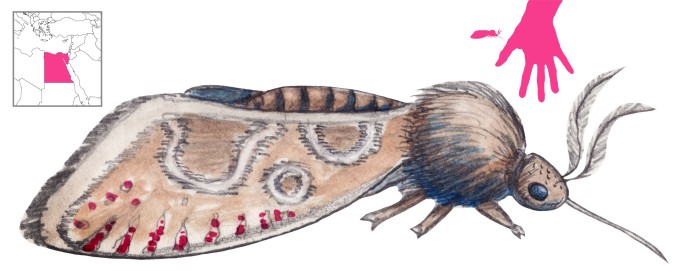
The kranokolaptes is an insect found in Egypt, and which develops in the persea tree (perhaps Mimusops). It has the appearance of a moth, with four downy felt-textured wings that leave an ashy dust behind. Philoumenos described it as green in color, but that is apparently a misreading of Nicander. The head of the kranokolaptes is hard, heavy, and nodding; its abdomen is thick and fat. It has a deadly stinger located below its head.
A kranokolaptes will use its stinger to attack the heads and necks of humans and cause instant death. Kranokolaptes stings are deadly unless victims are treated with its antidote – a kranokolaptes drowned in oil.
It has been suggested that hawkmoths (Sphingidae), with their impressive sizes, thick abdomens, and prominent probosces, are at the root of the kranokolaptes tale. The vampire moth Calyptra thalictri is even more compelling. Having evolved from fruit-piercing moths, vampire moths use the same methods to puncture skin and drink blood – and they rock their heads back and forth as they penetrate, explaining the “nodding” aspect. The similarities end here, however, as a bite from Calyptra merely causes swelling and irritation.
References
Beavis, I. C. (1988) Insects and other Invertebrates in Classical Antiquity. Alden Press, Osney Mead, Oxford.
Kitchell, K. F. (2014) Animals in the Ancient World from A to Z. Routledge, Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxon.